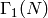 ¶
¶Bases: sage.modular.arithgroup.congroup_gammaH.GammaH_class
The congruence subgroup 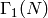 .
.
TESTS:
sage: [Gamma1(n).genus() for n in prime_range(2,100)]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 5, 7, 12, 22, 26, 40, 51, 57, 70, 92, 117, 126, 155, 176, 187, 222, 247, 287, 345]
sage: [Gamma1(n).index() for n in [1..10]]
[1, 3, 8, 12, 24, 24, 48, 48, 72, 72]
sage: [Gamma1(n).dimension_cusp_forms() for n in [1..20]]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 5, 2, 7, 3]
sage: [Gamma1(n).dimension_cusp_forms(1) for n in [1..20]]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(4).dimension_cusp_forms(k) for k in [1..20]]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8]
sage: Gamma1(23).dimension_cusp_forms(1)
...
NotImplementedError: Computation of dimensions of weight 1 cusp forms spaces not implemented in general
Return the dimension of the space of cusp forms for self, or the dimension of the subspace corresponding to the given character if one is supplied.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
We compute the same dimension in two different ways
sage: K = CyclotomicField(3)
sage: eps = DirichletGroup(7*43,K).0^2
sage: G = Gamma1(7*43)
Via Cohen–Oesterle:
sage: Gamma1(7*43).dimension_cusp_forms(2, eps)
28
Via Quer’s method:
sage: Gamma1(7*43).dimension_cusp_forms(2, eps, algorithm="Quer")
28
Some more examples:
sage: G.<eps> = DirichletGroup(9)
sage: [Gamma1(9).dimension_cusp_forms(k, eps) for k in [1..10]]
[0, 0, 1, 0, 3, 0, 5, 0, 7, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(9).dimension_cusp_forms(k, eps^2) for k in [1..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4, 0, 6, 0, 8]
Return the dimension of the space of Eisenstein series forms for self, or the dimension of the subspace corresponding to the given character if one is supplied.
INPUT:
AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
The following two computations use different algorithms:
sage: [Gamma1(36).dimension_eis(1,eps) for eps in DirichletGroup(36)]
[0, 4, 3, 0, 0, 2, 6, 0, 0, 2, 3, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(36).dimension_eis(1,eps,algorithm="Quer") for eps in DirichletGroup(36)]
[0, 4, 3, 0, 0, 2, 6, 0, 0, 2, 3, 0]
So do these:
sage: [Gamma1(48).dimension_eis(3,eps) for eps in DirichletGroup(48)]
[0, 12, 0, 4, 0, 8, 0, 4, 12, 0, 4, 0, 8, 0, 4, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(48).dimension_eis(3,eps,algorithm="Quer") for eps in DirichletGroup(48)]
[0, 12, 0, 4, 0, 8, 0, 4, 12, 0, 4, 0, 8, 0, 4, 0]
Return the dimension of the space of modular forms for self, or the dimension of the subspace corresponding to the given character if one is supplied.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: K = CyclotomicField(3)
sage: eps = DirichletGroup(7*43,K).0^2
sage: G = Gamma1(7*43)
sage: G.dimension_modular_forms(2, eps)
32
sage: G.dimension_modular_forms(2, eps, algorithm="Quer")
32
Dimension of the new subspace (or  -new subspace) of cusp forms of
weight
-new subspace) of cusp forms of
weight 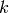 and character
and character  .
.
INPUT:
 -new subspace if given
-new subspace if givenEXAMPLES:
sage: G = DirichletGroup(9)
sage: eps = G.0^3
sage: eps.conductor()
3
sage: [Gamma1(9).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, eps) for k in [2..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(9).dimension_cusp_forms(k, eps) for k in [2..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4, 0, 6, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(9).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, eps, 3) for k in [2..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0]
Double check using modular symbols (independent calculation):
sage: [ModularSymbols(eps,k,sign=1).cuspidal_subspace().new_subspace().dimension() for k in [2..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0]
sage: [ModularSymbols(eps,k,sign=1).cuspidal_subspace().new_subspace(3).dimension() for k in [2..10]]
[0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0]
Another example at level 33:
sage: G = DirichletGroup(33)
sage: eps = G.1
sage: eps.conductor()
11
sage: [Gamma1(33).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, G.1) for k in [2..4]]
[0, 4, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(33).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, G.1, algorithm="Quer") for k in [2..4]]
[0, 4, 0]
sage: [Gamma1(33).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, G.1^2) for k in [2..4]]
[2, 0, 6]
sage: [Gamma1(33).dimension_new_cusp_forms(k, G.1^2, p=3) for k in [2..4]]
[2, 0, 6]
Return generators for this congruence subgroup.
The result is cached.
EXAMPLE:
sage: for g in Gamma1(3).generators():
... print g
... print '---'
[1 1]
[0 1]
---
[-20 9]
[ 51 -23]
---
[ 4 1]
[-9 -2]
---
...
---
[ 4 -1]
[ 9 -2]
---
[ -5 3]
[-12 7]
---
Return the index of self in the full modular group. This is given by the formula
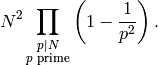
EXAMPLE:
sage: Gamma1(180).index()
20736
sage: [Gamma1(n).projective_index() for n in [1..16]]
[1, 3, 4, 6, 12, 12, 24, 24, 36, 36, 60, 48, 84, 72, 96, 96]
Return True precisely if this subgroup contains the matrix -1.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma1(1).is_even()
True
sage: Gamma1(2).is_even()
True
sage: Gamma1(15).is_even()
False
Return True if self is a subgroup of right.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma1(3).is_subgroup(SL2Z)
True
sage: Gamma1(3).is_subgroup(Gamma1(5))
False
sage: Gamma1(3).is_subgroup(Gamma1(6))
False
sage: Gamma1(6).is_subgroup(Gamma1(3))
True
sage: Gamma1(6).is_subgroup(Gamma0(2))
True
sage: Gamma1(80).is_subgroup(GammaH(40, []))
True
sage: Gamma1(80).is_subgroup(GammaH(40, [21]))
True
Return the number of cusps of this subgroup 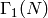 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: [Gamma1(n).ncusps() for n in [1..15]]
[1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6, 8, 8, 10, 10, 12, 12, 16]
sage: [Gamma1(n).ncusps() for n in prime_range(2, 100)]
[2, 2, 4, 6, 10, 12, 16, 18, 22, 28, 30, 36, 40, 42, 46, 52, 58, 60, 66, 70, 72, 78, 82, 88, 96]
Calculate the number of orbits of elliptic points of order 2 for this
subgroup 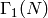 . This is known to be 0 if N > 2.
. This is known to be 0 if N > 2.
EXAMPLE:
sage: Gamma1(2).nu2()
1
sage: Gamma1(457).nu2()
0
sage: [Gamma1(n).nu2() for n in [1..16]]
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Calculate the number of orbits of elliptic points of order 3 for this
subgroup 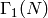 . This is known to be 0 if N > 3.
. This is known to be 0 if N > 3.
EXAMPLE:
sage: Gamma1(2).nu3()
0
sage: Gamma1(3).nu3()
1
sage: Gamma1(457).nu3()
0
sage: [Gamma1(n).nu3() for n in [1..10]]
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Return the congruence subgroup 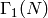 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: Gamma1(5) # indirect doctest
Congruence Subgroup Gamma1(5)
sage: G = Gamma1(23)
sage: G is Gamma1(23)
True
sage: G == loads(dumps(G))
True
sage: G is loads(dumps(G))
True
Return True if x is a congruence subgroup of type Gamma1.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.arithgroup.all import is_Gamma1
sage: is_Gamma1(SL2Z)
False
sage: is_Gamma1(Gamma1(13))
True
sage: is_Gamma1(Gamma0(6))
False
sage: is_Gamma1(GammaH(12, []))
False