AUTHORS:
- David Roe (2010-1-14) -- factored out of sage.structure.element
Bases: sage.structure.element.FieldElement
Return the additive order of this finite field element.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = FiniteField(2^12, 'a')
sage: b = a^3 + a + 1
sage: b.additive_order()
2
sage: k(0).additive_order()
1
Return the characteristic polynomial of self as a polynomial with given variable.
INPUT:
The result is not cached.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = GF(19^2)
sage: parent(a)
Finite Field in a of size 19^2
sage: a.charpoly('X')
X^2 + 18*X + 2
sage: a^2 + 18*a + 2
0
sage: a.charpoly('X', algorithm='pari')
X^2 + 18*X + 2
Return the 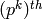 power of self, where
power of self, where  is the
characteristic of the field.
is the
characteristic of the field.
INPUT:
Note that if 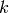 is negative, then this computes the appropriate root.
is negative, then this computes the appropriate root.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F.<a> = GF(29^2)
sage: z = a^2 + 5*a + 1
sage: z.pth_power()
19*a + 20
sage: z.pth_power(10)
10*a + 28
sage: z.pth_power(-10) == z
True
sage: F.<b> = GF(2^12)
sage: y = b^3 + b + 1
sage: y == (y.pth_power(-3))^(2^3)
True
sage: y.pth_power(2)
b^7 + b^6 + b^5 + b^4 + b^3 + b
See _matrix_().
EXAMPLE:
sage: k.<a> = GF(2^16)
sage: e = a^2 + 1
sage: e.matrix() # random-ish error message
doctest:1: DeprecationWarning:The function matrix is replaced by _matrix_.
[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1]
[0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1]
Returns the minimal polynomial of this element (over the corresponding prime subfield).
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = FiniteField(3^4)
sage: parent(a)
Finite Field in a of size 3^4
sage: b=a**20;p=charpoly(b,"y");p
y^4 + 2*y^2 + 1
sage: factor(p)
(y^2 + 1)^2
sage: b.minimal_polynomial('y')
y^2 + 1
Returns the minimal polynomial of this element (over the corresponding prime subfield).
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = FiniteField(19^2)
sage: parent(a)
Finite Field in a of size 19^2
sage: b=a**20;p=b.charpoly("x");p
x^2 + 15*x + 4
sage: factor(p)
(x + 17)^2
sage: b.minpoly('x')
x + 17
Return the norm of self down to the prime subfield.
This is the product of the Galois conjugates of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S.<b> = GF(5^2); S
Finite Field in b of size 5^2
sage: b.norm()
2
sage: b.charpoly('t')
t^2 + 4*t + 2
Next we consider a cubic extension:
sage: S.<a> = GF(5^3); S
Finite Field in a of size 5^3
sage: a.norm()
2
sage: a.charpoly('t')
t^3 + 3*t + 3
sage: a * a^5 * (a^25)
2
Returns an nth root of self.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
If self has an nth root, returns one (if all == False) or a list of all of them (if all == True). Otherwise, raises a ValueError (if extend = False) or a NotImplementedError (if extend = True).
Warning
The ‘extend’ option is not implemented (yet).
AUTHOR:
Return the 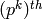 power of self, where
power of self, where  is the
characteristic of the field.
is the
characteristic of the field.
INPUT:
Note that if 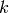 is negative, then this computes the appropriate root.
is negative, then this computes the appropriate root.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F.<a> = GF(29^2)
sage: z = a^2 + 5*a + 1
sage: z.pth_power()
19*a + 20
sage: z.pth_power(10)
10*a + 28
sage: z.pth_power(-10) == z
True
sage: F.<b> = GF(2^12)
sage: y = b^3 + b + 1
sage: y == (y.pth_power(-3))^(2^3)
True
sage: y.pth_power(2)
b^7 + b^6 + b^5 + b^4 + b^3 + b
Return the 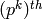 root of self, where
root of self, where  is the characteristic
of the field.
is the characteristic
of the field.
INPUT:
Note that if 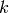 is negative, then this computes the appropriate power.
is negative, then this computes the appropriate power.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F.<b> = GF(2^12)
sage: y = b^3 + b + 1
sage: y == (y.pth_root(3))^(2^3)
True
sage: y.pth_root(2)
b^11 + b^10 + b^9 + b^7 + b^5 + b^4 + b^2 + b
Return the trace of this element, which is the sum of the Galois conjugates.
EXAMPLES:
sage: S.<a> = GF(5^3); S
Finite Field in a of size 5^3
sage: a.trace()
0
sage: a.charpoly('t')
t^3 + 3*t + 3
sage: a + a^5 + a^25
0
sage: z = a^2 + a + 1
sage: z.trace()
2
sage: z.charpoly('t')
t^3 + 3*t^2 + 2*t + 2
sage: z + z^5 + z^25
2
See _vector_().
EXAMPLE:
sage: k.<a> = GF(2^16)
sage: e = a^2 + 1
sage: e.vector() # random-ish error message
doctest:1: DeprecationWarning:The function vector is replaced by _vector_.
(1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
Returns if x is a finite field element.
EXAMPLE:
sage: from sage.rings.finite_rings.element_ext_pari import is_FiniteFieldElement
sage: is_FiniteFieldElement(1)
False
sage: is_FiniteFieldElement(IntegerRing())
False
sage: is_FiniteFieldElement(GF(5)(2))
True