Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- L-Functions »
AUTHORS:
TODO:
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
Dokchitser’s 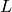 -functions Calculator
-functions Calculator
Create a Dokchitser 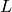 -series with
-series with
Dokchitser(conductor, gammaV, weight, eps, poles, residues, init, prec)
where
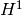 of curves/
of curves/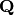
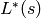 has
(simple) poles; only poles with
has
(simple) poles; only poles with 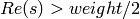 should be
included
should be
included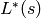 in those poles or
set residues=’automatic’ (default value)
in those poles or
set residues=’automatic’ (default value)RIEMANN ZETA FUNCTION:
We compute with the Riemann Zeta function.
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0], weight=1, eps=1, poles=[1], residues=[-1], init='1')
sage: L
Dokchitser L-series of conductor 1 and weight 1
sage: L(1)
...
ArithmeticError: ### user error: L*(s) has a pole at s=1.000000000000000000
sage: L(2)
1.64493406684823
sage: L(2, 1.1)
1.64493406684823
sage: L.derivative(2)
-0.937548254315844
sage: h = RR('0.0000000000001')
sage: (zeta(2+h) - zeta(2.))/h
-0.937028232783632
sage: L.taylor_series(2, k=5)
1.64493406684823 - 0.937548254315844*z + 0.994640117149451*z^2 - 1.00002430047384*z^3 + 1.00006193307235*z^4 + O(z^5)
RANK 1 ELLIPTIC CURVE:
We compute with the 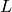 -series of a rank
-series of a rank 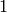 curve.
curve.
sage: E = EllipticCurve('37a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser(); L
Dokchitser L-function associated to Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 + y = x^3 - x over Rational Field
sage: L(1)
0
sage: L.derivative(1)
0.305999773834052
sage: L.derivative(1,2)
0.373095594536324
sage: L.num_coeffs()
48
sage: L.taylor_series(1,4)
0.305999773834052*z + 0.186547797268162*z^2 - 0.136791463097188*z^3 + O(z^4)
sage: L.check_functional_equation()
6.11218974800000e-18 # 32-bit
6.04442711160669e-18 # 64-bit
RANK 2 ELLIPTIC CURVE:
We compute the leading coefficient and Taylor expansion of the
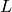 -series of a rank
-series of a rank 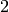 curve.
curve.
sage: E = EllipticCurve('389a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L.num_coeffs ()
156
sage: L.derivative(1,E.rank())
1.51863300057685
sage: L.taylor_series(1,4)
-1.28158145691931e-23 + (7.26268290635587e-24)*z + 0.759316500288427*z^2 - 0.430302337583362*z^3 + O(z^4) # 32-bit
-2.69129566562797e-23 + (1.52514901968783e-23)*z + 0.759316500288427*z^2 - 0.430302337583362*z^3 + O(z^4) # 64-bit
RAMANUJAN DELTA L-FUNCTION:
The coefficients are given by Ramanujan’s tau function:
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0,1], weight=12, eps=1)
sage: pari_precode = 'tau(n)=(5*sigma(n,3)+7*sigma(n,5))*n/12 - 35*sum(k=1,n-1,(6*k-4*(n-k))*sigma(k,3)*sigma(n-k,5))'
sage: L.init_coeffs('tau(k)', pari_precode=pari_precode)
We redefine the default bound on the coefficients: Deligne’s estimate on tau(n) is better than the default coefgrow(n)=`(4n)^{11/2}` (by a factor 1024), so re-defining coefgrow() improves efficiency (slightly faster).
sage: L.num_coeffs()
12
sage: L.set_coeff_growth('2*n^(11/2)')
sage: L.num_coeffs()
11
Now we’re ready to evaluate, etc.
sage: L(1)
0.0374412812685155
sage: L(1, 1.1)
0.0374412812685155
sage: L.taylor_series(1,3)
0.0374412812685155 + 0.0709221123619322*z + 0.0380744761270520*z^2 + O(z^3)
Verifies how well numerically the functional equation is satisfied, and also determines the residues if self.poles != [] and residues=’automatic’.
More specifically: for 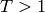 (default 1.2),
self.check_functional_equation(T) should ideally
return 0 (to the current precision).
(default 1.2),
self.check_functional_equation(T) should ideally
return 0 (to the current precision).
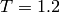 seems to give a reasonable
balance
seems to give a reasonable
balanceEXAMPLES:
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0], weight=1, eps=1, poles=[1], residues=[-1], init='1')
sage: L.check_functional_equation ()
-2.71050543200000e-20 # 32-bit
-2.71050543121376e-20 # 64-bit
If we choose the sign in functional equation for the
 function incorrectly, the functional equation
doesn’t check out.
function incorrectly, the functional equation
doesn’t check out.
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0], weight=1, eps=-11, poles=[1], residues=[-1], init='1')
sage: L.check_functional_equation ()
-9.73967861488124
Return the 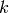 -th derivative of the
-th derivative of the 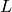 -series at
-series at
 .
.
Warning
If 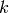 is greater than the order of vanishing of
is greater than the order of vanishing of
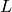 at
at  you may get nonsense.
you may get nonsense.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = EllipticCurve('389a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L.derivative(1,E.rank())
1.51863300057685
Return the gp interpreter that is used to implement this Dokchitser L-function.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = EllipticCurve('11a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L(2)
0.546048036215014
sage: L.gp()
GP/PARI interpreter
Set the coefficients 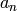 of the
of the 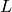 -series. If
-series. If
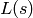 is not equal to its dual, pass the coefficients of
the dual as the second optional argument.
is not equal to its dual, pass the coefficients of
the dual as the second optional argument.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0,1], weight=12, eps=1)
sage: pari_precode = 'tau(n)=(5*sigma(n,3)+7*sigma(n,5))*n/12 - 35*sum(k=1,n-1,(6*k-4*(n-k))*sigma(k,3)*sigma(n-k,5))'
sage: L.init_coeffs('tau(k)', pari_precode=pari_precode)
Return number of coefficients 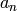 that are needed in
order to perform most relevant
that are needed in
order to perform most relevant 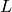 -function computations to
the desired precision.
-function computations to
the desired precision.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = EllipticCurve('11a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L.num_coeffs()
26
sage: E = EllipticCurve('5077a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L.num_coeffs()
568
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0], weight=1, eps=1, poles=[1], residues=[-1], init='1')
sage: L.num_coeffs()
4
You might have to redefine the coefficient growth function if the
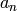 of the
of the 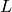 -series are not given by the
following PARI function:
-series are not given by the
following PARI function:
coefgrow(n) = if(length(Lpoles),
1.5*n^(vecmax(real(Lpoles))-1),
sqrt(4*n)^(weight-1));
INPUT:
EXAMPLE:
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0,1], weight=12, eps=1)
sage: pari_precode = 'tau(n)=(5*sigma(n,3)+7*sigma(n,5))*n/12 - 35*sum(k=1,n-1,(6*k-4*(n-k))*sigma(k,3)*sigma(n-k,5))'
sage: L.init_coeffs('tau(k)', pari_precode=pari_precode)
sage: L.set_coeff_growth('2*n^(11/2)')
sage: L(1)
0.0374412812685155
Return the first 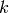 terms of the Taylor series expansion
of the
terms of the Taylor series expansion
of the 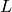 -series about
-series about  .
.
This is returned as a series in var, where you
should view var as equal to  . Thus
this function returns the formal power series whose coefficients
are
. Thus
this function returns the formal power series whose coefficients
are 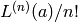 .
.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: L = Dokchitser(conductor=1, gammaV=[0], weight=1, eps=1, poles=[1], residues=[-1], init='1')
sage: L.taylor_series(2, 3)
1.64493406684823 - 0.937548254315844*z + 0.994640117149451*z^2 + O(z^3)
sage: E = EllipticCurve('37a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser()
sage: L.taylor_series(1)
0.305999773834052*z + 0.186547797268162*z^2 - 0.136791463097188*z^3 + 0.0161066468496401*z^4 + 0.0185955175398802*z^5 + O(z^6)
We compute a Taylor series where each coefficient is to high precision.
sage: E = EllipticCurve('389a')
sage: L = E.lseries().dokchitser(200)
sage: L.taylor_series(1,3)
6.2239725530250970363983975962696997888173850098274602272589e-73 + (-3.527106203544994604921190324282024612952450859320...e-73)*z + 0.75931650028842677023019260789472201907809751649492435158581*z^2 + O(z^3) # 32-bit
6.2239725530250970363983942830358807065824196704980264311105e-73 + (-3.5271062035449946049211884466825561834034352383203420991340e-73)*z + 0.75931650028842677023019260789472201907809751649492435158581*z^2 + O(z^3) # 64-bit