AUTHORS:
Bases: sage.schemes.generic.scheme.Scheme
An abstract affine scheme.
Return the scheme morphism from self to Y defined by x.
If Y is not given, try to determine from context.
EXAMPLES: We construct the inclusion from
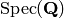 into
into 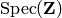 induced by the inclusion from
induced by the inclusion from 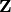 into
into
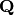 .
.
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.hom(ZZ.hom(QQ))
Affine Scheme morphism:
From: Spectrum of Rational Field
To: Spectrum of Integer Ring
Defn: Ring Coercion morphism:
From: Integer Ring
To: Rational Field
Bases: sage.structure.parent.Parent
Y is either a scheme in the same category as self or a ring.
EXAMPLES:
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.base_scheme()
Spectrum of Integer Ring
sage: X.base_extend(QQ)
...
NotImplementedError
Return the structure morphism from the scheme self to its base scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = AffineSpace(4, QQ)
sage: A.base_morphism()
Scheme morphism:
From: Affine Space of dimension 4 over Rational Field
To: Spectrum of Rational Field
Defn: Structure map
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.base_morphism()
Scheme morphism:
From: Spectrum of Rational Field
To: Spectrum of Integer Ring
Defn: Structure map
Return the base ring of the scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = AffineSpace(4, QQ)
sage: A.base_ring()
Rational Field
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.base_ring()
Integer Ring
Return the base scheme of the scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = AffineSpace(4, QQ)
sage: A.base_scheme()
Spectrum of Rational Field
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.base_scheme()
Spectrum of Integer Ring
Return the coordinate ring of this scheme, if defined. Otherwise raise a ValueError.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x, y> = QQ[]
sage: I = (x^2 - y^2)*R
sage: X = Spec(R.quotient(I))
sage: X.coordinate_ring()
Quotient of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y over Rational Field by the ideal (x^2 - y^2)
Count points over
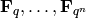 on a scheme over
a finite field
on a scheme over
a finite field 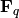 .
.
Note
This is currently only implemented for schemes over prime order finite fields.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(3))
sage: C = HyperellipticCurve(x^3+x^2+1)
sage: C.count_points(4)
[6, 12, 18, 96]
sage: C.base_extend(GF(9,'a')).count_points(2)
...
NotImplementedError: Point counting only implemented for schemes over prime fields
Return the absolute dimension of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x, y> = QQ[]
sage: I = (x^2 - y^2)*R
sage: X = Spec(R.quotient(I))
sage: X.dimension_absolute()
...
NotImplementedError
sage: X.dimension()
...
NotImplementedError
Return the absolute dimension of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x, y> = QQ[]
sage: I = (x^2 - y^2)*R
sage: X = Spec(R.quotient(I))
sage: X.dimension_absolute()
...
NotImplementedError
sage: X.dimension()
...
NotImplementedError
Return the relative dimension of this scheme over its base.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x, y> = QQ[]
sage: I = (x^2 - y^2)*R
sage: X = Spec(R.quotient(I))
sage: X.dimension_relative()
...
NotImplementedError
Return the scheme morphism from self to Y defined by x. If x is a scheme, try to determine a natural map to x.
If Y is not given, try to determine Y from context.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = ProjectiveSpace(ZZ, 3)
sage: P.hom(Spec(ZZ))
Scheme morphism:
From: Projective Space of dimension 3 over Integer Ring
To: Spectrum of Integer Ring
Defn: Structure map
Return the identity morphism of the scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.identity_morphism()
Scheme endomorphism of Spectrum of Rational Field
Defn: Identity map
Return the set of S-valued points of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = ProjectiveSpace(ZZ, 3)
sage: P.point_homset(ZZ)
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Integer Ring
sage: P.point_homset(QQ)
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Rational Field
sage: P.point_homset(GF(11))
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Finite Field of size 11
Return the set of S-valued points of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = ProjectiveSpace(ZZ, 3)
sage: P.point_homset(ZZ)
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Integer Ring
sage: P.point_homset(QQ)
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Rational Field
sage: P.point_homset(GF(11))
Set of Rational Points of Projective Space of dimension 3 over Finite Field of size 11
Return the structure morphism from the scheme self to its base scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = AffineSpace(4, QQ)
sage: A.base_morphism()
Scheme morphism:
From: Affine Space of dimension 4 over Rational Field
To: Spectrum of Rational Field
Defn: Structure map
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: X.base_morphism()
Scheme morphism:
From: Spectrum of Rational Field
To: Spectrum of Integer Ring
Defn: Structure map
Return the disjoint union of the schemes self and X.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = Spec(QQ)
sage: X = AffineSpace(1, QQ)
sage: S.union(X)
...
NotImplementedError
Compute a power series approximation to the zeta function of a scheme over a finite field.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: A power series approximating the zeta function of self
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(3))
sage: C = HyperellipticCurve(x^3+x^2+1)
sage: R.<t> = PowerSeriesRing(Integers())
sage: C.zeta_series(4,t)
1 + 6*t + 24*t^2 + 78*t^3 + 240*t^4 + O(t^5)
sage: (1+2*t+3*t^2)/(1-t)/(1-3*t) + O(t^5)
1 + 6*t + 24*t^2 + 78*t^3 + 240*t^4 + O(t^5)
Note that this function depends on count_points, which is only defined for prime order fields:
sage: C.base_extend(GF(9,'a')).zeta_series(4,t)
...
NotImplementedError: Point counting only implemented for schemes over prime fields
Return True if 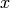 is an affine scheme.
is an affine scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.schemes.generic.scheme import is_AffineScheme
sage: is_AffineScheme(5)
False
sage: E = Spec(QQ)
sage: is_AffineScheme(E)
True
Return True if 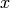 is a scheme.
is a scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.schemes.generic.scheme import is_Scheme
sage: is_Scheme(5)
False
sage: X = Spec(QQ)
sage: is_Scheme(X)
True