This module implements the group operation in the Picard group of a hyperelliptic curve, represented as divisors in Mumford representation, using Cantor’s algorithm.
A divisor on the hyperelliptic curve 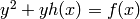 is stored in Mumford representation, that is, as two polynomials
is stored in Mumford representation, that is, as two polynomials
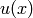 and
and 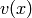 such that:
such that:
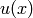 is monic,
is monic,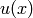 divides
divides 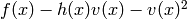 ,
,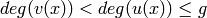 .
.REFERENCES:
A readable introduction to divisors, the Picard group, Mumford representation, and Cantor’s algorithm:
A standard reference in the field of cryptography:
EXAMPLES: The following curve is the reduction of a curve whose Jacobian has complex multiplication.
sage: x = GF(37)['x'].gen()
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(x^5 + 12*x^4 + 13*x^3 + 15*x^2 + 33*x); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field of size 37 defined by y^2 = x^5 + 12*x^4 + 13*x^3 + 15*x^2 + 33*x
At this time, Jacobians of hyperelliptic curves are handled differently than elliptic curves:
sage: J = H.jacobian(); J
Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field of size 37 defined by y^2 = x^5 + 12*x^4 + 13*x^3 + 15*x^2 + 33*x
sage: J = J(J.base_ring()); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field of size 37 defined by y^2 = x^5 + 12*x^4 + 13*x^3 + 15*x^2 + 33*x defined over Finite Field of size 37
Points on the Jacobian are represented by Mumford’s polynomials. First we find a couple of points on the curve:
sage: P1 = H.lift_x(2); P1
(2 : 11 : 1)
sage: Q1 = H.lift_x(10); Q1
(10 : 18 : 1)
Observe that 2 and 10 are the roots of the polynomials in x, respectively:
sage: P = J(P1); P
(x + 35, y + 26)
sage: Q = J(Q1); Q
(x + 27, y + 19)
sage: P + Q
(x^2 + 25*x + 20, y + 13*x)
sage: (x^2 + 25*x + 20).roots(multiplicities=False)
[10, 2]
Frobenius satisfies
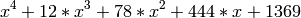
on the Jacobian of this reduction and the order of the Jacobian is
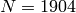 .
.
sage: 1904*P
(1)
sage: 34*P == 0
True
sage: 35*P == P
True
sage: 33*P == -P
True
sage: Q*1904
(1)
sage: Q*238 == 0
True
sage: Q*239 == Q
True
sage: Q*237 == -Q
True
Bases: sage.structure.element.AdditiveGroupElement, sage.schemes.generic.morphism.SchemeMorphism
An element of a Jacobian defined over a field, i.e. in
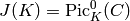 .
.
Return the scheme this morphism maps to; or, where this divisor lives.
Warning
Although a pointset is defined over a specific field, the scheme returned may be over a different (usually smaller) field. The example below demonstrates this: the pointset is determined over a number field of absolute degree 2 but the scheme returned is defined over the rationals.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = QQ['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^5 + x
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f)
sage: F.<a> = NumberField(x^2 - 2, 'a')
sage: J = H.jacobian()(F); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 + x defined over Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 - 2
sage: P = J(H.lift_x(F(1)))
sage: P.scheme()
Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 + x
EXAMPLES:
sage: F.<a> = GF(7^2, 'a')
sage: x = F['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^7 + x^2 + a
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f, 2*x); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field in a of size 7^2 defined by y^2 + 2*x*y = x^7 + x^2 + a
sage: J = H.jacobian()(F); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field in a of size 7^2 defined by y^2 + 2*x*y = x^7 + x^2 + a defined over Finite Field in a of size 7^2
sage: Q = J(H.lift_x(F(1))); Q
(x + 6, y + 2*a + 2)
sage: 10*Q # indirect doctest
(x^3 + (3*a + 1)*x^2 + (2*a + 5)*x + a + 5, y + (4*a + 5)*x^2 + (a + 1)*x + 6*a + 3)
sage: 7*8297*Q
(1)
sage: Q = J(H.lift_x(F(a+1))); Q
(x + 6*a + 6, y + 2)
sage: 7*8297*Q # indirect doctest
(1)
A test over a prime field:
sage: F = GF(next_prime(10^30))
sage: x = F['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^7 + x^2 + 1
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f, 2*x); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field of size 1000000000000000000000000000057 defined by y^2 + 2*x*y = x^7 + x^2 + 1
sage: J = H.jacobian()(F); J
verbose 0 (...: multi_polynomial_ideal.py, dimension) Warning: falling back to very slow toy implementation.
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Finite Field of size 1000000000000000000000000000057 defined by y^2 + 2*x*y = x^7 + x^2 + 1 defined over Finite Field of size 1000000000000000000000000000057
sage: Q = J(H.lift_x(F(1))); Q
(x + 1000000000000000000000000000056, y + 1000000000000000000000000000056)
sage: 10*Q # indirect doctest
(x^3 + 150296037169838934997145567227*x^2 + 377701248971234560956743242408*x + 509456150352486043408603286615, y + 514451014495791237681619598519*x^2 + 875375621665039398768235387900*x + 861429240012590886251910326876)
sage: 7*8297*Q
(x^3 + 35410976139548567549919839063*x^2 + 26230404235226464545886889960*x + 681571430588959705539385624700, y + 999722365017286747841221441793*x^2 + 262703715994522725686603955650*x + 626219823403254233972118260890)
Given 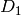 and
and 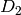 two reduced Mumford
divisors on the Jacobian of the curve
two reduced Mumford
divisors on the Jacobian of the curve 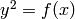 ,
computes a representative
,
computes a representative 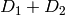 .
.
Warning
The representative computed is NOT reduced! Use cantor_reduction_simple() to reduce it.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = QQ['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^5 + x
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 + x
sage: F.<a> = NumberField(x^2 - 2, 'a')
sage: J = H.jacobian()(F); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 + x defined over Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 - 2
sage: P = J(H.lift_x(F(1))); P
(x - 1, y - a)
sage: Q = J(H.lift_x(F(0))); Q
(x, y)
sage: 2*P + 2*Q # indirect doctest
(x^2 - 2*x + 1, y - 3/2*a*x + 1/2*a)
sage: 2*(P + Q) # indirect doctest
(x^2 - 2*x + 1, y - 3/2*a*x + 1/2*a)
sage: 3*P # indirect doctest
(x^2 - 25/32*x + 49/32, y - 45/256*a*x - 315/256*a)
Return the unique reduced divisor linearly equivalent to
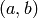 on the curve
on the curve 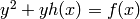 .
.
See the docstring of sage.schemes.hyperelliptic_curves.jacobian_morphism for information about divisors, linear equivalence, and reduction.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = QQ['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^5 - x
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f, x); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 + x*y = x^5 - x
sage: J = H.jacobian()(QQ); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 + x*y = x^5 - x defined over Rational Field
The following point is 2-torsion:
sage: Q = J(H.lift_x(0)); Q
(x, y)
sage: 2*Q # indirect doctest
(1)
The next point is not 2-torsion:
sage: P = J(H.lift_x(-1)); P
(x + 1, y - 1)
sage: 2 * J(H.lift_x(-1)) # indirect doctest
(x^2 + 2*x + 1, y - 3*x - 4)
sage: 3 * J(H.lift_x(-1)) # indirect doctest
(x^2 - 487*x - 324, y - 10754*x - 7146)
Return the unique reduced divisor linearly equivalent to
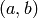 on the curve
on the curve 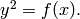
See the docstring of sage.schemes.hyperelliptic_curves.jacobian_morphism for information about divisors, linear equivalence, and reduction.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = QQ['x'].gen()
sage: f = x^5 - x
sage: H = HyperellipticCurve(f); H
Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 - x
sage: J = H.jacobian()(QQ); J
Set of points of Jacobian of Hyperelliptic Curve over Rational Field defined by y^2 = x^5 - x defined over Rational Field
The following point is 2-torsion:
sage: P = J(H.lift_x(-1)); P
(x + 1, y)
sage: 2 * P # indirect doctest
(1)