AUTHOR:
This is an implementation of the algebraic numbers (the complex
numbers which are the zero of a polynomial in ![\ZZ[x]](../../_images/math/997bd738c8f73a5487d82a0af9f18a75a09c06ec.png) ; in other
words, the algebraic closure of
; in other
words, the algebraic closure of 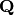 , with an embedding into
, with an embedding into 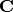 ).
All computations are exact. We also include an implementation of the
algebraic reals (the intersection of the algebraic numbers with
).
All computations are exact. We also include an implementation of the
algebraic reals (the intersection of the algebraic numbers with
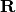 ). The field of algebraic numbers
). The field of algebraic numbers 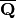 is available with
abbreviation QQbar; the field of algebraic reals has abbreviation
AA.
is available with
abbreviation QQbar; the field of algebraic reals has abbreviation
AA.
As with many other implementations of the algebraic numbers, we try hard to avoid computing a number field and working in the number field; instead, we use floating-point interval arithmetic whenever possible (basically whenever we need to prove non-equalities), and resort to symbolic computation only as needed (basically to prove equalities).
Algebraic numbers exist in one of the following forms:
 ‘th root of unity
‘th root of unityThe multiplicative subgroup of the algebraic numbers generated by the rational numbers and the roots of unity is handled particularly efficiently, as long as these roots of unity come from the QQbar.zeta() method. Cyclotomic fields in general are fairly efficient, again as long as they are derived from QQbar.zeta().
An algebraic number can be coerced into ComplexIntervalField (or RealIntervalField, for algebraic reals); every algebraic number has a cached interval of the highest precision yet calculated.
Everything is done with intervals except for comparisons. By default, comparisons compute the two algebraic numbers with 128-bit precision intervals; if this does not suffice to prove that the numbers are different, then we fall back on exact computation.
Note that division involves an implicit comparison of the divisor against zero, and may thus trigger exact computation.
Also, using an algebraic number in the leading coefficient of a polynomial also involves an implicit comparison against zero, which again may trigger exact computation.
Note that we work fairly hard to avoid computing new number fields; to help, we keep a lattice of already-computed number fields and their inclusions.
EXAMPLES:
sage: sqrt(AA(2)) > 0
True
sage: (sqrt(5 + 2*sqrt(QQbar(6))) - sqrt(QQbar(3)))^2 == 2
True
sage: AA((sqrt(5 + 2*sqrt(6)) - sqrt(3))^2) == 2
True
For a monic cubic polynomial 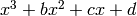 with roots
with roots 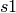 ,
,
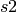 ,
, 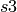 , the discriminant is defined as
, the discriminant is defined as
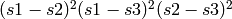 and can be computed as
and can be computed as 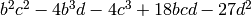 . We can test that these definitions do give the
same result:
. We can test that these definitions do give the
same result:
sage: def disc1(b, c, d):
... return b^2*c^2 - 4*b^3*d - 4*c^3 + 18*b*c*d - 27*d^2
sage: def disc2(s1, s2, s3):
... return ((s1-s2)*(s1-s3)*(s2-s3))^2
sage: x = polygen(AA)
sage: p = x*(x-2)*(x-4)
sage: cp = AA.common_polynomial(p)
sage: d, c, b, _ = p.list()
sage: s1 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(-1, 1))
sage: s2 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(1, 3))
sage: s3 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(3, 5))
sage: disc1(b, c, d) == disc2(s1, s2, s3)
True
sage: p = p + 1
sage: cp = AA.common_polynomial(p)
sage: d, c, b, _ = p.list()
sage: s1 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(-1, 1))
sage: s2 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(1, 3))
sage: s3 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(3, 5))
sage: disc1(b, c, d) == disc2(s1, s2, s3)
True
sage: p = (x-sqrt(AA(2)))*(x-AA(2).nth_root(3))*(x-sqrt(AA(3)))
sage: cp = AA.common_polynomial(p)
sage: d, c, b, _ = p.list()
sage: s1 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(1.4, 1.5))
sage: s2 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(1.7, 1.8))
sage: s3 = AA.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(1.2, 1.3))
sage: disc1(b, c, d) == disc2(s1, s2, s3)
True
We can coerce from symbolic expressions:
sage: QQbar(sqrt(-5))
2.236067977499790?*I
sage: AA(sqrt(2) + sqrt(3))
3.146264369941973?
sage: QQbar(sqrt(2)) + sqrt(3)
3.146264369941973?
sage: sqrt(2) + QQbar(sqrt(3))
3.146264369941973?
sage: QQbar(I)
1*I
sage: AA(I)
...
TypeError: Illegal initializer for algebraic number
sage: QQbar(I * golden_ratio)
1.618033988749895?*I
sage: AA(golden_ratio)^2 - AA(golden_ratio)
1
sage: QQbar((-8)^(1/3))
1.000000000000000? + 1.732050807568878?*I
sage: AA((-8)^(1/3))
-2
sage: QQbar((-4)^(1/4))
1 + 1*I
sage: AA((-4)^(1/4))
...
ValueError: Cannot coerce algebraic number with non-zero imaginary part to algebraic real
Note the different behavior in taking roots: for AA we prefer real roots if they exist, but for QQbar we take the principal root:
sage: AA(-1)^(1/3)
-1
sage: QQbar(-1)^(1/3)
0.500000000000000? + 0.866025403784439?*I
We can explicitly coerce from ![\QQ[I]](../../_images/math/74da8cbb0024b396ebb2498b87465ec60a5a27b8.png) . (Technically, this is not quite
kosher, since
. (Technically, this is not quite
kosher, since ![\QQ[I]](../../_images/math/74da8cbb0024b396ebb2498b87465ec60a5a27b8.png) doesn’t come with an embedding; we do not know
whether the field generator is supposed to map to
doesn’t come with an embedding; we do not know
whether the field generator is supposed to map to 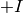 or
or 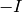 . We assume
that for any quadratic field with polynomial
. We assume
that for any quadratic field with polynomial 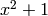 , the generator maps
to
, the generator maps
to 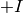 .):
.):
sage: K.<im> = QQ[I]
sage: pythag = QQbar(3/5 + 4*im/5); pythag
4/5*I + 3/5
sage: pythag.abs() == 1
True
However, implicit coercion from ![\QQ[I]](../../_images/math/74da8cbb0024b396ebb2498b87465ec60a5a27b8.png) is not allowed:
is not allowed:
sage: QQbar(1) + im
...
TypeError: unsupported operand parent(s) for '+': 'Algebraic Field' and 'Number Field in I with defining polynomial x^2 + 1'
We can implicitly coerce from algebraic reals to algebraic numbers:
sage: a = QQbar(1); print a, a.parent()
1 Algebraic Field
sage: b = AA(1); print b, b.parent()
1 Algebraic Real Field
sage: c = a + b; print c, c.parent()
2 Algebraic Field
Some computation with radicals:
sage: phi = (1 + sqrt(AA(5))) / 2
sage: phi^2 == phi + 1
True
sage: tau = (1 - sqrt(AA(5))) / 2
sage: tau^2 == tau + 1
True
sage: phi + tau == 1
True
sage: tau < 0
True
sage: rt23 = sqrt(AA(2/3))
sage: rt35 = sqrt(AA(3/5))
sage: rt25 = sqrt(AA(2/5))
sage: rt23 * rt35 == rt25
True
The Sage rings AA and QQbar can decide equalities between radical expressions (over the reals and complex numbers respectively):
sage: a = AA((2/(3*sqrt(3)) + 10/27)^(1/3) - 2/(9*(2/(3*sqrt(3)) + 10/27)^(1/3)) + 1/3)
sage: a
1.000000000000000?
sage: a == 1
True
Algebraic numbers which are known to be rational print as rationals; otherwise they print as intervals (with 53-bit precision):
sage: AA(2)/3
2/3
sage: QQbar(5/7)
5/7
sage: QQbar(1/3 - 1/4*I)
-1/4*I + 1/3
sage: two = QQbar(4).nth_root(4)^2; two
2.000000000000000?
sage: two == 2; two
True
2
sage: phi
1.618033988749895?
We can find the real and imaginary parts of an algebraic number (exactly):
sage: r = QQbar.polynomial_root(x^5 - x - 1, CIF(RIF(0.1, 0.2), RIF(1.0, 1.1))); r
0.1812324444698754? + 1.083954101317711?*I
sage: r.real()
0.1812324444698754?
sage: r.imag()
1.083954101317711?
sage: r.minpoly()
x^5 - x - 1
sage: r.real().minpoly()
x^10 + 3/16*x^6 + 11/32*x^5 - 1/64*x^2 + 1/128*x - 1/1024
sage: r.imag().minpoly() # this takes a long time (143s on my laptop)
x^20 - 5/8*x^16 - 95/256*x^12 - 625/1024*x^10 - 5/512*x^8 - 1875/8192*x^6 + 25/4096*x^4 - 625/32768*x^2 + 2869/1048576
We can find the absolute value and norm of an algebraic number exactly. (Note that we define the norm as the product of a number and its complex conjugate; this is the algebraic definition of norm, if we view QQbar as AA[I].):
sage: R.<x> = QQ[]
sage: r = (x^3 + 8).roots(QQbar, multiplicities=False)[2]; r
1.000000000000000? + 1.732050807568878?*I
sage: r.abs() == 2
True
sage: r.norm() == 4
True
sage: (r+I).norm().minpoly()
x^2 - 10*x + 13
sage: r = AA.polynomial_root(x^2 - x - 1, RIF(-1, 0)); r
-0.618033988749895?
sage: r.abs().minpoly()
x^2 + x - 1
We can compute the multiplicative order of an algebraic number:
sage: QQbar(-1/2 + I*sqrt(3)/2).multiplicative_order()
3
sage: QQbar(-sqrt(3)/2 + I/2).multiplicative_order()
12
sage: QQbar.zeta(12345).multiplicative_order()
12345
Cyclotomic fields are very fast as long as we only multiply and divide:
sage: z3_3 = QQbar.zeta(3) * 3
sage: z4_4 = QQbar.zeta(4) * 4
sage: z5_5 = QQbar.zeta(5) * 5
sage: z6_6 = QQbar.zeta(6) * 6
sage: z20_20 = QQbar.zeta(20) * 20
sage: z3_3 * z4_4 * z5_5 * z6_6 * z20_20
7200
And they are still pretty fast even if you add and subtract, and trigger exact computation:
sage: (z3_3 + z4_4 + z5_5 + z6_6 + z20_20)._exact_value()
4*zeta60^15 + 5*zeta60^12 + 9*zeta60^10 + 20*zeta60^3 - 3 where a^16 + a^14 - a^10 - a^8 - a^6 + a^2 + 1 = 0 and a in 0.994521895368274? + 0.1045284632676535?*I
The paper “ARPREC: An Arbitrary Precision Computation Package” by Bailey, Yozo, Li and Thompson discusses this result. Evidently it is difficult to find, but we can easily verify it.
sage: alpha = QQbar.polynomial_root(x^10 + x^9 - x^7 - x^6 - x^5 - x^4 - x^3 + x + 1, RIF(1, 1.2))
sage: lhs = alpha^630 - 1
sage: rhs_num = (alpha^315 - 1) * (alpha^210 - 1) * (alpha^126 - 1)^2 * (alpha^90 - 1) * (alpha^3 - 1)^3 * (alpha^2 - 1)^5 * (alpha - 1)^3
sage: rhs_den = (alpha^35 - 1) * (alpha^15 - 1)^2 * (alpha^14 - 1)^2 * (alpha^5 - 1)^6 * alpha^68
sage: rhs = rhs_num / rhs_den
sage: lhs
2.642040335819351?e44
sage: rhs
2.642040335819351?e44
sage: lhs - rhs
0.?e29
sage: lhs == rhs
True
sage: lhs - rhs
0
sage: lhs._exact_value()
-242494609856316402264822833062350847769474540*a^9 + 862295472068289472491654837785947906234680703*a^8 - 829559238431038252116584538075753012193290520*a^7 - 125882239615006638366472766103700441555126185*a^6 + 1399067970863104691667276008776398309383579345*a^5 - 1561176687069361567616835847286958553574223422*a^4 + 761706318888840943058230840550737823821027895*a^3 + 580740464974951394762758666210754821723780266*a^2 - 954587496403409756503464154898858512440951323*a + 546081123623099782018260884934770383777092602 where a^10 - 4*a^9 + 5*a^8 - a^7 - 6*a^6 + 9*a^5 - 6*a^4 - a^3 + 5*a^2 - 4*a + 1 = 0 and a in 0.4440633440090926?
Given an algebraic number, we can produce a string that will reproduce that algebraic number if you type the string into Sage. We can see that until exact computation is triggered, an algebraic number keeps track of the computation steps used to produce that number:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: n = (rt2 + rt3)^5; n
308.3018001722975?
sage: sage_input(n)
v1 = sqrt(AA(2)) + sqrt(AA(3))
v2 = v1*v1
v2*v2*v1
But once exact computation is triggered, the computation tree is discarded, and we get a way to produce the number directly:
sage: n == 109*rt2 + 89*rt3
True
sage: sage_input(n)
R.<x> = AA[]
v = AA.polynomial_root(AA.common_polynomial(x^4 - 4*x^2 + 1), RIF(RR(0.51763809020504148), RR(0.51763809020504159)))
-109*v^3 - 89*v^2 + 327*v + 178
We can also see that some computations (basically, those which are easy to perform exactly) are performed directly, instead of storing the computation tree:
sage: z3_3 = QQbar.zeta(3) * 3
sage: z4_4 = QQbar.zeta(4) * 4
sage: z5_5 = QQbar.zeta(5) * 5
sage: sage_input(z3_3 * z4_4 * z5_5)
-60*QQbar.zeta(60)^17
Note that the verify=True argument to sage_input will always trigger exact computation, so running sage_input twice in a row on the same number will actually give different answers. In the following, running sage_input on n will also trigger exact computation on rt2, as you can see by the fact that the third output is different than the first:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: n = rt2^2
sage: sage_input(n, verify=True)
# Verified
v = sqrt(AA(2))
v*v
sage: sage_input(n, verify=True)
# Verified
AA(2)
sage: n = rt2^2
sage: sage_input(n, verify=True)
# Verified
AA(2)
Just for fun, let’s try sage_input on a very complicated expression:
sage: rt2 = sqrt(AA(2))
sage: rt3 = sqrt(QQbar(3))
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: nrt3 = AA.polynomial_root((x-rt2)*(x+rt3), RIF(-2, -1))
sage: one = AA.polynomial_root((x-rt2)*(x-rt3)*(x-nrt3)*(x-1-rt3-nrt3), RIF(0.9, 1.1))
sage: one
1.000000000000000?
sage: sage_input(one, verify=True)
# Verified
R.<x> = QQbar[]
v1 = AA(2)
v2 = QQbar(sqrt(v1))
v3 = QQbar(3)
v4 = sqrt(v3)
v5 = v2*v4
v6 = (1 - v2)*(1 - v4) - 1 - v5
v7 = QQbar(sqrt(v1))
v8 = sqrt(v3)
si1 = v7*v8
cp = AA.common_polynomial(x^2 + ((1 - v7)*(1 + v8) - 1 + si1)*x - si1)
v9 = QQbar.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(-RR(1.7320508075688774), -RR(1.7320508075688772)))
v10 = 1 - v9
v11 = v6 + (v10 - 1)
v12 = -1 - v4 - QQbar.polynomial_root(cp, RIF(-RR(1.7320508075688774), -RR(1.7320508075688772)))
v13 = 1 + v12
v14 = v10*(v6 + v5) - (v6 - v5*v9)
si2 = v5*v9
AA.polynomial_root(AA.common_polynomial(x^4 + (v11 + (v13 - 1))*x^3 + (v14 + (v13*v11 - v11))*x^2 + (v13*(v14 - si2) - (v14 - si2*v12))*x - si2*v12), RIF(RR(0.99999999999999989), RR(1.0000000000000002)))
sage: one
1
We can pickle and unpickle algebraic fields (and they are globally unique):
sage: loads(dumps(AlgebraicField())) is AlgebraicField()
True
sage: loads(dumps(AlgebraicRealField())) is AlgebraicRealField()
True
We can pickle and unpickle algebraic numbers:
sage: loads(dumps(QQbar(10))) == QQbar(10)
True
sage: loads(dumps(QQbar(5/2))) == QQbar(5/2)
True
sage: loads(dumps(QQbar.zeta(5))) == QQbar.zeta(5)
True
sage: t = QQbar(sqrt(2)); type(t._descr)
<class 'sage.rings.qqbar.ANRoot'>
sage: loads(dumps(t)) == QQbar(sqrt(2))
True
sage: t.exactify(); type(t._descr)
<class 'sage.rings.qqbar.ANExtensionElement'>
sage: loads(dumps(t)) == QQbar(sqrt(2))
True
sage: t = ~QQbar(sqrt(2)); type(t._descr)
<class 'sage.rings.qqbar.ANUnaryExpr'>
sage: loads(dumps(t)) == 1/QQbar(sqrt(2))
True
sage: t = QQbar(sqrt(2)) + QQbar(sqrt(3)); type(t._descr)
<class 'sage.rings.qqbar.ANBinaryExpr'>
sage: loads(dumps(t)) == QQbar(sqrt(2)) + QQbar(sqrt(3))
True
We can convert elements of QQbar and AA into the following types: float, complex, RDF, CDF, RR, CC, RIF, CIF, ZZ, and QQ, with a few exceptions. (For the arbitrary-precision types, RR, CC, RIF, and CIF, it can convert into a field of arbitrary precision.)
Converting from QQbar to a real type (float, RDF, RR, RIF, ZZ, or QQ) succeeds only if the QQbar is actually real (has an imaginary component of exactly zero). Converting from either AA or QQbar to ZZ or QQ succeeds only if the number actually is an integer or rational. If conversion fails, a ValueError will be raised.
Here are examples of all of these conversions:
sage: all_vals = [AA(42), AA(22/7), AA(golden_ratio), QQbar(-13), QQbar(89/55), QQbar(-sqrt(7)), QQbar.zeta(5)]
sage: def convert_test_all(ty):
... def convert_test(v):
... try:
... return ty(v)
... except ValueError:
... return None
... return map(convert_test, all_vals)
sage: convert_test_all(float)
[42.0, 3.1428571428571432, 1.6180339887498949, -13.0, 1.6181818181818182, -2.6457513110645907, None]
sage: convert_test_all(complex)
[(42+0j), (3.1428571428571432+0j), (1.6180339887498949+0j), (-13+0j), (1.6181818181818182+0j), (-2.6457513110645907+0j), (0.30901699437494745+0.95105651629515364j)]
sage: convert_test_all(RDF)
[42.0, 3.14285714286, 1.61803398875, -13.0, 1.61818181818, -2.64575131106, None]
sage: convert_test_all(CDF)
[42.0, 3.14285714286, 1.61803398875, -13.0, 1.61818181818, -2.64575131106, 0.309016994375 + 0.951056516295*I]
sage: convert_test_all(RR)
[42.0000000000000, 3.14285714285714, 1.61803398874989, -13.0000000000000, 1.61818181818182, -2.64575131106459, None]
sage: convert_test_all(CC)
[42.0000000000000, 3.14285714285714, 1.61803398874989, -13.0000000000000, 1.61818181818182, -2.64575131106459, 0.309016994374947 + 0.951056516295154*I]
sage: convert_test_all(RIF)
[42, 3.142857142857143?, 1.618033988749895?, -13, 1.618181818181819?, -2.645751311064591?, None]
sage: convert_test_all(CIF)
[42, 3.142857142857143?, 1.618033988749895?, -13, 1.618181818181819?, -2.645751311064591?, 0.3090169943749474? + 0.9510565162951536?*I]
sage: convert_test_all(ZZ)
[42, None, None, -13, None, None, None]
sage: convert_test_all(QQ)
[42, 22/7, None, -13, 89/55, None, None]
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
TESTS:
We check to make sure that this method still works even. We do this by increasing the recursion level at each step and decrease it before we return:
sage: import sys; sys.getrecursionlimit()
1000
sage: s = SFASchur(QQ)
sage: a=s([3,2]).expand(8)(flatten([[QQbar.zeta(3)^d for d in range(3)], [QQbar.zeta(5)^d for d in range(5)]]))
sage: a.exactify(); a #long
0
sage: sys.getrecursionlimit()
1000
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (always True for ANBinaryExpr).
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage_input(2 + sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
2 + sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(sqrt(AA(2)) + 2, verify=True)
# Verified
sqrt(AA(2)) + 2
sage: sage_input(2 - sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
2 - sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(2 / sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
2/sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(2 + (-1*sqrt(AA(2))), verify=True)
# Verified
2 - sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(2*sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
2*sqrt(AA(2))
sage: rt2 = sqrt(AA(2))
sage: one = rt2/rt2
sage: n = one+3
sage: sage_input(n)
v = sqrt(AA(2))
v/v + 3
sage: one == 1
True
sage: sage_input(n)
1 + AA(3)
sage: rt3 = QQbar(sqrt(3))
sage: one = rt3/rt3
sage: n = sqrt(AA(2))+one
sage: one == 1
True
sage: sage_input(n)
QQbar(sqrt(AA(2))) + 1
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: binexp = ANBinaryExpr(AA(3), AA(5), '*')
sage: binexp.handle_sage_input(sib, False, False)
({binop:* {atomic:3} {call: {atomic:AA}({atomic:5})}}, True)
sage: binexp.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({call: {atomic:QQbar}({binop:* {atomic:3} {call: {atomic:AA}({atomic:5})}})}, True)
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
An AlgebraicNumber or AlgebraicReal is a wrapper around an ANDescr object. ANDescr is an abstract base class, which should never be directly instantiated; its concrete subclasses are ANRational, ANBinaryExpr, ANUnaryExpr, ANRootOfUnity, ANRoot, and ANExtensionElement. ANDescr and all of its subclasses are private, and should not be used directly.
Returns True if self is an ANRational, ANRootOfUnity, or ANExtensionElement.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANRational
sage: ANRational(1/2).is_exact()
True
sage: QQbar(3+I)._descr.is_exact()
True
sage: QQbar.zeta(17)._descr.is_exact()
True
Returns True if self is an ANExtensionElement.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANExtensionElement, ANRoot, AlgebraicGenerator
sage: _.<y> = QQ['y']
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: nf2 = NumberField(y^2 - 2, name='a', check=False)
sage: root2 = ANRoot(x^2 - 2, RIF(1, 2))
sage: gen2 = AlgebraicGenerator(nf2, root2)
sage: sqrt2 = ANExtensionElement(gen2, nf2.gen())
sage: sqrt2.is_field_element()
True
Returns True if self is an ANRational object. (Note that the constructors for ANExtensionElement and ANRootOfUnity will actually return ANRational objects for rational numbers.)
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANRational
sage: ANRational(3/7).is_rational()
True
Checks whether this descriptor represents a value with the same algebraic degree as the number field associated with the descriptor.
Returns True if self is an ANRational, ANRootOfUnit, or a minimal ANExtensionElement.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANRational
sage: ANRational(1/2).is_simple()
True
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: rt2b = rt3 + rt2 - rt3
sage: rt2.exactify()
sage: rt2._descr.is_simple()
True
sage: rt2b.exactify()
sage: rt2b._descr.is_simple()
False
sage: rt2b.simplify()
sage: rt2b._descr.is_simple()
True
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
The subclass of ANDescr that represents a number field element in terms of a specific generator. Consists of a polynomial with rational coefficients in terms of the generator, and the generator itself, an AlgebraicGenerator.
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (always True, for ANExtensionElement).
EXAMPLES:
sage: I = QQbar(I)
sage: sage_input(3+4*I, verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar(3 + 4*I)
sage: v = QQbar.zeta(3) + QQbar.zeta(5)
sage: v - v == 0
True
sage: sage_input(vector(QQbar, (4-3*I, QQbar.zeta(7))), verify=True)
# Verified
vector(QQbar, [4 - 3*I, QQbar.zeta(7)])
sage: sage_input(v, verify=True)
# Verified
v = QQbar.zeta(15)
v^5 + v^3
sage: v = QQbar(sqrt(AA(2)))
sage: v.exactify()
sage: sage_input(v, verify=True)
# Verified
R.<x> = AA[]
QQbar(AA.polynomial_root(AA.common_polynomial(x^2 - 2), RIF(RR(1.4142135623730949), RR(1.4142135623730951))))
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: extel = ANExtensionElement(QQbar_I_generator, QQbar_I_generator.field().gen() + 1)
sage: extel.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({call: {atomic:QQbar}({binop:+ {atomic:1} {atomic:I}})}, True)
Checks whether this descriptor represents a value with the same algebraic degree as the number field associated with the descriptor.
For ANExtensionElement elements, we check this by comparing the degree of the minimal polynomial to the degree of the field.
EXAMPLES:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: rt2b = rt3 + rt2 - rt3
sage: rt2.exactify()
sage: rt2._descr
a where a^2 - 2 = 0 and a in 1.414213562373095?
sage: rt2._descr.is_simple()
True
sage: rt2b.exactify()
sage: rt2b._descr
a^3 - 3*a where a^4 - 4*a^2 + 1 = 0 and a in 1.931851652578137?
sage: rt2b._descr.is_simple()
False
Compute the minimal polynomial of this algebraic number.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = AA(sqrt(2)) + QQbar(I); a
1.414213562373095? + 1*I
sage: p = a.minpoly(); p
x^4 - 2*x^2 + 9
sage: p(a)
0
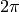 times some rational number,
return that rational; otherwise, return None.
times some rational number,
return that rational; otherwise, return None.Compute an exact representation for this descriptor, in the smallest possible number field.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: rt2b = rt3 + rt2 - rt3
sage: rt2b.exactify()
sage: rt2b._descr
a^3 - 3*a where a^4 - 4*a^2 + 1 = 0 and a in 1.931851652578137?
sage: rt2b._descr.simplify(rt2b)
a where a^2 - 2 = 0 and a in 1.414213562373095?
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
The subclass of ANDescr that represents an arbitrary rational. This class is private, and should not be used directly.
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (always False, for rationals).
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage_input(QQbar(22/7), verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar(22/7)
sage: sage_input(-AA(3)/5, verify=True)
# Verified
AA(-3/5)
sage: sage_input(vector(AA, (0, 1/2, 1/3)), verify=True)
# Verified
vector(AA, [0, 1/2, 1/3])
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: rat = ANRational(9/10)
sage: rat.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({call: {atomic:QQbar}({binop:/ {atomic:9} {atomic:10}})}, False)
Checks whether this descriptor represents a value with the same algebraic degree as the number field associated with the descriptor.
This is always true for rational numbers.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(1/2)._descr.is_simple()
True
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
The subclass of ANDescr that represents a particular root of a polynomial with algebraic coefficients. This class is private, and should not be used directly.
Returns either an ANRational or an ANExtensionElement with the same value as this number.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANRoot
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: two = ANRoot((x-2)*(x-sqrt(QQbar(2))), RIF(1.9, 2.1))
sage: two.exactify()
2
sage: two.exactify().rational_value()
2
sage: strange = ANRoot(x^2 + sqrt(QQbar(3))*x - sqrt(QQbar(2)), RIF(-0, 1))
sage: strange.exactify()
a where a^8 - 6*a^6 + 5*a^4 - 12*a^2 + 4 = 0 and a in 0.6051012265139511?
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (always True, for ANRoot).
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage_input((AA(3)^(1/2))^(1/3), verify=True)
# Verified
sqrt(AA(3)).nth_root(3)
These two examples are too big to verify quickly. (Verification would create a field of degree 28.):
sage: sage_input((sqrt(AA(3))^(5/7))^(9/4))
(sqrt(AA(3))^(5/7))^(9/4)
sage: sage_input((sqrt(QQbar(-7))^(5/7))^(9/4))
(sqrt(QQbar(-7))^(5/7))^(9/4)
sage: x = polygen(QQ)
sage: sage_input(AA.polynomial_root(x^2-x-1, RIF(1, 2)), verify=True)
# Verified
R.<x> = AA[]
AA.polynomial_root(AA.common_polynomial(x^2 - x - 1), RIF(RR(1.6180339887498947), RR(1.6180339887498949)))
sage: sage_input(QQbar.polynomial_root(x^3-5, CIF(RIF(-3, 0), RIF(0, 3))), verify=True)
# Verified
R.<x> = AA[]
QQbar.polynomial_root(AA.common_polynomial(x^3 - 5), CIF(RIF(-RR(0.85498797333834853), -RR(0.85498797333834842)), RIF(RR(1.4808826096823642), RR(1.4808826096823644))))
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: rt = ANRoot(x^3 - 2, RIF(0, 4))
sage: rt.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({call: {getattr: {atomic:QQbar}.polynomial_root}({call: {getattr: {atomic:AA}.common_polynomial}({binop:- {binop:** {gen:x {constr_parent: {subscr: {atomic:AA}[{atomic:'x'}]} with gens: ('x',)}} {atomic:3}} {atomic:2}})}, {call: {atomic:RIF}({call: {atomic:RR}({atomic:1.259921049894873})}, {call: {atomic:RR}({atomic:1.2599210498948732})})})}, True)
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
The subclass of ANDescr that represents a rational multiplied by a root of unity. This class is private, and should not be used directly.
Such numbers are represented by a “rational angle” and a rational
scale. The “rational angle” is the argument of the number, divided by
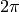 ; so given angle
; so given angle 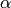 and scale
and scale  , the number is:
, the number is:
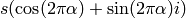 ; or equivalently
; or equivalently
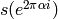 .
.
We normalize so that 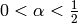 ; this requires
allowing both positive and negative scales. (Attempts to create
an ANRootOfUnity with an angle which is a multiple of
; this requires
allowing both positive and negative scales. (Attempts to create
an ANRootOfUnity with an angle which is a multiple of
 end up creating an ANRational instead.)
end up creating an ANRational instead.)
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (False for imaginary numbers, True for others).
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage_input(22/7*QQbar.zeta(4), verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar(22/7*I)
sage: sage_input((2*QQbar.zeta(12))^4, verify=True)
# Verified
16*QQbar.zeta(3)
sage: sage_input(QQbar.zeta(5)^2, verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar.zeta(5)^2
sage: sage_input(QQbar.zeta(5)^3, verify=True)
# Verified
-QQbar.zeta(10)
sage: sage_input(vector(QQbar, (I, 3*QQbar.zeta(9))), verify=True)
# Verified
vector(QQbar, [I, 3*QQbar.zeta(9)])
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: rtofunity = ANRootOfUnity(137/500, 1/1000)
sage: rtofunity.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({binop:* {binop:/ {atomic:1} {atomic:1000}} {binop:** {call: {getattr: {atomic:QQbar}.zeta}({atomic:500})} {atomic:137}}}, True)
Checks whether this descriptor represents a value with the same algebraic degree as the number field associated with the descriptor.
This is always true for ANRootOfUnity elements.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = QQbar.zeta(17)^5 * 4/3; a._descr
4/3*e^(2*pi*I*5/17)
sage: a._descr.is_simple()
True
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = QQbar.zeta(7) * 2; a
1.246979603717467? + 1.563662964936060?*I
sage: a.minpoly()
x^6 + 2*x^5 + 4*x^4 + 8*x^3 + 16*x^2 + 32*x + 64
sage: a.minpoly()(a)
0.?e-15 + 0.?e-15*I
sage: a.minpoly()(a) == 0
True
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.ANDescr
Produce an expression which will reproduce this value when evaluated, and an indication of whether this value is worth sharing (always True for ANUnaryExpr).
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage_input(-sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
-sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(~sqrt(AA(2)), verify=True)
# Verified
~sqrt(AA(2))
sage: sage_input(sqrt(QQbar(-3)).conjugate(), verify=True)
# Verified
sqrt(QQbar(-3)).conjugate()
sage: sage_input(QQbar.zeta(3).real(), verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar.zeta(3).real()
sage: sage_input(QQbar.zeta(3).imag(), verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar.zeta(3).imag()
sage: sage_input(abs(sqrt(QQbar(-3))), verify=True)
# Verified
abs(sqrt(QQbar(-3)))
sage: sage_input(sqrt(QQbar(-3)).norm(), verify=True)
# Verified
sqrt(QQbar(-3)).norm()
sage: sage_input(QQbar(QQbar.zeta(3).real()), verify=True)
# Verified
QQbar(QQbar.zeta(3).real())
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import *
sage: from sage.misc.sage_input import SageInputBuilder
sage: sib = SageInputBuilder()
sage: unexp = ANUnaryExpr(sqrt(AA(2)), '~')
sage: unexp.handle_sage_input(sib, False, False)
({unop:~ {call: {atomic:sqrt}({call: {atomic:AA}({atomic:2})})}}, True)
sage: unexp.handle_sage_input(sib, False, True)
({call: {atomic:QQbar}({unop:~ {call: {atomic:sqrt}({call: {atomic:AA}({atomic:2})})}})}, True)
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar._uniq_alg, sage.rings.qqbar.AlgebraicField_common
The field of algebraic numbers.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar.algebraic_closure()
Algebraic Field
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar.completion(infinity, 500)
Complex Field with 500 bits of precision
sage: QQbar.completion(infinity, prec=53, extras={'type':'RDF'})
Complex Double Field
sage: QQbar.completion(infinity, 53) is CC
True
sage: QQbar.completion(3, 20)
...
NotImplementedError
Given a polynomial with algebraic coefficients and an interval enclosing exactly one root of the polynomial, constructs an algebraic real representation of that root.
The polynomial need not be irreducible, or even squarefree; but
if the given root is a multiple root, its multiplicity must be
specified. (IMPORTANT NOTE: Currently, multiplicity-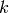 roots
are handled by taking the
roots
are handled by taking the 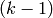 -st derivative of the polynomial.
This means that the interval must enclose exactly one root
of this derivative.)
-st derivative of the polynomial.
This means that the interval must enclose exactly one root
of this derivative.)
The conditions on the arguments (that the interval encloses exactly one root, and that multiple roots match the given multiplicity) are not checked; if they are not satisfied, an error may be thrown (possibly later, when the algebraic number is used), or wrong answers may result.
Note that if you are constructing multiple roots of a single polynomial, it is better to use QQbar.common_polynomial to get a shared polynomial.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: phi = QQbar.polynomial_root(x^2 - x - 1, RIF(0, 2)); phi
1.618033988749895?
sage: p = (x-1)^7 * (x-2)
sage: r = QQbar.polynomial_root(p, RIF(9/10, 11/10), multiplicity=7)
sage: r; r == 1
1
True
sage: p = (x-phi)*(x-sqrt(QQbar(2)))
sage: r = QQbar.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1, 3/2))
sage: r; r == sqrt(QQbar(2))
1.414213562373095?
True
Returns a primitive  ‘th root of unity, specifically
‘th root of unity, specifically 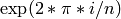 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar.zeta(1)
1
sage: QQbar.zeta(2)
-1
sage: QQbar.zeta(3)
-0.500000000000000? + 0.866025403784439?*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(4)
1*I
sage: QQbar.zeta()
1*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(5)
0.3090169943749474? + 0.9510565162951536?*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(314159)
0.9999999997999997? + 0.00002000001689195824?*I
Bases: sage.rings.ring.Field
Given a polynomial with algebraic coefficients, returns a wrapper that caches high-precision calculations and factorizations. This wrapper can be passed to polynomial_root in place of the polynomial.
Using common_polynomial makes no semantic difference, but will improve efficiency if you are dealing with multiple roots of a single polynomial.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = polygen(ZZ)
sage: p = AA.common_polynomial(x^2 - x - 1)
sage: phi = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1, 2))
sage: tau = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(-1, 0))
sage: phi + tau == 1
True
sage: phi * tau == -1
True
sage: x = polygen(SR)
sage: p = (x - sqrt(-5)) * (x - sqrt(3)); p
x^2 + (-sqrt(-5) - sqrt(3))*x + sqrt(-5)*sqrt(3)
sage: p = QQbar.common_polynomial(p)
sage: a = QQbar.polynomial_root(p, CIF(RIF(-0.1, 0.1), RIF(2, 3))); a
0.?e-18 + 2.236067977499790?*I
sage: b = QQbar.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1, 2)); b
1.732050807568878?
These “common polynomials” can be shared between real and complex roots:
sage: p = AA.common_polynomial(x^3 - x - 1)
sage: r1 = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1.3, 1.4)); r1
1.324717957244746?
sage: r2 = QQbar.polynomial_root(p, CIF(RIF(-0.7, -0.6), RIF(0.5, 0.6))); r2
-0.6623589786223730? + 0.5622795120623013?*I
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
An AlgebraicGenerator represents both an algebraic number 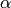 and
the number field
and
the number field ![\QQ[\alpha]](../../_images/math/0c80cf2c860b5ae56f41c1376e656dc9dc4bf73a.png) . There is a single AlgebraicGenerator
representing
. There is a single AlgebraicGenerator
representing 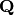 (with
(with 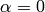 ).
).
The AlgebraicGenerator class is private, and should not be used directly.
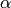 , return a
generator for the complex conjugate of
, return a
generator for the complex conjugate of 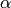 .
.Returns true iff this is the trivial generator (alpha == 1), which does not actually extend the rationals.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import qq_generator
sage: qq_generator.is_trivial()
True
Given a generator gen and another generator super, where super is the result of a tree of union() operations where one of the leaves is gen, gen.super_poly(super) returns a polynomial expressing the value of gen in terms of the value of super (except that if gen is qq_generator, super_poly() always returns None.)
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import AlgebraicGenerator, ANRoot, qq_generator
sage: _.<y> = QQ['y']
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: nf2 = NumberField(y^2 - 2, name='a', check=False)
sage: root2 = ANRoot(x^2 - 2, RIF(1, 2))
sage: gen2 = AlgebraicGenerator(nf2, root2)
sage: gen2
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2 with a in 1.414213562373095?
sage: nf3 = NumberField(y^2 - 3, name='a', check=False)
sage: root3 = ANRoot(x^2 - 3, RIF(1, 2))
sage: gen3 = AlgebraicGenerator(nf3, root3)
sage: gen3
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3 with a in 1.732050807568878?
sage: gen2_3 = gen2.union(gen3)
sage: gen2_3
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1 with a in 0.5176380902050415?
sage: qq_generator.super_poly(gen2) is None
True
sage: gen2.super_poly(gen2_3)
-a^3 + 3*a
sage: gen3.super_poly(gen2_3)
-a^2 + 2
Given generators alpha and beta,
alpha.union(beta) gives a generator for the number field
![\QQ[\alpha][\beta]](../../_images/math/98859f7849893949979dc414ff39226de28a732c.png) .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import ANRoot, AlgebraicGenerator, qq_generator
sage: _.<y> = QQ['y']
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: nf2 = NumberField(y^2 - 2, name='a', check=False)
sage: root2 = ANRoot(x^2 - 2, RIF(1, 2))
sage: gen2 = AlgebraicGenerator(nf2, root2)
sage: gen2
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2 with a in 1.414213562373095?
sage: nf3 = NumberField(y^2 - 3, name='a', check=False)
sage: root3 = ANRoot(x^2 - 3, RIF(1, 2))
sage: gen3 = AlgebraicGenerator(nf3, root3)
sage: gen3
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3 with a in 1.732050807568878?
sage: gen2.union(qq_generator) is gen2
True
sage: qq_generator.union(gen3) is gen3
True
sage: gen2.union(gen3)
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1 with a in 0.5176380902050415?
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
A simple class for maintaining relations in the lattice of algebraic extensions.
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.AlgebraicNumber_base
The class for algebraic numbers (complex numbers which are the roots of a polynomial with integer coefficients). Much of its functionality is inherited from AlgebraicNumber_base.
Given a ComplexField, return the best possible approximation of this number in that field. Note that if either component is sufficiently close to the halfway point between two floating-point numbers in the corresponding RealField, then this will trigger exact computation, which may be very slow.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = QQbar.zeta(9) + I + QQbar.zeta(9).conjugate(); a
1.532088886237957? + 1.000000000000000?*I
sage: a.complex_exact(CIF)
1.532088886237957? + 1*I
Given a ComplexField, compute a good approximation to self in that field. The approximation will be off by at most two ulp’s in each component, except for components which are very close to zero, which will have an absolute error at most 2**(-(field.prec()-1)).
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = QQbar.zeta(5)
sage: a.complex_number(CIF)
0.309016994374947 + 0.951056516295154*I
sage: (a + a.conjugate()).complex_number(CIF)
0.618033988749895 - 5.42101086242752e-20*I
Returns the complex conjugate of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(3 + 4*I).conjugate()
3 - 4*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(7).conjugate()
0.6234898018587335? - 0.7818314824680299?*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(7) + QQbar.zeta(7).conjugate()
1.246979603717467? + 0.?e-18*I
Given a ComplexIntervalField, compute the best possible approximation of this number in that field. Note that if either the real or imaginary parts of this number are sufficiently close to some floating-point number (and, in particular, if either is exactly representable in floating-point), then this will trigger exact computation, which may be very slow.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = QQbar(I).sqrt(); a
0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I
sage: a.interval_exact(CIF)
0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I
sage: b = QQbar((1+I)*sqrt(2)/2)
sage: (a - b).interval(CIF)
0.?e-19 + 0.?e-18*I
sage: (a - b).interval_exact(CIF)
0
Compute the multiplicative order of this algebraic real
number. That is, find the smallest positive integer  such
that
such
that 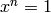 . If there is no such
. If there is no such  , returns +Infinity.
, returns +Infinity.
We first check that abs(x) is very close to 1. If so, we compute
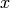 exactly and examine its argument.
exactly and examine its argument.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(-sqrt(3)/2 - I/2).multiplicative_order()
12
sage: QQbar(1).multiplicative_order()
1
sage: QQbar(-I).multiplicative_order()
4
sage: QQbar(707/1000 + 707/1000*I).multiplicative_order()
+Infinity
sage: QQbar(3/5 + 4/5*I).multiplicative_order()
+Infinity
Returns self * self.conjugate(). This is the algebraic definition of norm, if we view QQbar as AA[I].
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(3 + 4*I).norm()
25
sage: type(QQbar(I).norm())
<class 'sage.rings.qqbar.AlgebraicReal'>
sage: QQbar.zeta(1007).norm()
1
Returns the argument of self, divided by 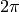 , as long as this
result is rational. Otherwise returns None. Always triggers
exact computation.
, as long as this
result is rational. Otherwise returns None. Always triggers
exact computation.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar((1+I)*(sqrt(2)+sqrt(5))).rational_argument()
1/8
sage: QQbar(-1 + I*sqrt(3)).rational_argument()
1/3
sage: QQbar(-1 - I*sqrt(3)).rational_argument()
-1/3
sage: QQbar(3+4*I).rational_argument() is None
True
sage: (QQbar.zeta(7654321)^65536).rational_argument()
65536/7654321
sage: (QQbar.zeta(3)^65536).rational_argument()
1/3
Bases: sage.structure.element.FieldElement
This is the common base class for algebraic numbers (complex
numbers which are the zero of a polynomial in ![\ZZ[x]](../../_images/math/997bd738c8f73a5487d82a0af9f18a75a09c06ec.png) ) and algebraic
reals (algebraic numbers which happen to be real).
) and algebraic
reals (algebraic numbers which happen to be real).
AlgebraicNumber objects can be created using QQbar (== AlgebraicNumberField()), and AlgebraicReal objects can be created using AA (== AlgebraicRealField()). They can be created either by coercing a rational or a symbolic expression, or by using the QQbar.polynomial_root() or AA.polynomial_root() method to construct a particular root of a polynomial with algebraic coefficients. Also, AlgebraicNumber and AlgebraicReal are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, division (except by 0), and rational powers (including roots), except that for a negative AlgebraicReal, taking a power with an even denominator returns an AlgebraicNumber instead of an AlgebraicReal.
AlgebraicNumber and AlgebraicReal objects can be approximated to any desired precision. They can be compared exactly; if the two numbers are very close, or are equal, this may require exact computation, which can be extremely slow.
As long as exact computation is not triggered, computation with algebraic numbers should not be too much slower than computation with intervals. As mentioned above, exact computation is triggered when comparing two algebraic numbers which are very close together. This can be an explicit comparison in user code, but the following list of actions (not necessarily complete) can also trigger exact computation:
The exact definition of “very close” is subject to change; currently, we compute our best approximation of the two numbers using 128-bit arithmetic, and see if that’s sufficient to decide the comparison. Note that comparing two algebraic numbers which are actually equal will always trigger exact computation, unless they are actually the same object.
EXAMPLES:
sage: sqrt(QQbar(2))
1.414213562373095?
sage: sqrt(QQbar(2))^2 == 2
True
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: phi = QQbar.polynomial_root(x^2 - x - 1, RIF(1, 2))
sage: phi
1.618033988749895?
sage: phi^2 == phi+1
True
sage: AA(sqrt(65537))
256.0019531175495?
Returns a number field containing this value, a representation of this value as an element of that number field, and a homomorphism from the number field back to AA or QQbar.
This may not return the smallest such number field, unless minimal=True is specified.
To compute a single number field containing multiple algebraic numbers, use the function number_field_elements_from_algebraics instead.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(sqrt(8)).as_number_field_element()
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2, 2*a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.414213562373095?)
sage: x = polygen(ZZ)
sage: p = x^3 + x^2 + x + 17
sage: (rt,) = p.roots(ring=AA, multiplicities=False); rt
-2.804642726932742?
sage: (nf, elt, hom) = rt.as_number_field_element(); (nf, elt, hom)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^3 - y^2 + y - 17, -a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^3 - y^2 + y - 17
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 2.804642726932742?)
sage: hom(elt) == rt
True
We see an example where we do not get the minimal number field unless we specify minimal=True:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: rt3b = rt2 + rt3 - rt2
sage: rt3b.as_number_field_element()
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1, -a^2 + 2, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 0.5176380902050415?)
sage: rt3b.as_number_field_element(minimal=True)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3, a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.732050807568878?)
Return the degree of this algebraic number (the degree of its minimal polynomial, or equivalently, the degree of the smallest algebraic extension of the rationals containing this number).
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(5/3).degree()
1
sage: sqrt(QQbar(2)).degree()
2
sage: QQbar(17).nth_root(5).degree()
5
sage: sqrt(3+sqrt(QQbar(8))).degree()
2
Compute an exact representation for this number.
EXAMPLES:
sage: two = QQbar(4).nth_root(4)^2
sage: two
2.000000000000000?
sage: two.exactify()
sage: two
2
Given an interval field (real or complex, as appropriate) of
precision  , compute an interval representation of self with
diameter() at most
, compute an interval representation of self with
diameter() at most 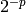 ; then round that representation into
the given field. Here diameter() is relative diameter for
intervals not containing 0, and absolute diameter for
intervals that do contain 0; thus, if the returned interval
does not contain 0, it has at least
; then round that representation into
the given field. Here diameter() is relative diameter for
intervals not containing 0, and absolute diameter for
intervals that do contain 0; thus, if the returned interval
does not contain 0, it has at least 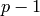 good bits.
good bits.
EXAMPLES:
sage: RIF64 = RealIntervalField(64)
sage: x = AA(2).sqrt()
sage: y = x*x
sage: y = 1000 * y - 999 * y
sage: y.interval_fast(RIF64)
2.000000000000000?
sage: y.interval(RIF64)
2.000000000000000000?
sage: CIF64 = ComplexIntervalField(64)
sage: x = QQbar.zeta(11)
sage: x.interval_fast(CIF64)
0.8412535328311811689? + 0.540640817455597582?*I
sage: x.interval(CIF64)
0.8412535328311811689? + 0.5406408174555975822?*I
Compute an interval representation of self with diameter() at most diam. The precision of the returned value is unpredictable.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(2).sqrt().interval_diameter(1e-10)
1.4142135623730950488?
sage: AA(2).sqrt().interval_diameter(1e-30)
1.41421356237309504880168872420969807857?
sage: QQbar(2).sqrt().interval_diameter(1e-10)
1.4142135623730950488?
sage: QQbar(2).sqrt().interval_diameter(1e-30)
1.41421356237309504880168872420969807857?
Given a RealIntervalField, compute the value of this number using interval arithmetic of at least the precision of the field, and return the value in that field. (More precision may be used in the computation.) The returned interval may be arbitrarily imprecise, if this number is the result of a sufficiently long computation chain.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = AA(2).sqrt()
sage: x.interval_fast(RIF)
1.414213562373095?
sage: x.interval_fast(RealIntervalField(200))
1.414213562373095048801688724209698078569671875376948073176680?
sage: x = QQbar(I).sqrt()
sage: x.interval_fast(CIF)
0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I
sage: x.interval_fast(RIF)
...
TypeError: Unable to convert number to real interval.
Return whether or not this number is square.
OUTPUT:
(boolean) True in all cases for elements of QQbar; True for non-negative elements of AA, otherwise False.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(2).is_square()
True
sage: AA(-2).is_square()
False
sage: QQbar(-2).is_square()
True
sage: QQbar(I).is_square()
True
Compute the minimal polynomial of this algebraic number. The minimal polynomial is the monic polynomial of least degree having this number as a root; it is unique.
EXAMPLES:
sage: QQbar(4).sqrt().minpoly()
x - 2
sage: ((QQbar(2).nth_root(4))^2).minpoly()
x^2 - 2
sage: v = sqrt(QQbar(2)) + sqrt(QQbar(3)); v
3.146264369941973?
sage: p = v.minpoly(); p
x^4 - 10*x^2 + 1
sage: p(RR(v.real()))
1.31006316905768e-14
Return the n-th root of this number.
Note that for odd  and negative real numbers, AlgebraicReal
and AlgebraicNumber values give different answers: AlgebraicReal
values prefer real results, and AlgebraicNumber values
return the principal root.
and negative real numbers, AlgebraicReal
and AlgebraicNumber values give different answers: AlgebraicReal
values prefer real results, and AlgebraicNumber values
return the principal root.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(-8).nth_root(3)
-2
sage: QQbar(-8).nth_root(3)
1.000000000000000? + 1.732050807568878?*I
sage: QQbar.zeta(12).nth_root(15)
0.9993908270190957? + 0.03489949670250097?*I
Compute an exact representation for this number, in the smallest possible number field.
EXAMPLES:
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2))
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3))
sage: rt2b = rt3 + rt2 - rt3
sage: rt2b.exactify()
sage: rt2b._exact_value()
a^3 - 3*a where a^4 - 4*a^2 + 1 = 0 and a in 1.931851652578137?
sage: rt2b.simplify()
sage: rt2b._exact_value()
a where a^2 - 2 = 0 and a in 1.414213562373095?
Return the square root(s) of this number.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Either the principal square root of self, or a list of its square roots (with the principal one first).
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(2).sqrt()
1.414213562373095?
sage: QQbar(I).sqrt()
0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I
sage: QQbar(I).sqrt(all=True)
[0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I, -0.7071067811865475? - 0.7071067811865475?*I]
sage: a = QQbar(0)
sage: a.sqrt()
0
sage: a.sqrt(all=True)
[0]
sage: a = AA(0)
sage: a.sqrt()
0
sage: a.sqrt(all=True)
[0]
This second example just shows that the program doesn’t care where 0 is defined, it gives the same answer regardless. After all, how many ways can you square-root zero?
sage: AA(-2).sqrt()
1.414213562373095?*I
sage: AA(-2).sqrt(all=True)
[1.414213562373095?*I, -1.414213562373095?*I]
sage: AA(-2).sqrt(extend=False)
...
ValueError: -2 is not a square in AA, being negative. Use extend = True for a square root in QQbar.
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
Keeps track of a polynomial used for algebraic numbers.
If multiple algebraic numbers are created as roots of a single polynomial, this allows the polynomial and information about the polynomial to be shared. This reduces work if the polynomial must be recomputed at higher precision, or if it must be factored.
This class is private, and should only be constructed by AA.common_polynomial() or QQbar.common_polynomial(), and should only be used as an argument to AA.polynomial_root() or QQbar.polynomial_root(). (It doesn’t matter whether you create the common polynomial with AA.common_polynomial() or QQbar.common_polynomial().)
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = polygen(QQbar)
sage: P = QQbar.common_polynomial(x^2 - x - 1)
sage: P
x^2 - x - 1
sage: QQbar.polynomial_root(P, RIF(1, 2))
1.618033988749895?
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = polygen(ZZ)
sage: cp = AA.common_polynomial(x^4 - 2)
Note that the precision is not guaranteed to find the tightest possible interval since complex_roots() depends on the underlying BLAS implementation.
sage: cp.complex_roots(30, 1)
[-1.18920711500272...?,
1.189207115002721?,
-1.189207115002721?*I,
1.189207115002721?*I]
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar.AlgebraicNumber_base
Returns the imaginary part of this algebraic real (so it always returns 0).
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = AA(sqrt(2) + sqrt(3))
sage: a.imag()
0
sage: parent(a.imag())
Algebraic Real Field
Given a RealIntervalField, compute the best possible approximation of this number in that field. Note that if this number is sufficiently close to some floating-point number (and, in particular, if this number is exactly representable in floating-point), then this will trigger exact computation, which may be very slow.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = AA(2).sqrt()
sage: y = x*x
sage: x.interval(RIF)
1.414213562373095?
sage: x.interval_exact(RIF)
1.414213562373095?
sage: y.interval(RIF)
2.000000000000000?
sage: y.interval_exact(RIF)
2
sage: z = 1 + AA(2).sqrt() / 2^200
sage: z.interval(RIF)
1.000000000000001?
sage: z.interval_exact(RIF)
1.000000000000001?
Returns the real part of this algebraic real (so it always returns self).
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = AA(sqrt(2) + sqrt(3))
sage: a.real()
3.146264369941973?
sage: a.real() is a
True
Given a RealField, compute the best possible approximation of this number in that field. Note that if this number is sufficiently close to the halfway point between two floating-point numbers in the field (for the default round-to-nearest mode) or if the number is sufficiently close to a floating-point number in the field (for directed rounding modes), then this will trigger exact computation, which may be very slow.
The rounding mode of the field is respected.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = AA(2).sqrt()^2
sage: x.real_exact(RR)
2.00000000000000
sage: x.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
2.00000000000000
sage: x.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
2.00000000000000
sage: x.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
2.00000000000000
sage: (-x).real_exact(RR)
-2.00000000000000
sage: (-x).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
-2.00000000000000
sage: (-x).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
-2.00000000000000
sage: (-x).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
-2.00000000000000
sage: (x-2).real_exact(RR)
0.000000000000000
sage: (x-2).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
0.000000000000000
sage: (x-2).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
0.000000000000000
sage: (x-2).real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
0.000000000000000
sage: y = AA(2).sqrt()
sage: y.real_exact(RR)
1.41421356237310
sage: y.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
1.41421356237309
sage: y.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
1.41421356237310
sage: y.real_exact(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
1.41421356237309
Given a RealField, compute a good approximation to self in that field. The approximation will be off by at most two ulp’s, except for numbers which are very close to 0, which will have an absolute error at most 2**(-(field.prec()-1)). Also, the rounding mode of the field is respected.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = AA(2).sqrt()^2
sage: x.real_number(RR)
2.00000000000000
sage: x.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
1.99999999999999
sage: x.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
2.00000000000001
sage: x.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
1.99999999999999
sage: (-x).real_number(RR)
-2.00000000000000
sage: (-x).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
-2.00000000000001
sage: (-x).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
-1.99999999999999
sage: (-x).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
-1.99999999999999
sage: (x-2).real_number(RR)
5.42101086242752e-20
sage: (x-2).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
-1.08420217248551e-19
sage: (x-2).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
2.16840434497101e-19
sage: (x-2).real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
0.000000000000000
sage: y = AA(2).sqrt()
sage: y.real_number(RR)
1.41421356237309
sage: y.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDD'))
1.41421356237309
sage: y.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDU'))
1.41421356237310
sage: y.real_number(RealField(53, rnd='RNDZ'))
1.41421356237309
Compute the sign of this algebraic number (return -1 if negative, 0 if zero, or 1 if positive).
Computes an interval enclosing this number using 128-bit interval arithmetic; if this interval includes 0, then fall back to exact computation (which can be very slow).
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA(-5).nth_root(7).sign()
-1
sage: (AA(2).sqrt() - AA(2).sqrt()).sign()
0
Bases: sage.rings.qqbar._uniq_alg_r, sage.rings.qqbar.AlgebraicField_common
The field of algebraic reals.
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA.algebraic_closure()
Algebraic Field
EXAMPLES:
sage: AA.completion(infinity, 500)
Real Field with 500 bits of precision
sage: AA.completion(infinity, prec=53, extras={'type':'RDF'})
Real Double Field
sage: AA.completion(infinity, 53) is RR
True
sage: AA.completion(7, 10)
...
NotImplementedError
Given a polynomial with algebraic coefficients and an interval enclosing exactly one root of the polynomial, constructs an algebraic real representation of that root.
The polynomial need not be irreducible, or even squarefree; but
if the given root is a multiple root, its multiplicity must be
specified. (IMPORTANT NOTE: Currently, multiplicity-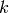 roots
are handled by taking the
roots
are handled by taking the 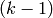 -st derivative of the polynomial.
This means that the interval must enclose exactly one root
of this derivative.)
-st derivative of the polynomial.
This means that the interval must enclose exactly one root
of this derivative.)
The conditions on the arguments (that the interval encloses exactly one root, and that multiple roots match the given multiplicity) are not checked; if they are not satisfied, an error may be thrown (possibly later, when the algebraic number is used), or wrong answers may result.
Note that if you are constructing multiple roots of a single polynomial, it is better to use AA.common_polynomial (or QQbar.common_polynomial; the two are equivalent) to get a shared polynomial.
EXAMPLES:
sage: x = polygen(AA)
sage: phi = AA.polynomial_root(x^2 - x - 1, RIF(1, 2)); phi
1.618033988749895?
sage: p = (x-1)^7 * (x-2)
sage: r = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(9/10, 11/10), multiplicity=7)
sage: r; r == 1
1.000000000000000?
True
sage: p = (x-phi)*(x-sqrt(AA(2)))
sage: r = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1, 3/2))
sage: r; r == sqrt(AA(2))
1.414213562373095?
True
We allow complex polynomials, as long as the particular root in question is real.
sage: K.<im> = QQ[I]
sage: x = polygen(K)
sage: p = (im + 1) * (x^3 - 2); p
(I + 1)*x^3 - 2*I - 2
sage: r = AA.polynomial_root(p, RIF(1, 2)); r^3
2.000000000000000?
Takes a monic polynomial and rescales the variable to get a monic
polynomial with “integral” coefficients. Works on any univariate
polynomial whose base ring has a denominator() method that returns
integers; for example, the base ring might be 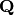 or a number
field.
or a number
field.
Returns the scale factor and the new polynomial.
(Inspired by Pari’s primitive_pol_to_monic().)
We assume that coefficient denominators are “small”; the algorithm factors the denominators, to give the smallest possible scale factor.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import clear_denominators
sage: _.<x> = QQ['x']
sage: clear_denominators(x + 3/2)
(2, x + 3)
sage: clear_denominators(x^2 + x/2 + 1/4)
(2, x^2 + x + 1)
If the interval v (which may be real or complex) includes some purely real numbers, return v' containing v such that v' == v'.conjugate(). Otherwise return v unchanged. (Note that if v' == v'.conjugate(), and v' includes one non-real root of a real polynomial, then v' also includes the conjugate of that root. Also note that the diameter of the return value is at most twice the diameter of the input.)
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import conjugate_expand
sage: conjugate_expand(CIF(RIF(0, 1), RIF(1, 2))).str(style='brackets')
'[0.00000000000000000 .. 1.0000000000000000] + [1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]*I'
sage: conjugate_expand(CIF(RIF(0, 1), RIF(0, 1))).str(style='brackets')
'[0.00000000000000000 .. 1.0000000000000000] + [-1.0000000000000000 .. 1.0000000000000000]*I'
sage: conjugate_expand(CIF(RIF(0, 1), RIF(-2, 1))).str(style='brackets')
'[0.00000000000000000 .. 1.0000000000000000] + [-2.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]*I'
sage: conjugate_expand(RIF(1, 2)).str(style='brackets')
'[1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]'
If the interval v includes some purely real numbers, return a real interval containing only those real numbers. Otherwise return v unchanged.
If v includes exactly one root of a real polynomial, and v was returned by conjugate_expand(), then conjugate_shrink(v) still includes that root, and is a RealIntervalFieldElement iff the root in question is real.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import conjugate_shrink
sage: conjugate_shrink(RIF(3, 4)).str(style='brackets')
'[3.0000000000000000 .. 4.0000000000000000]'
sage: conjugate_shrink(CIF(RIF(1, 2), RIF(1, 2))).str(style='brackets')
'[1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000] + [1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]*I'
sage: conjugate_shrink(CIF(RIF(1, 2), RIF(0, 1))).str(style='brackets')
'[1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]'
sage: conjugate_shrink(CIF(RIF(1, 2), RIF(-1, 2))).str(style='brackets')
'[1.0000000000000000 .. 2.0000000000000000]'
Find the polynomial of lowest discriminant that generates the same field as poly, out of those returned by the Pari polred routine. Returns a triple: (elt_fwd, elt_back, new_poly), where new_poly is the new polynomial, elt_fwd is a polynomial expression for a root of the new polynomial in terms of a root of the original polynomial, and elt_back is a polynomial expression for a root of the original polynomial in terms of a root of the new polynomial.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import do_polred
sage: _.<x> = QQ['x']
sage: do_polred(x^2-5)
(-1/2*x + 1/2, -2*x + 1, x^2 - x - 1)
sage: do_polred(x^2-x-11)
(-1/3*x + 2/3, -3*x + 2, x^2 - x - 1)
sage: do_polred(x^3 + 123456)
(-1/4*x, -4*x, x^3 - 1929)
l is a list of some sort. fn is a function which maps an element of l and a precision into an interval (either real or complex) of that precision, such that for sufficient precision, exactly one element of l results in an interval containing 0. Returns that one element of l.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import find_zero_result
sage: _.<x> = QQ['x']
sage: delta = 10^(-70)
sage: p1 = x - 1
sage: p2 = x - 1 - delta
sage: p3 = x - 1 + delta
sage: p2 == find_zero_result(lambda p, prec: p(RealIntervalField(prec)(1 + delta)), [p1, p2, p3])
True
intv_fn is a function that takes a precision and returns an interval of that precision containing some particular root of pol. (It must return better approximations as the precision increases.) pol is an irreducible polynomial with rational coefficients.
Returns an interval containing at most one root of pol.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import isolating_interval
sage: _.<x> = QQ['x']
sage: isolating_interval(lambda prec: sqrt(RealIntervalField(prec)(2)), x^2 - 2)
1.4142135623730950488?
And an example that requires more precision:
sage: delta = 10^(-70)
sage: p = (x - 1) * (x - 1 - delta) * (x - 1 + delta)
sage: isolating_interval(lambda prec: RealIntervalField(prec)(1 + delta), p)
1.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000?
The function also works with complex intervals and complex roots:
sage: p = x^2 - x + 13/36
sage: isolating_interval(lambda prec: ComplexIntervalField(prec)(1/2, 1/3), p)
0.500000000000000000000? + 0.3333333333333333334?*I
Given a sequence of elements of either AA or QQbar (or a mixture), computes a number field containing all of these elements, these elements as members of that number field, and a homomorphism from the number field back to AA or QQbar.
This may not return the smallest such number field, unless minimal=True is specified.
Also, a single number can be passed, rather than a sequence; and any values which are not elements of AA or QQbar will automatically be coerced to QQbar
This function may be useful for efficiency reasons: doing exact computations in the corresponding number field will be faster than doing exact computations directly in AA or QQbar.
EXAMPLES:
We can use this to compute the splitting field of a polynomial. (Unfortunately this takes an unreasonably long time for non-toy examples.):
sage: x = polygen(QQ)
sage: p = x^3 + x^2 + x + 17
sage: rts = p.roots(ring=QQbar, multiplicities=False)
sage: splitting = number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rts)[0]; splitting
Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^6 + 169*y^4 + 7968*y^2 + 121088
sage: p.roots(ring=splitting)
[(-9/2176*a^4 - 1121/2176*a^2 - 1625/136, 1), (9/17408*a^5 + 9/4352*a^4 + 1121/17408*a^3 + 1121/4352*a^2 + 1489/1088*a + 1489/272, 1), (-9/17408*a^5 + 9/4352*a^4 - 1121/17408*a^3 + 1121/4352*a^2 - 1489/1088*a + 1489/272, 1)]
sage: rt2 = AA(sqrt(2)); rt2
1.414213562373095?
sage: rt3 = AA(sqrt(3)); rt3
1.732050807568878?
sage: qqI = QQbar.zeta(4); qqI
1*I
sage: z3 = QQbar.zeta(3); z3
-0.500000000000000? + 0.866025403784439?*I
sage: rt2b = rt3 + rt2 - rt3; rt2b
1.414213562373095?
sage: rt2c = z3 + rt2 - z3; rt2c
1.414213562373095? + 0.?e-18*I
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt2)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2, a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.414213562373095?)
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics((rt2,rt3))
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1, [-a^3 + 3*a, -a^2 + 2], Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 0.5176380902050415?)
We’ve created rt2b in such a way that sage doesn’t initially know
that it’s in a degree-2 extension of 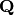 :
:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt2b)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1, -a^3 + 3*a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 4*y^2 + 1
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 0.5176380902050415?)
We can specify minimal=True if we want the smallest number field:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt2b, minimal=True)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2, a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.414213562373095?)
Things work fine with rational numbers, too:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics((QQbar(1/2), AA(17)))
(Rational Field, [1/2, 17], Ring morphism:
From: Rational Field
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: 1 |--> 1)
Or we can just pass in symbolic expressions, as long as they can be coerced into QQbar:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics((sqrt(7), sqrt(9), sqrt(11)))
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 9*y^2 + 1, [-a^3 + 8*a, 3, -a^3 + 10*a], Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 - 9*y^2 + 1
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 0.3354367396454047?)
Here we see an example of doing some computations with number field elements, and then mapping them back into QQbar:
sage: (fld,nums,hom) = number_field_elements_from_algebraics((rt2, rt3, qqI, z3))
sage: fld,nums,hom
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^8 - y^4 + 1, [-a^5 + a^3 + a, a^6 - 2*a^2, a^6, -a^4], Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^8 - y^4 + 1
To: Algebraic Field
Defn: a |--> -0.2588190451025208? - 0.9659258262890683?*I)
sage: (nfrt2, nfrt3, nfI, nfz3) = nums
sage: hom(nfrt2)
1.414213562373095? + 0.?e-18*I
sage: nfrt2^2
2
sage: nfrt3^2
3
sage: nfz3 + nfz3^2
-1
sage: nfI^2
-1
sage: sum = nfrt2 + nfrt3 + nfI + nfz3; sum
2*a^6 - a^5 - a^4 + a^3 - 2*a^2 + a
sage: hom(sum)
2.646264369941973? + 1.866025403784439?*I
sage: hom(sum) == rt2 + rt3 + qqI + z3
True
sage: [hom(n) for n in nums] == [rt2, rt3, qqI, z3]
True
TESTS:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt3)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3, a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 3
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.732050807568878?)
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics((rt2,qqI))
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 + 1, [a^3 - a, -a^2], Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 + 1
To: Algebraic Field
Defn: a |--> -0.7071067811865475? + 0.7071067811865475?*I)
Note that for the first example, where sage doesn’t realize that the number is real, we get a homomorphism to QQbar; but with minimal=True, we get a homomorphism to AA. Also note that the exact answer depends on a Pari function that gives different answers for 32-bit and 64-bit machines:
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt2c)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 + 2*y^2 + 4, 1/2*a^3, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^4 + 2*y^2 + 4
To: Algebraic Field
Defn: a |--> -0.7071067811865475? + 1.224744871391589?*I) # 32-bit
Defn: a |--> -0.7071067811865475? - 1.224744871391589?*I) # 64-bit
sage: number_field_elements_from_algebraics(rt2c, minimal=True)
(Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2, a, Ring morphism:
From: Number Field in a with defining polynomial y^2 - 2
To: Algebraic Real Field
Defn: a |--> 1.414213562373095?)
Checks whether the rational  is an exact
is an exact 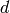 ‘th power. If so, returns
the
‘th power. If so, returns
the 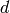 ‘th root of
‘th root of  ; otherwise, returns None.
; otherwise, returns None.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.rings.qqbar import rational_exact_root
sage: rational_exact_root(16/81, 4)
2/3
sage: rational_exact_root(8/81, 3) is None
True