 -adic curves with multiplicative reduction¶
-adic curves with multiplicative reduction¶Let 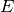 be an elliptic curve defined over the
be an elliptic curve defined over the  -adic numbers
-adic numbers 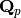 .
Suppose that
.
Suppose that 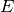 has multiplicative reduction, i.e. that the
has multiplicative reduction, i.e. that the 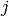 -invariant
of
-invariant
of 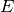 has negative valuation, say
has negative valuation, say  . Then there exists a parameter
. Then there exists a parameter
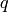 in
in 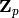 of valuation
of valuation  such that the points of
such that the points of 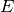 defined over
the algebraic closure
defined over
the algebraic closure 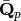 are in bijection with
are in bijection with
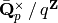 . More precisely there exists
the series
. More precisely there exists
the series 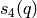 and
and 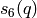 such that the
such that the
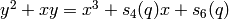 curve is isomorphic to
curve is isomorphic to 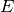 over
over
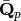 (or over
(or over 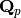 if the reduction is split multiplicative). There is
if the reduction is split multiplicative). There is  -adic analytic map from
-adic analytic map from
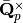 to this curve with kernel
to this curve with kernel 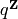 .
Points of good reduction correspond to points of valuation
.
Points of good reduction correspond to points of valuation
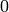 in
in 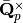 .
See chapter V of [Sil2] for more details.
.
See chapter V of [Sil2] for more details.
REFERENCES :
GTM 151, Springer 1994.
AUTHORS:
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
Tate’s  -adic uniformisation of an elliptic curve with
multiplicative reduction.
-adic uniformisation of an elliptic curve with
multiplicative reduction.
Note
Some of the methods of this Tate curve only work when the
reduction is split multiplicative over 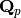 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve('130a1')
sage: eq = e.tate_curve(5); eq
5-adic Tate curve associated to the Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + x*y + y = x^3 - 33*x + 68 over Rational Field
sage: eq == loads(dumps(eq))
True
REFERENCES :
Returns the value of the  -adic Eisenstein series of weight 2 evaluated on the elliptic
curve having split multiplicative reduction.
-adic Eisenstein series of weight 2 evaluated on the elliptic
curve having split multiplicative reduction.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.E2(prec=10)
4 + 2*5^2 + 2*5^3 + 5^4 + 2*5^5 + 5^7 + 5^8 + 2*5^9 + O(5^10)
sage: T = EllipticCurve('14').tate_curve(7)
sage: T.E2(30)
2 + 4*7 + 7^2 + 3*7^3 + 6*7^4 + 5*7^5 + 2*7^6 + 7^7 + 5*7^8 + 6*7^9 + 5*7^10 + 2*7^11 + 6*7^12 + 4*7^13 + 3*7^15 + 5*7^16 + 4*7^17 + 4*7^18 + 2*7^20 + 7^21 + 5*7^22 + 4*7^23 + 4*7^24 + 3*7^25 + 6*7^26 + 3*7^27 + 6*7^28 + O(7^30)
Returns the mysterious 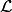 -invariant associated
to an elliptic curve with split multiplicative reduction. One
instance where this constant appears is in the exceptional
case of the
-invariant associated
to an elliptic curve with split multiplicative reduction. One
instance where this constant appears is in the exceptional
case of the  -adic Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture as
formulated in [MTT]. See [Col] for a detailed discussion.
-adic Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture as
formulated in [MTT]. See [Col] for a detailed discussion.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.REFERENCES:
 -adic analogues of the conjectures of Birch and
Swinnerton-Dyer, Inventiones mathematicae 84, (1986), 1-48.
-adic analogues of the conjectures of Birch and
Swinnerton-Dyer, Inventiones mathematicae 84, (1986), 1-48. et derivees de
valeurs propores de Frobenius, preprint, 2004.
et derivees de
valeurs propores de Frobenius, preprint, 2004.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.L_invariant(prec=10)
5^3 + 4*5^4 + 2*5^5 + 2*5^6 + 2*5^7 + 3*5^8 + 5^9 + O(5^10)
Returns the  -adic elliptic curve of the form
-adic elliptic curve of the form 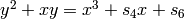 .
This curve with split multiplicative reduction is isomorphic to the given curve
over the algebraic closure of
.
This curve with split multiplicative reduction is isomorphic to the given curve
over the algebraic closure of 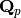 .
.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.curve(prec=5)
Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + (1+O(5^5))*x*y = x^3 +
(2*5^4+5^5+2*5^6+5^7+3*5^8+O(5^9))*x + (2*5^3+5^4+2*5^5+5^7+O(5^8)) over 5-adic
Field with capped relative precision 5
Returns True if the given elliptic curve has split multiplicative reduction.
EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.is_split()
True
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('37a1').tate_curve(37)
sage: eq.is_split()
False
Given a point 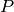 in the formal group of the elliptic curve
in the formal group of the elliptic curve 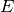 with split multiplicative reduction,
this produces an element
with split multiplicative reduction,
this produces an element 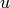 in
in 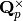 mapped to the point
mapped to the point 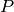 by the Tate parametrisation.
The algorithm return the unique such element in
by the Tate parametrisation.
The algorithm return the unique such element in 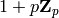 .
.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve('130a1')
sage: eq = e.tate_curve(5)
sage: P = e([-6,10])
sage: l = eq.lift(12*P, prec=10); l
1 + 4*5 + 5^3 + 5^4 + 4*5^5 + 5^6 + 5^7 + 4*5^8 + 5^9 + O(5^10)
Now we map the lift l back and check that it is indeed right.:
sage: eq.parametrisation_onto_original_curve(l)
(4*5^-2 + 2*5^-1 + 4*5 + 3*5^3 + 5^4 + 2*5^5 + 4*5^6 + O(5^7) : 2*5^-3 + 5^-1 + 4 + 4*5 + 5^2 + 3*5^3 + 4*5^4 + O(5^6) : 1 + O(5^20))
sage: e5 = e.change_ring(Qp(5,9))
sage: e5(12*P)
(4*5^-2 + 2*5^-1 + 4*5 + 3*5^3 + 5^4 + 2*5^5 + 4*5^6 + O(5^7) : 2*5^-3 + 5^-1 + 4 + 4*5 + 5^2 + 3*5^3 + 4*5^4 + O(5^6) : 1 + O(5^9))
Returns the elliptic curve the Tate curve was constructed from.
EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.original_curve()
Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + x*y + y = x^3 - 33*x + 68 over Rational Field
Returns the canonical  -adic height function on the original curve.
-adic height function on the original curve.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.OUTPUT:
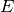 .
.EXAMPLES:
sage: e = EllipticCurve('130a1')
sage: eq = e.tate_curve(5)
sage: h = eq.padic_height(prec=10)
sage: P=e.gens()[0]
sage: h(P)
2*5^-1 + 1 + 2*5 + 2*5^2 + 3*5^3 + 3*5^6 + 5^7 + O(5^8)
Check that it is a quadratic function:
sage: h(3*P)-3^2*h(P)
O(5^8)
Computes the canonical  -adic regulator on the extended Mordell-Weil group as in [MTT]
(with the correction of [Wer] and sign convention in [SW].)
The
-adic regulator on the extended Mordell-Weil group as in [MTT]
(with the correction of [Wer] and sign convention in [SW].)
The  -adic Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture
predicts that this value appears in the formula for the leading term of the
-adic Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture
predicts that this value appears in the formula for the leading term of the
 -adic L-function.
-adic L-function.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.REFERENCES:
 -adic analogues of the conjectures of Birch and
Swinnerton-Dyer, Inventiones mathematicae 84, (1986), 1-48.
-adic analogues of the conjectures of Birch and
Swinnerton-Dyer, Inventiones mathematicae 84, (1986), 1-48.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.padic_regulator()
2*5^-1 + 1 + 2*5 + 2*5^2 + 3*5^3 + 3*5^6 + 5^7 + 3*5^9 + 3*5^10 + 3*5^12 + 4*5^13 + 3*5^15 + 2*5^16 + 3*5^18 + 4*5^19 + O(5^20)
Returns the Tate parameter 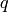 such that the curve is isomorphic
over the algebraic closure of
such that the curve is isomorphic
over the algebraic closure of 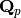 to the curve
to the curve
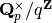 .
.
INPUT:
 -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.parameter(prec=5)
3*5^3 + 3*5^4 + 2*5^5 + 2*5^6 + 3*5^7 + O(5^8)
Given an element 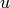 in
in 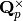 , this computes its image on the original curve
under the
, this computes its image on the original curve
under the  -adic uniformisation of
-adic uniformisation of 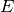 .
.
INPUT:
 -adic number.
-adic number. -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.parametrisation_onto_original_curve(1+5+5^2+O(5^10))
(4*5^-2 + 4*5^-1 + 4 + 2*5^3 + 3*5^4 + 2*5^6 + O(5^7) :
3*5^-3 + 5^-2 + 4*5^-1 + 1 + 4*5 + 5^2 + 3*5^5 + O(5^6) : 1 + O(5^20))
Here is how one gets a 4-torsion point on 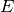 over
over 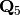 :
:
sage: R = Qp(5,10)
sage: i = R(-1).sqrt()
sage: T = eq.parametrisation_onto_original_curve(i); T
(2 + 3*5 + 4*5^2 + 2*5^3 + 5^4 + 4*5^5 + 2*5^7 + 5^8 + 5^9 + O(5^10) :
3*5 + 5^2 + 5^4 + 3*5^5 + 3*5^7 + 2*5^8 + 4*5^9 + O(5^10) : 1 + O(5^20))
sage: 4*T
(0 : 1 + O(5^20) : 0)
Given an element 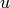 in
in 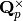 , this computes its image on the Tate curve
under the
, this computes its image on the Tate curve
under the  -adic uniformisation of
-adic uniformisation of 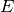 .
.
INPUT:
 -adic number.
-adic number. -adic precision, default is 20.
-adic precision, default is 20.EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.parametrisation_onto_tate_curve(1+5+5^2+O(5^10))
(5^-2 + 4*5^-1 + 1 + 2*5 + 3*5^2 + 2*5^5 + 3*5^6 + O(5^7) :
4*5^-3 + 2*5^-1 + 4 + 2*5 + 3*5^4 + 2*5^5 + O(5^6) : 1 + O(5^20))
Returns the residual characteristic  .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: eq = EllipticCurve('130a1').tate_curve(5)
sage: eq.original_curve()
Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + x*y + y = x^3 - 33*x + 68 over Rational Field
sage: eq.prime()
5