Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- Modular Symbols »
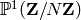 ) over
) over 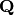 .¶
.¶Bases: object
The class for 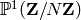 , the projective line modulo
, the projective line modulo 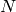 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = P1List(12); P
The projective line over the integers modulo 12
sage: list(P)
[(0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8), (1, 9), (1, 10), (1, 11), (2, 1), (2, 3), (2, 5), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 4), (3, 7), (4, 1), (4, 3), (4, 5), (6, 1)]
Saving and loading works.
sage: loads(dumps(P)) == P
True
Returns the level or modulus of this P1List.
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L.N()
120
Return the index of the result of applying the matrix
![I=[-1,0;0,1]](../../../_images/math/ba6723086ace2f0ebcb4743505814c3dde4cb95f.png) to the
to the 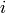 ‘th element of this P1List.
‘th element of this P1List.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L[10]
(1, 9)
sage: L.apply_I(10)
112
sage: L[112]
(1, 111)
sage: L.normalize(-1,9)
(1, 111)
This operation is an involution:
sage: all([L.apply_I(L.apply_I(i))==i for i in xrange(len(L))])
True
Return the index of the result of applying the matrix
![S=[0,-1;1,0]](../../../_images/math/e16b3bf4dcd3e2daa3628c5953bf3b37056abd87.png) to the
to the 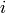 ‘th element of this P1List.
‘th element of this P1List.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L[10]
(1, 9)
sage: L.apply_S(10)
159
sage: L[159]
(3, 13)
sage: L.normalize(-9,1)
(3, 13)
This operation is an involution:
sage: all([L.apply_S(L.apply_S(i))==i for i in xrange(len(L))])
True
Return the index of the result of applying the matrix
![T=[0,1;-1,-1]](../../../_images/math/f7aa4ba524e55b2b1d90d28f9caf15213b176d95.png) to the
to the 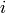 ‘th element of this P1List.
‘th element of this P1List.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L[10]
(1, 9)
sage: L.apply_T(10)
157
sage: L[157]
(3, 10)
sage: L.normalize(9,-10)
(3, 10)
This operation has order three:
sage: all([L.apply_T(L.apply_T(L.apply_T(i)))==i for i in xrange(len(L))])
True
Returns the index of the class of 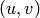 in the fixed list
of representatives of
in the fixed list
of representatives of
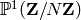 .
.
INPUT:
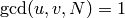 .
.OUTPUT:
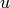 ,
,  , in the P1list.
, in the P1list.EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L[100]
(1, 99)
sage: L.index(1,99)
100
sage: all([L.index(L[i][0],L[i][1])==i for i in range(len(L))])
True
Returns the index of the class of 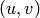 in the fixed list
of representatives of
in the fixed list
of representatives of
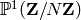 .
.
INPUT:
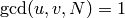 , normalized so they lie in the list.
, normalized so they lie in the list.OUTPUT:
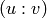 , in the P1list.
, in the P1list.EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: L[100]
(1, 99)
sage: L.index_of_normalized_pair(1,99)
100
sage: all([L.index_of_normalized_pair(L[i][0],L[i][1])==i for i in range(len(L))])
True
Lift the 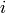 ‘th element of this P1list to an element of
‘th element of this P1list to an element of
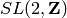 .
.
If the 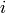 ‘th element is
‘th element is 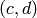 , this function computes and
returns a list
, this function computes and
returns a list ![[a,b, c',d']](../../../_images/math/464311ed8be70a4ba7545480f014a133624b7094.png) that defines a 2x2 matrix
with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that
that defines a 2x2 matrix
with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that 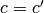 (mod
(mod
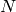 ) and
) and 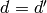 (mod
(mod 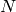 ).
).
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: p = P1List(11)
sage: p.list()[3]
(1, 2)
sage: p.lift_to_sl2z(3)
[0, -1, 1, 2]
AUTHORS:
Returns the underlying list of this P1List object.
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(8)
sage: type(L)
<type 'sage.modular.modsym.p1list.P1List'>
sage: type(L.list())
<type 'list'>
Returns a normalised element of 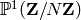 .
.
INPUT:
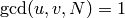 .
.OUTPUT:
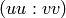 is a normalized
representative of
is a normalized
representative of 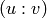 .
.NOTE: See also normalize_with_scalar() which also returns the normalizing scalar.
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: (u,v) = (555555555,7777)
sage: uu,vv = L.normalize(555555555,7777)
sage: (uu,vv)
(15, 13)
sage: (uu*v-vv*u) % L.N() == 0
True
Returns a normalised element of 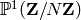 , together with
the normalizing scalar.
, together with
the normalizing scalar.
INPUT:
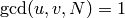 .
.OUTPUT:
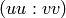 is a normalized
representative of
is a normalized
representative of 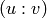 , and
, and 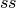 is a scalar such that
is a scalar such that
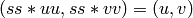 (mod
(mod 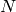 ).
).EXAMPLES:
sage: L = P1List(120)
sage: (u,v) = (555555555,7777)
sage: uu,vv,ss = L.normalize_with_scalar(555555555,7777)
sage: (uu,vv)
(15, 13)
sage: ((ss*uu-u)%L.N(), (ss*vv-v)%L.N())
(0, 0)
sage: (uu*v-vv*u) % L.N() == 0
True
Return a list of Python ints ![[a,b,c',d']](../../../_images/math/325f83571acdfa965c68cbe26fc59800965ca9c9.png) that are the entries of a
2x2 matrix with determinant 1 and lower two entries congruent to
that are the entries of a
2x2 matrix with determinant 1 and lower two entries congruent to
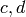 modulo
modulo 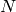 .
.
INPUT:
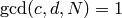 .
.EXAMPLES:
sage: lift_to_sl2z(2,3,6)
[1, 1, 2, 3]
sage: lift_to_sl2z(15,6,24)
[-2, -17, 15, 126]
sage: lift_to_sl2z(15,6,2400000)
[-2L, -320001L, 15L, 2400006L]
Lift a pair 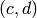 to an element of
to an element of 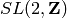 .
.
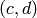 is assumed to be an element of
is assumed to be an element of
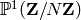 . This function computes
and returns a list
. This function computes
and returns a list ![[a, b, c', d']](../../../_images/math/62a8fd4975c4ef3dd338ca4643f2bf282c240a87.png) that defines a 2x2
matrix, with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that
that defines a 2x2
matrix, with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that
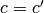 (mod
(mod 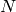 ) and
) and 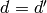 (mod
(mod 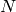 ).
).
INPUT:
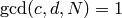 .
.EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import lift_to_sl2z_int
sage: lift_to_sl2z_int(2,6,11)
[1, 8, 2, 17]
sage: m=Matrix(Integers(),2,2,lift_to_sl2z_int(2,6,11))
sage: m
[ 1 8]
[ 2 17]
AUTHOR:
Lift a pair 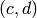 (modulo
(modulo 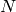 ) to an element of
) to an element of 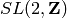 .
.
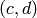 is assumed to be an element of
is assumed to be an element of
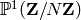 . This function computes and
returns a list
. This function computes and
returns a list ![[a, b, c', d']](../../../_images/math/62a8fd4975c4ef3dd338ca4643f2bf282c240a87.png) that defines a 2x2 matrix,
with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that
that defines a 2x2 matrix,
with determinant 1 and integer entries, such that 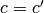 (mod
(mod 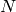 )
and
)
and 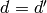 (mod
(mod 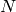 ).
).
INPUT:
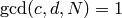 .
.EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import lift_to_sl2z_llong
sage: lift_to_sl2z_llong(2,6,11)
[1L, 8L, 2L, 17L]
sage: m=Matrix(Integers(),2,2,lift_to_sl2z_llong(2,6,11))
sage: m
[ 1 8]
[ 2 17]
AUTHOR:
Computes the canonical representative of
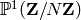 equivalent to
equivalent to
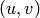 along with a transforming scalar.
along with a transforming scalar.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: If gcd(u,v,N) = 1, then returns
uu - an integer
vv - an integer
ss - an integer such that 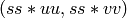 is equivalent to
is equivalent to 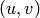 mod
mod 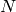 ;
;
if 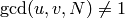 , returns 0, 0, 0.
, returns 0, 0, 0.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1_normalize
sage: p1_normalize(90,7,77)
(1, 11, 7)
sage: p1_normalize(90,7,78)
(1, 24, 7)
sage: (7*24-78*1) % 90
0
sage: (7*24) % 90
78
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1_normalize
sage: p1_normalize(50001,12345,54322)
(3, 4667, 4115)
sage: (12345*4667-54321*3) % 50001
3
sage: 4115*3 % 50001
12345
sage: 4115*4667 % 50001 == 54322 % 50001
True
Computes the canonical representative of
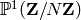 equivalent to
equivalent to
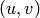 along with a transforming scalar.
along with a transforming scalar.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: If gcd(u,v,N) = 1, then returns
uu - an integer
vv - an integer
ss - an integer such that 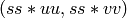 is congruent to
is congruent to 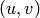 (mod
(mod 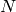 );
);
if
, returns 0, 0, 0.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1_normalize_int
sage: p1_normalize_int(90,7,77)
(1, 11, 7)
sage: p1_normalize_int(90,7,78)
(1, 24, 7)
sage: (7*24-78*1) % 90
0
sage: (7*24) % 90
78
Computes the canonical representative of
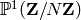 equivalent to
equivalent to
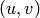 along with a transforming scalar.
along with a transforming scalar.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: If gcd(u,v,N) = 1, then returns
uu - an integer
vv - an integer
ss - an integer such that 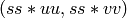 is equivalent to
is equivalent to 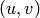 mod
mod 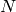 ;
;
if
, returns 0, 0, 0.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1_normalize_llong
sage: p1_normalize_llong(90000,7,77)
(1, 11, 7)
sage: p1_normalize_llong(90000,7,78)
(1, 77154, 7)
sage: (7*77154-78*1) % 90000
0
sage: (7*77154) % 90000
78
Returns the elements of the projective line modulo 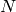 ,
,
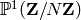 , as a plain list of 2-tuples.
, as a plain list of 2-tuples.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A list of the elements of the projective line
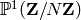 , as plain 2-tuples.
, as plain 2-tuples.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1list
sage: list(p1list(7))
[(0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6)]
sage: N=23456
sage: len(p1list(N)) == N*prod([1+1/p for p,e in N.factor()])
True
Returns a list of the normalized elements of
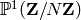 .
.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1list_int
sage: p1list_int(6)
[(0, 1),
(1, 0),
(1, 1),
(1, 2),
(1, 3),
(1, 4),
(1, 5),
(2, 1),
(2, 3),
(2, 5),
(3, 1),
(3, 2)]
sage: p1list_int(120)
[(0, 1),
(1, 0),
(1, 1),
(1, 2),
(1, 3),
...
(30, 7),
(40, 1),
(40, 3),
(40, 11),
(60, 1)]
Returns a list of the normalized elements of
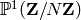 , as a plain list of
2-tuples.
, as a plain list of
2-tuples.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.modsym.p1list import p1list_llong
sage: N = 50000
sage: L = p1list_llong(50000)
sage: len(L) == N*prod([1+1/p for p,e in N.factor()])
True
sage: L[0]
(0, 1)
sage: L[len(L)-1]
(25000, 1)