AUTHORS:
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
The formal group associated to an elliptic curve.
The elliptic curve this formal group is associated to.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = EllipticCurve("37a")
sage: F = E.formal_group()
sage: F.curve()
Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + y = x^3 - x over Rational Field
Returns the power series 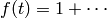 such that
such that
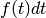 is the usual invariant differential
is the usual invariant differential
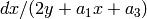 .
.
INPUT:
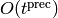
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal series
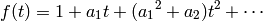
to precision 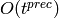 of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
The result is cached, and a cached version is returned if possible.
Warning
The resulting series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
EXAMPLES:
sage: EllipticCurve([-1, 1/4]).formal_group().differential(15)
1 - 2*t^4 + 3/4*t^6 + 6*t^8 - 5*t^10 - 305/16*t^12 + 105/4*t^14 + O(t^15)
sage: EllipticCurve(Integers(53), [-1, 1/4]).formal_group().differential(15)
1 + 51*t^4 + 14*t^6 + 6*t^8 + 48*t^10 + 24*t^12 + 13*t^14 + O(t^15)
AUTHOR:
The formal group law.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision in ZZ[[ ZZ[[‘t1’]],’t2’]]
DETAILS: Return the formal power series
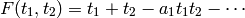
to precision 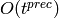 of page 115 of [Silverman AEC1].
of page 115 of [Silverman AEC1].
The result is cached, and a cached version is returned if possible.
Warning
The resulting power series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve([1, 2])
sage: F = e.formal_group().group_law(5); F
t1 + O(t1^5) + (1 - 2*t1^4 + O(t1^5))*t2 + (-4*t1^3 + O(t1^5))*t2^2 + (-4*t1^2 - 30*t1^4 + O(t1^5))*t2^3 + (-2*t1 - 30*t1^3 + O(t1^5))*t2^4 + O(t2^5)
sage: i = e.formal_group().inverse(5)
sage: Fx = F.base_extend(F.base_ring().base_extend(i.parent()))
sage: Fx (i.parent().gen()) (i)
O(t^5)
Let’s ensure caching with changed precision is working:
sage: e.formal_group().group_law(4)
t1 + O(t1^4) + (1 + O(t1^4))*t2 + (-4*t1^3 + O(t1^4))*t2^2 + (-4*t1^2 + O(t1^4))*t2^3 + O(t2^4)
The formal group inverse law i(t), which satisfies F(t, i(t)) = 0.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal power series
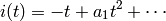
to precision 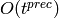 of page 114 of [Silverman AEC1].
of page 114 of [Silverman AEC1].
The result is cached, and a cached version is returned if possible.
Warning
The resulting power series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve([1, 2])
sage: F = e.formal_group().group_law(5)
sage: i = e.formal_group().inverse(5)
sage: Fx = F.base_extend(F.base_ring().base_extend(i.parent()))
sage: Fx (i) (i.parent().gen())
O(t^5)
Returns the power series 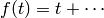 which is an
isomorphism to the additive formal group.
which is an
isomorphism to the additive formal group.
Generally this only makes sense in characteristic zero, although
the terms before 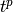 may work in characteristic
may work in characteristic
 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision
EXAMPLES:
sage: EllipticCurve([-1, 1/4]).formal_group().log(15)
t - 2/5*t^5 + 3/28*t^7 + 2/3*t^9 - 5/11*t^11 - 305/208*t^13 + O(t^15)
AUTHORS:
The formal ‘multiplication by n’ endomorphism ![[n]](../../../_images/math/0deff9086fd7840ef23860f5bc924f1d4d2d2310.png) .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal power series
 = n t + \cdots](../../../_images/math/7634c53215f9f43606c5db71aa8d23a832d52163.png)
to precision 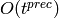 of Proposition 2.3 of [Silverman
AEC1].
of Proposition 2.3 of [Silverman
AEC1].
Warning
The resulting power series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve([1, 2, 3, 4, 6])
sage: e.formal_group().mult_by_n(0, 5)
O(t^5)
sage: e.formal_group().mult_by_n(1, 5)
t + O(t^5)
We verify an identity of low degree:
sage: none = e.formal_group().mult_by_n(-1, 5)
sage: two = e.formal_group().mult_by_n(2, 5)
sage: ntwo = e.formal_group().mult_by_n(-2, 5)
sage: ntwo - none(two)
O(t^5)
sage: ntwo - two(none)
O(t^5)
It’s quite fast:
sage: E = EllipticCurve("37a"); F = E.formal_group()
sage: F.mult_by_n(100, 20)
100*t - 49999950*t^4 + 3999999960*t^5 + 14285614285800*t^7 - 2999989920000150*t^8 + 133333325333333400*t^9 - 3571378571674999800*t^10 + 1402585362624965454000*t^11 - 146666057066712847999500*t^12 + 5336978000014213190385000*t^13 - 519472790950932256570002000*t^14 + 93851927683683567270392002800*t^15 - 6673787211563812368630730325175*t^16 + 320129060335050875009191524993000*t^17 - 45670288869783478472872833214986000*t^18 + 5302464956134111125466184947310391600*t^19 + O(t^20)
TESTS:
sage: F = EllipticCurve(GF(17), [1, 1]).formal_group()
sage: F.mult_by_n(10, 50)
10*t + 5*t^5 + 7*t^7 + 13*t^9 + t^11 + 16*t^13 + 13*t^15 + 9*t^17 + 16*t^19 + 15*t^23 + 15*t^25 + 2*t^27 + 10*t^29 + 8*t^31 + 15*t^33 + 6*t^35 + 7*t^37 + 9*t^39 + 10*t^41 + 5*t^43 + 4*t^45 + 6*t^47 + 13*t^49 + O(t^50)
sage: F = EllipticCurve(GF(101), [1, 1]).formal_group()
sage: F.mult_by_n(100, 20)
100*t + O(t^20)
EXAMPLE:
sage: E = EllipticCurve('14a')
sage: F = E.formal_group()
sage: F.sigma(5)
t + 1/2*t^2 + (1/2*c + 1/3)*t^3 + (3/4*c + 3/4)*t^4 + O(t^5)
The formal group power series w.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a power series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal power series
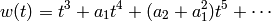
to precision 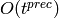 of Proposition IV.1.1 of
[Silverman AEC1]. This is the formal expansion of
of Proposition IV.1.1 of
[Silverman AEC1]. This is the formal expansion of
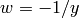 about the formal parameter
about the formal parameter 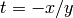 at
at
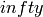 .
.
The result is cached, and a cached version is returned if possible.
Warning
The resulting power series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
ALGORITHM: Uses Newton’s method to solve the elliptic curve
equation at the origin. Complexity is roughly 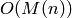 where
where  is the precision and
is the precision and 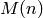 is the time
required to multiply polynomials of length
is the time
required to multiply polynomials of length  over the
coefficient ring of
over the
coefficient ring of 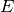 .
.
AUTHOR:
EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0])
sage: e.formal_group().w(10)
t^3 + t^6 - t^7 + 2*t^9 + O(t^10)
Check that caching works:
sage: e = EllipticCurve([3, 2, -4, -2, 5])
sage: e.formal_group().w(20)
t^3 + 3*t^4 + 11*t^5 + 35*t^6 + 101*t^7 + 237*t^8 + 312*t^9 - 949*t^10 - 10389*t^11 - 57087*t^12 - 244092*t^13 - 865333*t^14 - 2455206*t^15 - 4366196*t^16 + 6136610*t^17 + 109938783*t^18 + 688672497*t^19 + O(t^20)
sage: e.formal_group().w(7)
t^3 + 3*t^4 + 11*t^5 + 35*t^6 + O(t^7)
sage: e.formal_group().w(35)
t^3 + 3*t^4 + 11*t^5 + 35*t^6 + 101*t^7 + 237*t^8 + 312*t^9 - 949*t^10 - 10389*t^11 - 57087*t^12 - 244092*t^13 - 865333*t^14 - 2455206*t^15 - 4366196*t^16 + 6136610*t^17 + 109938783*t^18 + 688672497*t^19 + 3219525807*t^20 + 12337076504*t^21 + 38106669615*t^22 + 79452618700*t^23 - 33430470002*t^24 - 1522228110356*t^25 - 10561222329021*t^26 - 52449326572178*t^27 - 211701726058446*t^28 - 693522772940043*t^29 - 1613471639599050*t^30 - 421817906421378*t^31 + 23651687753515182*t^32 + 181817896829144595*t^33 + 950887648021211163*t^34 + O(t^35)
Return the formal series 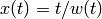 in terms of the
local parameter
in terms of the
local parameter 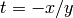 at infinity.
at infinity.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a Laurent series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal series
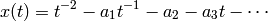
to precision 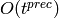 of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
Warning
The resulting series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
EXAMPLES:
sage: EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0]).formal_group().x(10)
t^-2 - t + t^2 - t^4 + 2*t^5 - t^6 - 2*t^7 + 6*t^8 - 6*t^9 + O(t^10)
Return the formal series 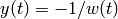 in terms of the
local parameter
in terms of the
local parameter 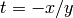 at infinity.
at infinity.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a Laurent series with given precision
DETAILS: Return the formal series
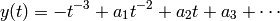
to precision 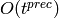 of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
of page 113 of [Silverman AEC1].
The result is cached, and a cached version is returned if possible.
Warning
The resulting series will have precision prec, but its parent PowerSeriesRing will have default precision 20 (or whatever the default default is).
EXAMPLES:
sage: EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0]).formal_group().y(10)
-t^-3 + 1 - t + t^3 - 2*t^4 + t^5 + 2*t^6 - 6*t^7 + 6*t^8 + 3*t^9 + O(t^10)