Bases: sage.structure.element.MultiplicativeGroupElement
An element of an arithmetic subgroup of 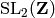 .
.
Return the upper left entry of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma0(13)([7,1,13,2]).a()
7
Return the result of the action of self on z as a fractional linear transformation.
EXAMPLES:
sage: G = Gamma0(15)
sage: g = G([1, 2, 15, 31])
An example of g acting on a symbolic variable:
sage: z = var('z')
sage: g.acton(z)
(z + 2)/(15*z + 31)
An example involving the Gaussian numbers:
sage: K.<i> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: g.acton(i)
1/1186*i + 77/1186
An example with complex numbers:
sage: C.<i> = ComplexField()
sage: g.acton(i)
0.0649241146711636 + 0.000843170320404721*I
Return the upper right entry of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma0(13)([7,1,13,2]).b()
1
Return the lower left entry of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma0(13)([7,1,13,2]).c()
13
Return the lower right entry of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma0(13)([7,1,13,2]).d()
2
Return the determinant of self, which is always 1.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma1(11)([12,11,-11,-10]).det()
1
Return the determinant of self, which is always 1.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma0(691)([1,0,691,1]).determinant()
1
Return the matrix corresponding to self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = Gamma1(3)([4,5,3,4]) ; x
[4 5]
[3 4]
sage: x.matrix()
[4 5]
[3 4]
sage: type(x.matrix())
<type 'sage.matrix.matrix_integer_2x2.Matrix_integer_2x2'>