Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- L-Functions »
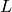 -function Calculator¶
-function Calculator¶SYMPOW is a package to compute special values of symmetric power elliptic curve L-functions. It can compute up to about 64 digits of precision. This interface provides complete access to sympow, which is a standard part of Sage (and includes the extra data files).
Note
Each call to sympow runs a complete sympow process. This incurs about 0.2 seconds overhead.
AUTHORS:
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT (from sympow readme):
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
Watkins Symmetric Power 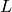 -function Calculator
-function Calculator
Type sympow.[tab] for a list of useful commands that are implemented using the command line interface, but return objects that make sense in Sage.
You can also use the complete command-line interface of sympow via this class. Type sympow.help() for a list of commands and how to call them.
Return 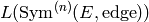 to prec digits of
precision, where edge is the right edge. Here
to prec digits of
precision, where edge is the right edge. Here  must be
even.
must be
even.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Note
Before using this function for the first time for a given
 , you may have to type sympow('-new_data n'),
where n is replaced by your value of
, you may have to type sympow('-new_data n'),
where n is replaced by your value of  .
.
If you would like to see the extensive output sympow prints when running this function, just type set_verbose(2).
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = sympow.L(EllipticCurve('11a'), 2, 16); a # optional
'1.057599244590958E+00'
sage: RR(a) # optional -- requires precomputations
1.05759924459096
Return 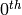 to
to 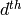 derivatives of
derivatives of
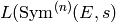 to prec digits of precision, where
to prec digits of precision, where
 is the right edge if
is the right edge if  is even and the center
if
is even and the center
if  is odd.
is odd.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: a string, exactly as output by sympow
Note
To use this function you may have to run a few commands like sympow('-new_data 1d2'), each which takes a few minutes. If this function fails it will indicate what commands have to be run.
EXAMPLES:
sage: print sympow.Lderivs(EllipticCurve('11a'), 1, 16, 2) # not tested
...
1n0: 2.538418608559107E-01
1w0: 2.538418608559108E-01
1n1: 1.032321840884568E-01
1w1: 1.059251499158892E-01
1n2: 3.238743180659171E-02
1w2: 3.414818600982502E-02
Return the analytic rank and leading 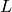 -value of the
elliptic curve
-value of the
elliptic curve 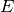 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Note
The analytic rank is not computed provably correctly in general.
Note
In computing the analytic rank we consider
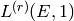 to be
to be 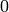 if
if
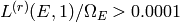 .
.
EXAMPLES: We compute the analytic ranks of the lowest known conductor curves of the first few ranks:
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve('11a'))
(0, '2.53842e-01')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve('37a'))
(1, '3.06000e-01')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve('389a'))
(2, '7.59317e-01')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve('5077a'))
(3, '1.73185e+00')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve([1, -1, 0, -79, 289]))
(4, '8.94385e+00')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -79, 342])) # long
(5, '3.02857e+01')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve([1, 1, 0, -2582, 48720])) # long
(6, '3.20781e+02')
sage: sympow.analytic_rank(EllipticCurve([0, 0, 0, -10012, 346900])) # long
(7, '1.32517e+03')
Return the modular degree of the elliptic curve E, assuming the Stevens conjecture.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES: We compute the modular degrees of the lowest known conductor curves of the first few ranks:
sage: sympow.modular_degree(EllipticCurve('11a'))
1
sage: sympow.modular_degree(EllipticCurve('37a'))
2
sage: sympow.modular_degree(EllipticCurve('389a'))
40
sage: sympow.modular_degree(EllipticCurve('5077a'))
1984
sage: sympow.modular_degree(EllipticCurve([1, -1, 0, -79, 289]))
334976