Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- Combinatorics »
- Words »
This module implements word paths, which is an application of Combinatorics on Words to Discrete Geometry. A word path is the representation of a word as a discrete path in a vector space using a one-to-one correspondence between the alphabet and a set of vectors called steps. Many problems surrounding 2d lattice polygons (such as questions of self-intersection, area, inertia moment, etc.) can be solved in linear time (linear in the length of the perimeter) using theory from Combinatorics on Words.
On the square grid, the encoding of a path using a four-letter alphabet (for East, North, West and South directions) is also known as the Freeman chain code [1,2] (see [3] for further reading).
AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
The combinatorial class of all paths defined over three given steps:
sage: P = WordPaths('abc', steps=[(1,2), (-3,4), (0,-3)]); P
Word Paths over 3 steps
This defines a one-to-one correspondence between alphabet and steps:
sage: d = P.letters_to_steps()
sage: sorted(d.items())
[('a', (1, 2)), ('b', (-3, 4)), ('c', (0, -3))]
Creation of a path from the combinatorial class P defined above:
sage: p = P('abaccba'); p
Path: abaccba
Many functions can be used on p: the coordinates of its trajectory, ask whether p is a closed path, plot it and many other:
sage: list(p.points())
[(0, 0), (1, 2), (-2, 6), (-1, 8), (-1, 5), (-1, 2), (-4, 6), (-3, 8)]
sage: p.is_closed()
False
sage: p.plot()
To obtain a list of all the available word path specific functions, use help(p):
sage: help(p)
Help on FiniteWordPath_2d_str in module sage.combinat.words.paths object:
...
Methods inherited from FiniteWordPath_2d:
...
Methods inherited from FiniteWordPath_all:
...
This only works on Python classes that derive from SageObject.
Since p is a finite word, many functions from the word library are available:
sage: p.crochemore_factorization()
(a, b, a, c, c, ba)
sage: p.is_palindrome()
False
sage: p[:3]
Path: aba
sage: len(p)
7
P also herits many functions from Words:
sage: P = WordPaths('rs', steps=[(1,2), (-1,4)]); P
Word Paths over 2 steps
sage: P.alphabet()
Ordered Alphabet ['r', 's']
sage: list(P.iterate_by_length(3))
[Path: rrr,
Path: rrs,
Path: rsr,
Path: rss,
Path: srr,
Path: srs,
Path: ssr,
Path: sss]
When the number of given steps is half the size of alphabet, the opposite of vectors are used:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', [(1,0), (0,1)])
sage: sorted(P.letters_to_steps().items())
[('a', (1, 0)), ('b', (0, 1)), ('c', (-1, 0)), ('d', (0, -1))]
Some built-in combinatorial classes of paths:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_grid'); P
Word Paths on the square grid
sage: D = WordPaths('()', steps='dyck'); D
Finite Dyck paths
sage: d = D('()()()(())'); d
Path: ()()()(())
sage: d.plot()
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle_grid')
sage: p = P('babaddefadabcadefaadfafabacdefa')
sage: p.plot()
Vector steps may be in more than 2 dimensions:
sage: d = [(1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,0,1)]
sage: P = WordPaths(alphabet='abc', steps=d); P
Word Paths over 3 steps
sage: p = P('abcabcabcabcaabacabcababcacbabacacabcaccbcac')
sage: p.plot()
sage: d = [(1,3,5,1), (-5,1,-6,0), (0,0,1,9), (4,2,-1,0)]
sage: P = WordPaths(alphabet='rstu', steps=d); P
Word Paths over 4 steps
sage: p = P('rtusuusususuturrsust'); p
Path: rtusuusususuturrsust
sage: p.end_point()
(5, 31, -26, 30)
sage: CubePaths = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='cube_grid'); CubePaths
Word Paths on the cube grid
sage: CubePaths('abcabaabcabAAAAA').plot()
The input data may be a str, a list, a tuple, a callable or a finite iterator:
sage: P = WordPaths([0, 1, 2, 3])
sage: P([0,1,2,3,2,1,2,3,2])
Path: 012321232
sage: P((0,1,2,3,2,1,2,3,2))
Path: 012321232
sage: P(lambda n:n%4, length=10)
Path: 0123012301
sage: P(iter([0,3,2,1]), length='finite')
Path: 0321
REFERENCES:
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all
Returns an animation object illustrating the path growing step by step.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: p = P('aaababbb')
sage: a = p.animate(); a
Animation with 9 frames
sage: show(a) # optional -- requires convert command
sage: a.gif(delay=35, iterations=3) # optional
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef',steps='triangle')
sage: p = P('abcdef')
sage: p.animate()
Animation with 8 frames
If the path is closed, the plain polygon is added at the end of the animation:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: p = P('ababAbABABaB')
sage: a = p.animate(); a
Animation with 14 frames
Another example illustrating a Fibonacci tile:
sage: w = words.fibonacci_tile(2)
sage: show(w.animate()) # optional
The first 4 Fibonacci tiles in an animation:
sage: a = words.fibonacci_tile(0).animate()
sage: b = words.fibonacci_tile(1).animate()
sage: c = words.fibonacci_tile(2).animate()
sage: d = words.fibonacci_tile(3).animate()
sage: (a*b*c*d).show() # optional
Note
If ImageMagick is not installed, you will get an error message like this:
/usr/local/share/sage/local/bin/sage-native-execute: 8: convert:
not found
Error: ImageMagick does not appear to be installed. Saving an
animation to a GIF file or displaying an animation requires
ImageMagick, so please install it and try again.
See www.imagemagick.org, for example.
Returns the area of a closed path.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd',steps=[(1,1),(-1,1),(-1,-1),(1,-1)])
sage: p = P('abcd')
sage: p.area() #todo: not implemented
2
Returns an arrow 2d graphics that goes from the start of the path to the end.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd'); P
Word Paths on the square grid
sage: p = P('aaaccaccacacacaccccccbbdd'); p
Path: aaaccaccacacacaccccccbbdd
sage: R = p.plot() + p.directive_vector()
sage: show(R, axes=False, aspect_ratio=1)
TESTS:
A closed path:
sage: P('acbd').directive_vector()
Returns the height of self.
The height of a 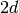 -path is merely the difference
between the highest and the lowest
-path is merely the difference
between the highest and the lowest 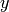 -coordinate of each
points traced by it.
-coordinate of each
points traced by it.
OUTPUT:
non negative real number
EXAMPLES:
sage: Freeman = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: Freeman('aababaabbbAA').height()
5
The function is well-defined if self is not simple or close:
sage: Freeman('aabAAB').height()
1
sage: Freeman('abbABa').height()
2
This works for any 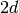 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,0),(1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('abbaa')
sage: p.height()
2
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.height()
2
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.height()
2.59807621135332
Returns a 2d Graphics illustrating the path.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
A non closed path on the square grid:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: P('abababAABAB').plot()
A closed path on the square grid:
sage: P('abababAABABB').plot()
A dyck path:
sage: P = WordPaths('()', steps='dyck')
sage: P('()()()((()))').plot()
A path in the triangle grid:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle_grid')
sage: P('abcdedededefab').plot()
A polygon of length 220 that tiles the plane in two ways:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: P('aBababAbabaBaBABaBabaBaBABAbABABaBabaBaBABaBababAbabaBaBABaBabaBaBABAbABABaBABAbAbabAbABABaBABAbABABaBabaBaBABAbABABaBABAbAbabAbABAbAbabaBababAbABAbAbabAbABABaBABAbAbabAbABAbAbabaBababAbabaBaBABaBababAbabaBababAbABAbAbab').plot()
With gridlines:
sage: P('ababababab').plot(gridlines=True)
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: P().plot()
sage: sum(map(plot,map(P,['a','A','b','B'])))
Returns the width of self.
The height of a 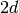 -path is merely the difference
between the rightmost and the leftmost
-path is merely the difference
between the rightmost and the leftmost 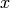 -coordinate of each
points traced by it.
-coordinate of each
points traced by it.
OUTPUT:
non negative real number
EXAMPLES:
sage: Freeman = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: Freeman('aababaabbbAA').width()
5
The function is well-defined if self is not simple or close:
sage: Freeman('aabAAB').width()
2
sage: Freeman('abbABa').width()
1
This works for any 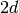 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,0),(1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('abbaa')
sage: p.width()
5
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.width()
6
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.width()
4.50000000000000
Returns the maximum of the x-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('0123')
sage: p = P('0101013332')
sage: p.xmax()
3
This works for any 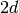 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,-1),(-1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('ababa')
sage: p.xmax()
1
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.xmax()
6
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.xmax()
4.50000000000000
Returns the minimum of the x-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('0123')
sage: p = P('0101013332')
sage: p.xmin()
0
This works for any 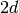 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,0),(-1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('abbba')
sage: p.xmin()
-2
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.xmin()
0
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.xmin()
0.000000000000000
Returns the maximum of the y-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('0123')
sage: p = P('0101013332')
sage: p.ymax()
3
This works for any 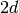 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,-1),(-1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('ababa')
sage: p.ymax()
0
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.ymax()
2
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.ymax()
2.59807621135332
Returns the minimum of the y-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('0123')
sage: p = P('0101013332')
sage: p.ymin()
0
This works for any 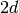 -paths:
-paths:
sage: Paths = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,-1),(-1,1)])
sage: p = Paths('ababa')
sage: p.ymin()
-1
sage: DyckPaths = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = DyckPaths('abaabb')
sage: p.ymin()
0
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.ymin()
0.000000000000000
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2),(3,4)])
sage: p = P(['a','b','a']);p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2),(3,4)])
sage: p = P('aba'); p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2),(3,4)])
sage: p = P(('a','b','a'));p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all
INPUT:
pathoptions - (dict, default:dict(rgbcolor=’red’,arrow_head=True, thickness=3)), options for the path drawing
startpoint - (boolean, default: True), draw the start point?
options for the start point drawing
EXAMPLES:
sage: d = ( vector((1,3,2)), vector((2,-4,5)) )
sage: P = WordPaths(alphabet='ab', steps=d); P
Word Paths over 2 steps
sage: p = P('ababab'); p
Path: ababab
sage: p.plot()
sage: P = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='cube_grid')
sage: p = P('abcabcAABBC')
sage: p.plot()
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2,0),(3,4,0)])
sage: p = P(['a','b','a']);p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2,0),(3,4,0)])
sage: p = P('aba'); p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2,0),(3,4,0)])
sage: p = P(('a','b','a'));p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_3d_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
Returns the end point of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordPaths('abcdef')('abababab').end_point()
(6, 2*sqrt3)
sage: WordPaths('abAB')('abababab').end_point()
(4, 4)
sage: P = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='cube_grid')
sage: P('ababababCC').end_point()
(4, 4, -2)
sage: WordPaths('abcdef')('abcdef').end_point()
(0, 0)
sage: P = WordPaths('abc', steps=[(1,3,7,9),(-4,1,0,0),(0,32,1,8)])
sage: P('abcabababacaacccbbcac').end_point()
(-16, 254, 63, 128)
Returns True if the path is closed, i.e. if the origin and the end of the path are equal.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', steps=[(1,0),(0,1),(-1,0),(0,-1)])
sage: P('abcd').is_closed()
True
sage: P('abc').is_closed()
False
sage: P().is_closed()
True
sage: P('aacacc').is_closed()
True
Returns True if the path is simple, i.e. if all its points are distincts.
If the path is closed, the last point is not considered.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef',steps='triangle_grid');P
Word Paths on the triangle grid
sage: P('abc').is_simple()
True
sage: P('abcde').is_simple()
True
sage: P('abcdef').is_simple()
True
sage: P('ad').is_simple()
True
sage: P('aabdee').is_simple()
False
Returns an iterator yielding a list of points used to draw the path represented by this word.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
A simple closed square:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB')
sage: list(P('abAB').points())
[(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1), (0, 0)]
A simple closed square without the last point:
sage: list(P('abAB').points(include_last=False))
[(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1)]
sage: list(P('abaB').points())
[(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (2, 1), (2, 0)]
Return the starting point of self.
OUTPUT:
vector
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordPaths('abcdef')('abcdef').start_point()
(0, 0)
sage: WordPaths('abcdef', steps='cube_grid')('abcdef').start_point()
(0, 0, 0)
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,0,0,0),(0,1,0,0)])
sage: P('abbba').start_point()
(0, 0, 0, 0)
Returns the trajectory of self as a tikz str.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef')
sage: p = P('abcde')
sage: p.tikz_trajectory()
'(0.000, 0.000) -- (1.00, 0.000) -- (1.50, 0.866) -- (1.00, 1.73) -- (0.000, 1.73) -- (-0.500, 0.866)'
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths(['a','b'],[(1,2,0,0),(3,4,0,0)])
sage: p = P(['a','b','a']);p
Path: aba
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab',[(1,2,0,0),(3,4,0,0)])
sage: p = P('aabbb'); p
Path: aabbb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab',[(1,2,0,0),(3,4,0,0)])
sage: p = P( ('a','b','b') ); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_all_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='cube')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='cube')
sage: p = P('abb'); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='cube')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_cube_grid_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = P('abb'); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='dyck')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_dyck_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='hexagon')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='hexagon')
sage: p = P('abb'); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='hexagon')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_hexagonal_grid_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='ne')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='ne')
sage: p = P('abb'); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('ab', steps='ne')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_north_east_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d
Returns the area of a closed path.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_grid')
sage: P('abAB').area()
1
sage: P('aabbAABB').area()
4
sage: P('aabbABAB').area()
3
The area of the Fibonacci tiles:
sage: [words.fibonacci_tile(i).area() for i in range(6)]
[1, 5, 29, 169, 985, 5741]
sage: [words.dual_fibonacci_tile(i).area() for i in range(6)]
[1, 5, 29, 169, 985, 5741]
sage: sloane_find(_, nresults=1) #optional - internet
Searching Sloane's online database...
[[1653,
'Numbers n such that 2*n^2 - 1 is a square.',
[1,
5,
29,
169,
985,
5741,
33461,
195025,
1136689,
6625109,
38613965,
225058681,
1311738121,
7645370045,
44560482149,
259717522849,
1513744654945,
8822750406821,
51422757785981,
299713796309065,
1746860020068409]]]
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_grid')
sage: P('a').area()
...
TypeError: the path must be closed to compute its area
Returns True if self represents a closed path and False otherwise.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_grid')
sage: P('aA').is_closed()
True
sage: P('abAB').is_closed()
True
sage: P('ababAABB').is_closed()
True
sage: P('aaabbbAABB').is_closed()
False
sage: P('ab').is_closed()
False
Returns True if the path is simple, i.e. if all its points are distincts.
If the path is closed, the last point is not considered.
Note
The linear algorithm described in the thesis of Xavier Provençal should be implemented here.
EXAMPLES:
sage: P = WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_grid')
sage: P('abab').is_simple()
True
sage: P('abAB').is_simple()
True
sage: P('abA').is_simple()
True
sage: P('aabABB').is_simple()
False
sage: P().is_simple()
True
sage: P('A').is_simple()
True
sage: P('aA').is_simple()
True
sage: P('aaA').is_simple()
False
REFERENCES:
Returns the trajectory of self as a tikz str.
EXAMPLES:
sage: f = words.fibonacci_tile(1)
sage: f.tikz_trajectory()
'(0, 0) -- (0, -1) -- (-1, -1) -- (-1, -2) -- (0, -2) -- (0, -3) -- (1, -3) -- (1, -2) -- (2, -2) -- (2, -1) -- (1, -1) -- (1, 0) -- (0, 0)'
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', steps='square')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', steps='square')
sage: p = P('abccc'); p
Path: abccc
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', steps='square')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_square_grid_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_2d
Returns the maximum of the x-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.xmax()
4.50000000000000
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ABAcacacababababcbcbAC')
sage: w.xmax()
4.00000000000000
Returns the minimum of the x-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.xmin()
0.000000000000000
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ABAcacacababababcbcbAC')
sage: w.xmin()
-3.00000000000000
Returns the maximum of the y-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.ymax()
2.59807621135332
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ABAcacacababababcbcbAC')
sage: w.ymax()
8.66025403784439
Returns the minimum of the y-coordinates of the path.
EXAMPLES:
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ababcaaBC')
sage: w.ymin()
0.000000000000000
sage: w = WordPaths('abcABC', steps='triangle')('ABAcacacababababcbcbAC')
sage: w.ymin()
-0.866025403784439
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_list, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle')
sage: p = P(['a','b','b']); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid_list'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_str, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle')
sage: p = P('abb'); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid_str'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Bases: sage.combinat.words.word_datatypes.WordDatatype_tuple, sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid, sage.combinat.words.finite_word.FiniteWord_class
TESTS:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle')
sage: p = P(('a','b','b')); p
Path: abb
sage: type(p)
<class 'sage.combinat.words.paths.FiniteWordPath_triangle_grid_tuple'>
sage: p == loads(dumps(p))
True
Returns the combinatorial class of paths of the given type of steps.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES:
The steps can be given explicitely:
sage: WordPaths('abc', steps=[(1,2), (-1,4), (0,-3)])
Word Paths over 3 steps
Different type of input alphabet:
sage: WordPaths(range(3), steps=[(1,2), (-1,4), (0,-3)])
Word Paths over 3 steps
sage: WordPaths(['cric','crac','croc'], steps=[(1,2), (1,4), (0,3)])
Word Paths over 3 steps
Directions can be in three dimensions as well:
sage: WordPaths('ab', steps=[(1,2,2),(-1,4,2)])
Word Paths over 2 steps
When the number of given steps is half the size of alphabet, the opposite of vectors are used:
sage: P = WordPaths('abcd', [(1,0), (0,1)])
sage: P
Word Paths over 4 steps
sage: sorted(P.letters_to_steps().items())
[('a', (1, 0)), ('b', (0, 1)), ('c', (-1, 0)), ('d', (0, -1))]
When no steps are given, default classes are returned:
sage: WordPaths('ab')
Word Paths in North and East steps
sage: WordPaths(range(4))
Word Paths on the square grid
sage: WordPaths(range(6))
Word Paths on the hexagonal grid
There are many type of built-in steps...
On a two letters alphabet:
sage: WordPaths('ab', steps='north_east')
Word Paths in North and East steps
sage: WordPaths('()', steps='dyck')
Finite Dyck paths
On a four letters alphabet:
sage: WordPaths('ruld', steps='square_grid')
Word Paths on the square grid
On a six letters alphabet:
sage: WordPaths('abcdef', steps='hexagonal_grid')
Word Paths on the hexagonal grid
sage: WordPaths('abcdef', steps='triangle_grid')
Word Paths on the triangle grid
sage: WordPaths('abcdef', steps='cube_grid')
Word Paths on the cube grid
TESTS:
sage: WordPaths(range(5))
...
TypeError: Unable to make a class WordPaths from Ordered Alphabet [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
sage: WordPaths('abAB', steps='square_gridd')
...
TypeError: Unknown type of steps : square_gridd
Bases: sage.combinat.words.words.Words_over_OrderedAlphabet
The combinatorial class of all paths, i.e of all words over an alphabet where each letter is mapped to a step (a vector).
Returns the dictionary mapping letters to vectors (steps).
EXAMPLES:
sage: d = WordPaths('ab').letters_to_steps()
sage: sorted(d.items())
[('a', (0, 1)), ('b', (1, 0))]
sage: d = WordPaths('abcd').letters_to_steps()
sage: sorted(d.items())
[('a', (1, 0)), ('b', (0, 1)), ('c', (-1, 0)), ('d', (0, -1))]
sage: d = WordPaths('abcdef').letters_to_steps()
sage: sorted(d.items())
[('a', (1, 0)),
('b', (1/2, 1/2*sqrt3)),
('c', (-1/2, 1/2*sqrt3)),
('d', (-1, 0)),
('e', (-1/2, -1/2*sqrt3)),
('f', (1/2, -1/2*sqrt3))]
Return the vector space over which the steps of the paths are defined.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordPaths('ab',steps='dyck').vector_space()
Ambient free module of rank 2 over the principal ideal domain Integer Ring
sage: WordPaths('ab',steps='north_east').vector_space()
Ambient free module of rank 2 over the principal ideal domain Integer Ring
sage: WordPaths('abcd',steps='square_grid').vector_space()
Ambient free module of rank 2 over the principal ideal domain Integer Ring
sage: WordPaths('abcdef',steps='hexagonal_grid').vector_space()
Vector space of dimension 2 over Number Field in sqrt3 with defining polynomial x^2 - 3
sage: WordPaths('abcdef',steps='cube_grid').vector_space()
Ambient free module of rank 3 over the principal ideal domain Integer Ring
sage: WordPaths('abcdef',steps='triangle_grid').vector_space()
Vector space of dimension 2 over Number Field in sqrt3 with defining polynomial x^2 - 3
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_all
The combinatorial class of all paths on the cube grid.
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_all
The combinatorial class of all dyck paths.
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_triangle_grid
The combinatorial class of all paths on the hexagonal grid.
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_all
The combinatorial class of all paths using North and East directions.
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_all
The combinatorial class of all paths on the square grid.
Bases: sage.combinat.words.paths.WordPaths_all
The combinatorial class of all paths on the triangle grid.