Bases: sage.schemes.generic.scheme.Scheme, sage.structure.parent.Parent
Base class for ambient spaces over a ring.
INPUT:
Return the ambient space of the scheme self, in this case self itself.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = ProjectiveSpace(4, ZZ)
sage: P.ambient_space() is P
True
sage: A = AffineSpace(2, GF(3))
sage: A.ambient_space()
Affine Space of dimension 2 over Finite Field of size 3
Return the base change of self to the ring 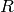 , via the natural map
from the base ring of self to
, via the natural map
from the base ring of self to 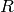 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Note
A ValueError is raised if there is no such natural map. If you do not want to do this check, use self.change_ring(R) instead.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x, y, z> = ProjectiveSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: PQ = P.base_extend(QQ); PQ
Projective Space of dimension 2 over Rational Field
sage: PQ.base_extend(GF(5))
...
ValueError: no natural map from the base ring (=Rational Field) to R (=Finite Field of size 5)!
Return an ambient space over ring 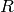 and otherwise the same as self.
and otherwise the same as self.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Note
There is no need to have any relation between 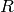 and the base ring
of self, if you want to have such a relation, use
self.base_extend(R) instead.
and the base ring
of self, if you want to have such a relation, use
self.base_extend(R) instead.
TESTS:
sage: from sage.schemes.generic.ambient_space import AmbientSpace
sage: A = AmbientSpace(5)
sage: A.change_ring(QQ)
...
NotImplementedError: ambient spaces must override "change_ring" method!
Return the defining polynomials of the scheme self. Since self is an ambient space, this is an empty list.
EXAMPLES:
sage: ProjectiveSpace(2, QQ).defining_polynomials()
()
sage: AffineSpace(0, ZZ).defining_polynomials()
()
Return the absolute dimension of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A2Q = AffineSpace(2, QQ)
sage: A2Q.dimension_absolute()
2
sage: A2Q.dimension()
2
sage: A2Z = AffineSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: A2Z.dimension_absolute()
3
sage: A2Z.dimension()
3
Return the absolute dimension of this scheme.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A2Q = AffineSpace(2, QQ)
sage: A2Q.dimension_absolute()
2
sage: A2Q.dimension()
2
sage: A2Z = AffineSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: A2Z.dimension_absolute()
3
sage: A2Z.dimension()
3
Return the relative dimension of this scheme over its base.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A2Q = AffineSpace(2, QQ)
sage: A2Q.dimension_relative()
2
sage: A2Z = AffineSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: A2Z.dimension_relative()
2
Return the  -th generator of the coordinate ring of the
scheme self.
-th generator of the coordinate ring of the
scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x, y, z> = ProjectiveSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: P.gen(1)
y
Return the generators of the coordinate ring of the scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AffineSpace(0, QQ).gens()
()
sage: P.<x, y, z> = ProjectiveSpace(2, GF(5))
sage: P.gens()
(x, y, z)
Return whether this ambient space is projective n-space.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AffineSpace(3,QQ).is_projective()
False
sage: ProjectiveSpace(3,QQ).is_projective()
True
Return the number of generators of the coordinate ring of the scheme self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AffineSpace(0, QQ).ngens()
0
sage: ProjectiveSpace(50, ZZ).ngens()
51
Return True if 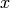 is an ambient space.
is an ambient space.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.schemes.generic.ambient_space import is_AmbientSpace
sage: is_AmbientSpace(ProjectiveSpace(3, ZZ))
True
sage: is_AmbientSpace(AffineSpace(2, QQ))
True
sage: P.<x, y, z> = ProjectiveSpace(2, ZZ)
sage: is_AmbientSpace(P.subscheme([x+y+z]))
False