Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- Category Theory »
Bases: sage.structure.unique_representation.UniqueRepresentation, sage.structure.parent.Parent
An example of a finite semigroup
This class provides a minimal implementation of a finite semigroup.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example(); S
An example of a finite semigroup: the left regular band generated by ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd')
This is the semigroup generated by:
sage: S.semigroup_generators()
Family ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd')
such that 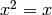 and
and 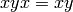 for any
for any 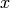 and
and 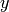 in
in 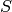 :
:
sage: S('dab')
'dab'
sage: S('dab') * S('acb')
'dabc'
It follows that the elements of 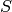 are strings without
repetitions over the alphabet
are strings without
repetitions over the alphabet  ,
, 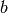 ,
,  ,
, 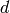 :
:
sage: S.list()
['a', 'c', 'b', 'bd', 'bda', 'd', 'bdc', 'bc', 'bcd', 'cb',
'ca', 'ac', 'cba', 'ba', 'cbd', 'bdca', 'db', 'dc', 'cd',
'bdac', 'ab', 'abd', 'da', 'ad', 'cbad', 'acb', 'abc',
'abcd', 'acbd', 'cda', 'cdb', 'dac', 'dba', 'dbc', 'dbca',
'dcb', 'abdc', 'cdab', 'bcda', 'dab', 'acd', 'dabc', 'cbda',
'bca', 'dacb', 'bad', 'adb', 'bac', 'cab', 'adc', 'cdba',
'dca', 'cad', 'adbc', 'adcb', 'dbac', 'dcba', 'acdb', 'bacd',
'cabd', 'cadb', 'badc', 'bcad', 'dcab']
It also follows that there are finitely many of them:
sage: S.cardinality()
64
Indeed:
sage: 4 * ( 1 + 3 * (1 + 2 * (1 + 1)))
64
As expected, all the elements of 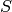 are idempotents:
are idempotents:
sage: all( x.is_idempotent() for x in S )
True
Now, let us look at the structure of the semigroup:
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example(alphabet = ('a','b','c'))
sage: S.cayley_graph(side="left", simple=True).plot()
sage: S.j_transversal_of_idempotents() # random (arbitrary choice)
['acb', 'ac', 'ab', 'bc', 'a', 'c', 'b']
We conclude by running systematic tests on this semigroup:
sage: TestSuite(S).run(verbose = True)
running ._test_an_element() . . . pass
running ._test_associativity() . . . pass
running ._test_category() . . . pass
running ._test_elements() . . .
Running the test suite of self.an_element()
running ._test_category() . . . pass
running ._test_eq() . . . pass
running ._test_not_implemented_methods() . . . pass
running ._test_pickling() . . . pass
pass
running ._test_elements_eq() . . . pass
running ._test_enumerated_set_contains() . . . pass
running ._test_enumerated_set_iter_cardinality() . . . pass
running ._test_enumerated_set_iter_list() . . . pass
running ._test_eq() . . . pass
running ._test_not_implemented_methods() . . . pass
running ._test_pickling() . . . pass
running ._test_some_elements() . . . pass
Returns an element of the semigroup.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example()
sage: S.an_element()
'cdab'
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example(("b"))
sage: S.an_element()
'b'
Returns the product of two elements of the semigroup.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example()
sage: S('a') * S('b')
'ab'
sage: S('a') * S('b') * S('a')
'ab'
sage: S('a') * S('a')
'a'
Returns the generators of the semigroup.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = FiniteSemigroups().example(alphabet=('x','y'))
sage: S.semigroup_generators()
Family ('x', 'y')