Bases: sage.rings.ring.CommutativeRing
Return a new multivariate polynomial ring which isomorphic to self, but has a different ordering given by the parameter ‘order’ or names given by the parameter ‘names’.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x,y,z> = PolynomialRing(GF(127),3,order='lex')
sage: x > y^2
True
sage: Q.<x,y,z> = P.change_ring(order='degrevlex')
sage: x > y^2
False
Return the characteristic of this polynomial ring.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R = PolynomialRing(QQ, 'x', 3)
sage: R.characteristic()
0
sage: R = PolynomialRing(GF(7),'x', 20)
sage: R.characteristic()
7
Returns a functor F and base ring R such that F(R) == self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S = ZZ['x,y']
sage: F, R = S.construction(); R
Integer Ring
sage: F
MPoly[x,y]
sage: F(R) == S
True
sage: F(R) == ZZ['x']['y']
False
Return the irrelevant ideal of this multivariate polynomial ring, which is the ideal generated by all of the indeterminate generators of this ring.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x,y,z> = QQ[]
sage: R.irrelevant_ideal()
Ideal (x, y, z) of Multivariate Polynomial Ring in x, y, z over Rational Field
EXAMPLES:
sage: ZZ['x,y'].is_integral_domain()
True
sage: Integers(8)['x,y'].is_integral_domain()
False
EXAMPLES:
sage: ZZ['x,y'].is_noetherian()
True
sage: Integers(8)['x,y'].is_noetherian()
True
Return a random polynomial of at most degree 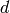 and at most
and at most 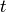 terms.
terms.
First monomials are chosen uniformly random from the set of all
possible monomials of degree up to 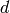 (inclusive). This means
that it is more likely that a monomial of degree
(inclusive). This means
that it is more likely that a monomial of degree 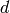 appears than
a monomial of degree
appears than
a monomial of degree 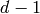 because the former class is bigger.
because the former class is bigger.
Exactly 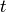 distinct monomials are chosen this way and each one gets
a random coefficient (possibly zero) from the base ring assigned.
distinct monomials are chosen this way and each one gets
a random coefficient (possibly zero) from the base ring assigned.
The returned polynomial is the sum of this list of terms.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x,y,z> = PolynomialRing(QQ)
sage: P.random_element(2, 5)
-6/5*x^2 + 2/3*z^2 - 1
sage: P.random_element(2, 5, choose_degree=True)
-1/4*x*y - 1/5*x*z - 1/14*y*z - z^2
Stacked rings:
sage: R = QQ['x,y']
sage: S = R['t,u']
sage: S.random_element(degree=2, terms=1)
-3*x*y + 5/2*y^2 - 1/2*x - 1/4*y + 4
sage: S.random_element(degree=2, terms=1)
(-1/2*x^2 - x*y - 2/7*y^2 + 3/2*x - y)*t*u
Default values apply if no degree and/or number of terms is provided:
sage: random_matrix(QQ['x,y,z'], 2, 2)
[ 2*y^2 - 2/27*y*z - z^2 + 2*z 1/2*x*y - 1/2*y^2 + 2*x - 2*y]
[-1/27*x^2 + 2/5*y^2 - 1/10*z^2 - 2*z -13*y^2 + 2/3*z^2 + 2*y]
sage: random_matrix(QQ['x,y,z'], 2, 2, terms=1, degree=2)
[-1/4*x 1/2]
[ 1/3*x x*y]
sage: P.random_element(0, 1)
-1
sage: P.random_element(2, 0)
0
sage: R.<x> = PolynomialRing(Integers(3), 1)
sage: R.random_element()
x + 1
Return structured string representation of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P.<x,y,z> = PolynomialRing(QQ,order=TermOrder('degrevlex',1)+TermOrder('lex',2))
sage: print P.repr_long()
Polynomial Ring
Base Ring : Rational Field
Size : 3 Variables
Block 0 : Ordering : degrevlex
Names : x
Block 1 : Ordering : lex
Names : y, z
Returns the list of variable names of this and its base rings, as if it were a single multi-variate polynomial.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R = QQ['x,y']['z,w']
sage: R.variable_names_recursive()
('x', 'y', 'z', 'w')
sage: R.variable_names_recursive(3)
('y', 'z', 'w')