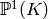 of cusps of a number field K.¶
of cusps of a number field K.¶AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
The space of cusps over a number field k:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 5)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k); kCusps
Set of all cusps of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: kCusps is NFCusps(k)
True
Define a cusp over a number field:
sage: NFCusp(k, a, 2/(a+1))
Cusp [a - 5: 2] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: kCusps((a,2))
Cusp [a: 2] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k,oo)
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
Different operations with cusps over a number field:
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 3, 1/a + 2); alpha
Cusp [a + 10: 7] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: alpha.numerator()
a + 10
sage: alpha.denominator()
7
sage: alpha.ideal()
Fractional ideal (7, a + 3)
sage: alpha.ABmatrix()
[a + 10, 3*a - 1, 7, 2*a]
sage: alpha.apply([0, 1, -1,0])
Cusp [7: -a - 10] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
Check Gamma0(N)-equivalence of cusps:
sage: N = k.ideal(3)
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 3, a + 1)
sage: beta = kCusps((2, a - 3))
sage: alpha.is_Gamma0_equivalent(beta, N)
True
Obtain transformation matrix for equivalent cusps:
sage: t, M = alpha.is_Gamma0_equivalent(beta, N, Transformation=True)
sage: M
[2*a - 4, -3*a - 4, -5*a + 2, 3*a + 13]
sage: alpha.apply(M) == beta
True
List representatives for Gamma_0(N) - equivalence classes of cusps:
sage: Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
[Cusp [0: 1] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5,
Cusp [1: 3] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5,
...]
Returns a list of inequivalent cusps for 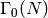 , i.e., a set of
representatives for the orbits of self on
, i.e., a set of
representatives for the orbits of self on 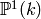 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A list of inequivalent number field cusps.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 5)
sage: N = k.ideal(3)
sage: L = Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
The cusps in the list are inequivalent:
sage: all([not L[i].is_Gamma0_equivalent(L[j], N) for i, j in \
mrange([len(L), len(L)]) if i<j])
True
We test that we obtain the right number of orbits:
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps
sage: len(L) == number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
True
Another example:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^4 - x^3 -21*x^2 + 17*x + 133)
sage: N = k.ideal(5)
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps
sage: len(Gamma0_NFCusps(N)) == number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps(N) # long time (over 1 sec)
True
Bases: sage.structure.element.Element
Creates a number field cusp, i.e., an element of 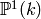 .
.
A cusp on a number field is either an element of the field or infinity, i.e., an element of the projective line over the number field. It is stored as a pair (a,b), where a, b are integral elements of the number field.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
[a: b] – a number field cusp.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 5)
sage: NFCusp(k, a, 2)
Cusp [a: 2] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, (a,2))
Cusp [a: 2] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, a, 2/(a+1))
Cusp [a - 5: 2] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
Cusp Infinity:
sage: NFCusp(k, 0)
Cusp [0: 1] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, oo)
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, 3*a, oo)
Cusp [0: 1] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, a + 5, 0)
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
Saving and loading works:
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, a, 2/(a+1))
sage: loads(dumps(alpha))==alpha
True
Some tests:
sage: I*I
-1
sage: NFCusp(k, I)
...
TypeError: Unable to convert I to a cusp of the number field
sage: NFCusp(k, oo, oo)
...
TypeError: Unable to convert (+Infinity, +Infinity) to a cusp of the number field
sage: NFCusp(k, 0, 0)
...
TypeError: Unable to convert (0, 0) to a cusp of the number field
sage: NFCusp(k, "a + 2", a)
Cusp [-2*a + 5: 5] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: NFCusp(k, NFCusp(k, oo))
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: c = NFCusp(k, 3, 2*a)
sage: NFCusp(k, c, a + 1)
Cusp [-a - 5: 20] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: L.<b> = NumberField(x^2 + 2)
sage: NFCusp(L, c)
...
ValueError: Cannot coerce cusps from one field to another
Returns AB-matrix associated to the cusp self.
Given R a Dedekind domain and A, B ideals of R in inverse classes, an AB-matrix is a matrix realizing the isomorphism between R+R and A+B. An AB-matrix associated to a cusp [a1: a2] is an AB-matrix with A the ideal associated to the cusp (A=<a1, a2>) and first column given by the coefficients of the cusp.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 11)
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, oo)
sage: alpha.ABmatrix()
[1, 0, 0, 1]
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 0)
sage: alpha.ABmatrix()
[0, -1, 1, 0]
Note that the AB-matrix associated to a cusp is not unique, and the output of the ABmatrix function may change.
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 3/2, a-1)
sage: M = alpha.ABmatrix()
sage: M # random
[-a^2 - a - 1, -3*a - 7, 8, -2*a^2 - 3*a + 4]
sage: M[0] == alpha.numerator() and M[2]==alpha.denominator()
True
An AB-matrix associated to a cusp alpha will send Infinity to alpha:
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 3, a-1)
sage: M = alpha.ABmatrix()
sage: (k.ideal(M[1], M[3])*alpha.ideal()).is_principal()
True
sage: M[0] == alpha.numerator() and M[2]==alpha.denominator()
True
sage: NFCusp(k, oo).apply(M) == alpha
True
Return g(self), where g is a 2x2 matrix, which we view as a linear fractional transformation.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A number field cusp, obtained by the action of g on the cusp self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 23)
sage: beta = NFCusp(k, 0, 1)
sage: beta.apply([0, -1, 1, 0])
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 23
sage: beta.apply([1, a, 0, 1])
Cusp [a: 1] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 23
Return the denominator of the cusp self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: c = NFCusp(k, a, 2)
sage: c.denominator()
2
sage: d = NFCusp(k, 1, a + 1);d
Cusp [1: a + 1] of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 1
sage: d.denominator()
a + 1
sage: NFCusp(k, oo).denominator()
0
Returns the ideal associated to the cusp self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 23)
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 3, a-1)
sage: alpha.ideal()
Fractional ideal (3, -1/2*a + 1/2)
sage: NFCusp(k, oo).ideal()
Fractional ideal (1)
Checks if cusps self and other are 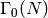 - equivalent.
- equivalent.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
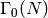 such that M * self = other if other
and self are
such that M * self = other if other
and self are 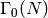 - equivalent. If self and other
are not equivalent it returns zero.
- equivalent. If self and other
are not equivalent it returns zero.EXAMPLES:
sage: K.<a> = NumberField(x^3-10)
sage: N = K.ideal(a-1)
sage: alpha = NFCusp(K, 0)
sage: beta = NFCusp(K, oo)
sage: alpha.is_Gamma0_equivalent(beta, N)
False
sage: alpha.is_Gamma0_equivalent(beta, K.ideal(1))
True
sage: b, M = alpha.is_Gamma0_equivalent(beta, K.ideal(1),Transformation=True)
sage: alpha.apply(M)
Cusp Infinity of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^3 - 10
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2+23)
sage: N = k.ideal(3)
sage: alpha1 = NFCusp(k, a+1, 4)
sage: alpha2 = NFCusp(k, a-8, 29)
sage: alpha1.is_Gamma0_equivalent(alpha2, N)
True
sage: b, M = alpha1.is_Gamma0_equivalent(alpha2, N, Transformation=True)
sage: alpha1.apply(M) == alpha2
True
Returns True if this is the cusp infinity.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: NFCusp(k, a, 2).is_infinity()
False
sage: NFCusp(k, 2, 0).is_infinity()
True
sage: NFCusp(k, oo).is_infinity()
True
Returns the number field of definition of the cusp self
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 2)
sage: alpha = NFCusp(k, 1, a + 1)
sage: alpha.number_field()
Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 2
Return the numerator of the cusp self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: c = NFCusp(k, a, 2)
sage: c.numerator()
a
sage: d = NFCusp(k, 1, a)
sage: d.numerator()
1
sage: NFCusp(k, oo).numerator()
1
The set of cusps of a number field 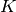 , i.e.
, i.e. 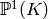 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
The set of cusps over the given number field.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 5)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k); kCusps
Set of all cusps of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
sage: kCusps is NFCusps(k)
True
Saving and loading works:
sage: loads(kCusps.dumps()) == kCusps
True
We test use_cache:
sage: NFCusps_clear_cache()
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 11)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k, use_cache=False)
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._nfcusps_cache
{}
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k, use_cache=True)
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._nfcusps_cache
{Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 11: ...}
sage: kCusps is NFCusps(k, use_cache=False)
False
sage: kCusps is NFCusps(k, use_cache=True)
True
Bases: sage.structure.parent_base.ParentWithBase
The set of cusps of a number field. See NFCusps for full documentation.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 5)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k); kCusps
Set of all cusps of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 5
Return the number field that this set of cusps is attached to.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k)
sage: kCusps.number_field()
Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^2 + 1
Clear the global cache of sets of cusps over number fields.
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf.NFCusps_clear_cache()
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 51)
sage: kCusps = NFCusps(k); kCusps
Set of all cusps of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^3 + 51
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._nfcusps_cache.keys()
[Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^3 + 51]
sage: NFCusps_clear_cache()
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._nfcusps_cache.keys()
[]
Clear the global cache of lists of representatives for ideal classes.
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf.NFCusps_clear_list_reprs_cache()
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 11)
sage: N = k.ideal(a+1)
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf.list_of_representatives(N)
(Fractional ideal (1), Fractional ideal (17, a - 5))
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._list_reprs_cache.keys()
[Fractional ideal (a + 1)]
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf.NFCusps_clear_list_reprs_cache()
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._list_reprs_cache.keys()
[]
Returns a list of lists (nlists different lists) of prime ideals, coprime to N, representing every ideal class of the number field.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A list of lists of ideals representatives of the ideal classes, all coprime to N, representing every ideal.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 11)
sage: N = k.ideal(5, a + 1)
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN
sage: NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN(N)
[(Fractional ideal (1), Fractional ideal (2, a + 1))]
sage: L = NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN(N, 3)
sage: all([len(L[i])==k.class_number() for i in range(len(L))])
True
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^4 - x^3 -21*x^2 + 17*x + 133)
sage: N = k.ideal(6)
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN
sage: NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN(N)
[(Fractional ideal (1),
Fractional ideal (13, a - 2),
Fractional ideal (43, a - 1),
Fractional ideal (67, a + 17))]
sage: L = NFCusps_ideal_reps_for_levelN(N, 5)
sage: all([len(L[i])==k.class_number() for i in range(len(L))])
True
Returns a list of ideals, coprime to the ideal N, representatives of the ideal classes of the corresponding number field.
Note: This list, used every time we check 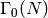 - equivalence of
cusps, is cached.
- equivalence of
cusps, is cached.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A list of ideals coprime to the ideal N, such that they are representatives of all the ideal classes of the number field.
EXAMPLES:
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf.NFCusps_clear_list_reprs_cache()
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._list_reprs_cache.keys()
[]
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import list_of_representatives
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^4 + 13*x^3 - 11)
sage: N = k.ideal(713, a + 208)
sage: L = list_of_representatives(N); L
(Fractional ideal (1),
Fractional ideal (37, a + 12),
Fractional ideal (47, a - 9))
The output of list_of_representatives has been cached:
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._list_reprs_cache.keys()
[Fractional ideal (713, a + 208)]
sage: sage.modular.cusps_nf._list_reprs_cache[N]
(Fractional ideal (1),
Fractional ideal (37, a + 12),
Fractional ideal (47, a - 9))
Returns the total number of orbits of cusps under the action of the
congruence subgroup 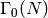 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
ingeter – the number of orbits of cusps under Gamma0(N)-action.
EXAMPLES:
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 11)
sage: N = k.ideal(2, a+1)
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps
sage: number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
4
sage: L = Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
sage: len(L) == number_of_Gamma0_NFCusps(N)
True
Returns integral elements of the number field representing the images of the global units modulo the ideal I.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A list of integral elements of the number field representing the images of the global units modulo the ideal I. Elements of the list might be equivalent to each other mod I.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import units_mod_ideal
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^2 + 1)
sage: I = k.ideal(a + 1)
sage: units_mod_ideal(I)
[1]
sage: I = k.ideal(3)
sage: units_mod_ideal(I)
[1, a, -1, -a]
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import units_mod_ideal
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^3 + 11)
sage: k.unit_group()
Unit group with structure C2 x Z of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^3 + 11
sage: I = k.ideal(5, a + 1)
sage: units_mod_ideal(I)
[1,
2*a^2 + 4*a - 1,
...]
sage: from sage.modular.cusps_nf import units_mod_ideal
sage: k.<a> = NumberField(x^4 - x^3 -21*x^2 + 17*x + 133)
sage: k.unit_group()
Unit group with structure C6 x Z of Number Field in a with defining polynomial x^4 - x^3 - 21*x^2 + 17*x + 133
sage: I = k.ideal(3)
sage: U = units_mod_ideal(I)
sage: all([U[j].is_unit() and not (U[j] in I) for j in range(len(U))])
True