Collection of functions for calculating Wigner 3j, 6j, 9j, Clebsch-Gordan, Racah as well as Gaunt coefficients exactly, all evaluating to a rational number times the square root of a rational number [Rasch03].
Please see the description of the individual functions for further details and examples.
REFERENCES:
| [Rasch03] | (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) J. Rasch and A. C. H. Yu, ‘Efficient Storage Scheme for Pre-calculated Wigner 3j, 6j and Gaunt Coefficients’, SIAM J. Sci. Comput. Volume 25, Issue 4, pp. 1416-1428 (2003) |
AUTHORS:
Calculates the Clebsch-Gordan coefficient
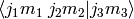 .
.
The reference for this function is [Edmonds74].
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
sage: simplify(clebsch_gordan(3/2,1/2,2, 3/2,1/2,2))
1
sage: clebsch_gordan(1.5,0.5,1, 1.5,-0.5,1)
1/2*sqrt(3)
sage: clebsch_gordan(3/2,1/2,1, -1/2,1/2,0)
-sqrt(1/6)*sqrt(3)
NOTES:
The Clebsch-Gordan coefficient will be evaluated via its relation to Wigner 3j symbols:
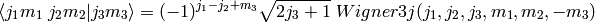
See also the documentation on Wigner 3j symbols which exhibit much higher symmetry relations than the Clebsch-Gordan coefficient.
AUTHORS:
Calculate the Gaunt coefficient.
The Gaunt coefficient is defined as the integral over three spherical harmonics:
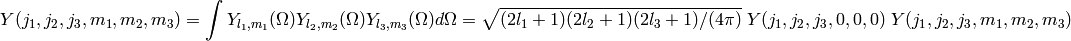
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
sage: gaunt(1,0,1,1,0,-1)
-1/2/sqrt(pi)
sage: gaunt(1,0,1,1,0,0)
0
sage: gaunt(29,29,34,10,-5,-5)
1821867940156/215552371055153321*sqrt(22134)/sqrt(pi)
sage: gaunt(20,20,40,1,-1,0)
28384503878959800/74029560764440771/sqrt(pi)
sage: gaunt(12,15,5,2,3,-5)
91/124062*sqrt(36890)/sqrt(pi)
sage: gaunt(10,10,12,9,3,-12)
-98/62031*sqrt(6279)/sqrt(pi)
sage: gaunt(1000,1000,1200,9,3,-12).n(64)
0.00689500421922113448
It is an error to use non-integer values for 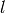 and
and 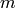 :
:
sage: gaunt(1.2,0,1.2,0,0,0)
...
ValueError: l values must be integer
sage: gaunt(1,0,1,1.1,0,-1.1)
...
ValueError: m values must be integer
NOTES:
The Gaunt coefficient obeys the following symmetry rules:
invariant under any permutation of the columns
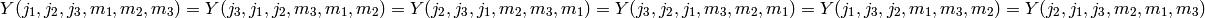
invariant under space inflection, i.e.
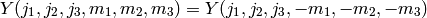
symmetric with respect to the 72 Regge symmetries as inherited
for the  symbols [Regge58]
symbols [Regge58]
zero for 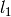 ,
, 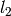 ,
, 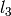 not fulfilling triangle relation
not fulfilling triangle relation
zero for violating any one of the conditions: 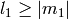 ,
,
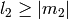 ,
, 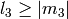
non-zero only for an even sum of the 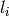 , i.e.
, i.e.
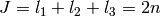 for
for  in
in 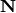
ALGORITHM:
This function uses the algorithm of [Liberatodebrito82] to calculate the value of the Gaunt coefficient exactly. Note that the formula contains alternating sums over large factorials and is therefore unsuitable for finite precision arithmetic and only useful for a computer algebra system [Rasch03].
REFERENCES:
| [Liberatodebrito82] | ‘FORTRAN program for the integral of three spherical harmonics’, A. Liberato de Brito, Comput. Phys. Commun., Volume 25, pp. 81-85 (1982) |
AUTHORS:
Calculate the Racah symbol 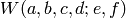 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
sage: racah(3,3,3,3,3,3)
-1/14
NOTES:
The Racah symbol is related to the Wigner 6j symbol:
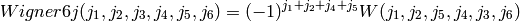
Please see the 6j symbol for its much richer symmetries and for additional properties.
ALGORITHM:
This function uses the algorithm of [Edmonds74] to calculate the value of the 6j symbol exactly. Note that the formula contains alternating sums over large factorials and is therefore unsuitable for finite precision arithmetic and only useful for a computer algebra system [Rasch03].
AUTHORS:
Calculate the Wigner 3j symbol 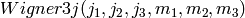 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
sage: wigner_3j(2, 6, 4, 0, 0, 0)
sqrt(5/143)
sage: wigner_3j(2, 6, 4, 0, 0, 1)
0
sage: wigner_3j(0.5, 0.5, 1, 0.5, -0.5, 0)
sqrt(1/6)
sage: wigner_3j(40, 100, 60, -10, 60, -50)
95608/18702538494885*sqrt(21082735836735314343364163310/220491455010479533763)
sage: wigner_3j(2500, 2500, 5000, 2488, 2400, -4888, prec=64)
7.60424456883448589e-12
It is an error to have arguments that are not integer or half integer values:
sage: wigner_3j(2.1, 6, 4, 0, 0, 0)
...
ValueError: j values must be integer or half integer
sage: wigner_3j(2, 6, 4, 1, 0, -1.1)
...
ValueError: m values must be integer or half integer
NOTES:
The Wigner 3j symbol obeys the following symmetry rules:
invariant under any permutation of the columns (with the
exception of a sign change where 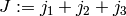 ):
):
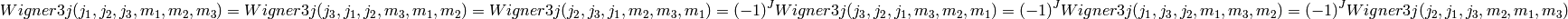
invariant under space inflection, i.e.
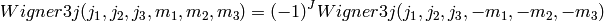
symmetric with respect to the 72 additional symmetries based on the work by [Regge58]
zero for 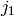 ,
, 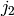 ,
, 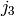 not fulfilling triangle relation
not fulfilling triangle relation
zero for 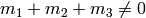
zero for violating any one of the conditions
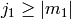 ,
, 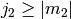 ,
, 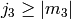
ALGORITHM:
This function uses the algorithm of [Edmonds74] to calculate the value of the 3j symbol exactly. Note that the formula contains alternating sums over large factorials and is therefore unsuitable for finite precision arithmetic and only useful for a computer algebra system [Rasch03].
REFERENCES:
| [Regge58] | (1, 2) ‘Symmetry Properties of Clebsch-Gordan Coefficients’, T. Regge, Nuovo Cimento, Volume 10, pp. 544 (1958) |
| [Edmonds74] | (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) ‘Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics’, A. R. Edmonds, Princeton University Press (1974) |
AUTHORS:
Calculate the Wigner 6j symbol 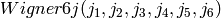 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
sage: wigner_6j(3,3,3,3,3,3)
-1/14
sage: wigner_6j(5,5,5,5,5,5)
1/52
sage: wigner_6j(6,6,6,6,6,6)
309/10868
sage: wigner_6j(8,8,8,8,8,8)
-12219/965770
sage: wigner_6j(30,30,30,30,30,30)
36082186869033479581/87954851694828981714124
sage: wigner_6j(0.5,0.5,1,0.5,0.5,1)
1/6
sage: wigner_6j(200,200,200,200,200,200, prec=1000)*1.0
0.000155903212413242
It is an error to have arguments that are not integer or half integer values or do not fulfill the triangle relation:
sage: wigner_6j(2.5,2.5,2.5,2.5,2.5,2.5)
...
ValueError: j values must be integer or half integer and fulfill the triangle relation
sage: wigner_6j(0.5,0.5,1.1,0.5,0.5,1.1)
...
ValueError: j values must be integer or half integer and fulfill the triangle relation
NOTES:
The Wigner 6j symbol is related to the Racah symbol but exhibits more symmetries as detailed below.
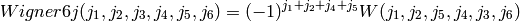
The Wigner 6j symbol obeys the following symmetry rules:
Wigner 6j symbols are left invariant under any permutation of the columns:
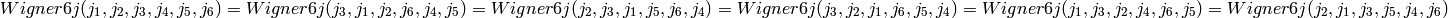
They are invariant under the exchange of the upper and lower arguments in each of any two columns, i.e.
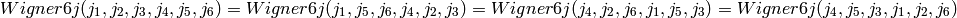
additional 6 symmetries [Regge59] giving rise to 144 symmetries in total
only non-zero if any triple of 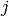 ‘s fulfill a triangle relation
‘s fulfill a triangle relation
ALGORITHM:
This function uses the algorithm of [Edmonds74] to calculate the value of the 6j symbol exactly. Note that the formula contains alternating sums over large factorials and is therefore unsuitable for finite precision arithmetic and only useful for a computer algebra system [Rasch03].
REFERENCES:
| [Regge59] | ‘Symmetry Properties of Racah Coefficients’, T. Regge, Nuovo Cimento, Volume 11, pp. 116 (1959) |
Calculate the Wigner 9j symbol
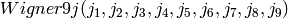 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Rational number times the square root of a rational number (if prec=None), or real number if a precision is given.
EXAMPLES:
A couple of examples and test cases, note that for speed reasons a precision is given:
sage: wigner_9j(1,1,1, 1,1,1, 1,1,0 ,prec=64) # ==1/18
0.0555555555555555555
sage: wigner_9j(1,1,1, 1,1,1, 1,1,1)
0
sage: wigner_9j(1,1,1, 1,1,1, 1,1,2 ,prec=64) # ==1/18
0.0555555555555555556
sage: wigner_9j(1,2,1, 2,2,2, 1,2,1 ,prec=64) # ==-1/150
-0.00666666666666666667
sage: wigner_9j(3,3,2, 2,2,2, 3,3,2 ,prec=64) # ==157/14700
0.0106802721088435374
sage: wigner_9j(3,3,2, 3,3,2, 3,3,2 ,prec=64) # ==3221*sqrt(70)/(246960*sqrt(105)) - 365/(3528*sqrt(70)*sqrt(105))
0.00944247746651111739
sage: wigner_9j(3,3,1, 3.5,3.5,2, 3.5,3.5,1 ,prec=64) # ==3221*sqrt(70)/(246960*sqrt(105)) - 365/(3528*sqrt(70)*sqrt(105))
0.0110216678544351364
sage: wigner_9j(100,80,50, 50,100,70, 60,50,100 ,prec=1000)*1.0
1.05597798065761e-7
sage: wigner_9j(30,30,10, 30.5,30.5,20, 30.5,30.5,10 ,prec=1000)*1.0 # ==(80944680186359968990/95103769817469)*sqrt(1/682288158959699477295)
0.0000325841699408828
sage: wigner_9j(64,62.5,114.5, 61.5,61,112.5, 113.5,110.5,60, prec=1000)*1.0
-3.41407910055520e-39
sage: wigner_9j(15,15,15, 15,3,15, 15,18,10, prec=1000)*1.0
-0.0000778324615309539
sage: wigner_9j(1.5,1,1.5, 1,1,1, 1.5,1,1.5)
0
It is an error to have arguments that are not integer or half integer values or do not fulfill the triangle relation:
sage: wigner_9j(0.5,0.5,0.5, 0.5,0.5,0.5, 0.5,0.5,0.5,prec=64)
...
ValueError: j values must be integer or half integer and fulfill the triangle relation
sage: wigner_9j(1,1,1, 0.5,1,1.5, 0.5,1,2.5,prec=64)
...
ValueError: j values must be integer or half integer and fulfill the triangle relation
ALGORITHM:
This function uses the algorithm of [Edmonds74] to calculate the value of the 3j symbol exactly. Note that the formula contains alternating sums over large factorials and is therefore unsuitable for finite precision arithmetic and only useful for a computer algebra system [Rasch03].