Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- Combinatorics »
- Words »
This modules implements morphisms over finite and infinite words.
AUTHORS:
EXAMPLES:
Creation of a morphism from a dictionary or a string:
sage: n = WordMorphism({0:[0,2,2,1],1:[0,2],2:[2,2,1]})
sage: m = WordMorphism('x->xyxsxss,s->xyss,y->ys')
sage: n
Morphism from Words over Ordered Alphabet [0, 1, 2] to Words over Ordered Alphabet [0, 1, 2]
sage: m
Morphism from Words over Ordered Alphabet ['s', 'x', 'y'] to Words over Ordered Alphabet ['s', 'x', 'y']
The codomain may be specified:
sage: WordMorphism({0:[0,2,2,1],1:[0,2],2:[2,2,1]}, codomain=Words([0,1,2,3,4]))
Morphism from Words over Ordered Alphabet [0, 1, 2] to Words over Ordered Alphabet [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Power of a morphism:
sage: print n^2
WordMorphism: 0->022122122102, 1->0221221, 2->22122102
Image under a morphism:
sage: m('y')
word: ys
sage: m('xxxsy')
word: xyxsxssxyxsxssxyxsxssxyssys
Iterated image under a morphism:
sage: m('y', 3)
word: ysxyssxyxsxssysxyssxyss
Infinite fixed point of morphism:
sage: fix = m.fixed_point('x')
sage: fix
word: xyxsxssysxyxsxssxyssxyxsxssxyssxyssysxys...
sage: fix.length()
+Infinity
Incidence matrix:
sage: matrix(m)
[2 3 1]
[1 3 0]
[1 1 1]
Many other functionalities...:
sage: m.is_identity()
False
sage: m.is_endomorphism()
True
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
WordMorphism class
EXAMPLES:
sage: n = WordMorphism({0:[0,2,2,1],1:[0,2],2:[2,2,1]})
sage: m = WordMorphism('x->xyxsxss,s->xyss,y->ys')
Power of a morphism:
sage: print n^2
WordMorphism: 0->022122122102, 1->0221221, 2->22122102
Image under a morphism:
sage: m('y')
word: ys
sage: m('xxxsy')
word: xyxsxssxyxsxssxyxsxssxyssys
Iterated image under a morphism:
sage: m('y', 3)
word: ysxyssxyxsxssysxyssxyss
See more examples in the documentation of the call method (m.__call__?).
Infinite fixed point of morphism:
sage: fix = m.fixed_point('x')
sage: fix
word: xyxsxssysxyxsxssxyssxyxsxssxyssxyssysxys...
sage: fix.length()
+Infinity
Incidence matrix:
sage: matrix(m)
[2 3 1]
[1 3 0]
[1 1 1]
Many other functionalities...:
sage: m.is_identity()
False
sage: m.is_endomorphism()
True
TESTS:
sage: wm = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba')
sage: wm == loads(dumps(wm))
True
Returns the codomain of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').codomain()
Words over Ordered Alphabet ['a', 'b']
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').codomain()
Words over Ordered Alphabet ['5', 'a', 'b', 'd', 's']
Returns the morphism where the image of the letter by self is conjugated of parameter pos.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abcde')
sage: m.conjugate(0) == m
True
sage: print m.conjugate(1)
WordMorphism: a->bcdea
sage: print m.conjugate(3)
WordMorphism: a->deabc
sage: print WordMorphism('').conjugate(4)
WordMorphism:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abcde,b->xyz')
sage: print m.conjugate(2)
WordMorphism: a->cdeab, b->zxy
Returns domain of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').domain()
Words over Ordered Alphabet ['a', 'b']
sage: WordMorphism('b->ba,a->ab').domain()
Words over Ordered Alphabet ['a', 'b']
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').domain()
Words over Ordered Alphabet ['0', '6', 'y']
Returns self extended by other.
Let 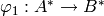 and
and 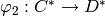 be two morphisms. A morphism
be two morphisms. A morphism 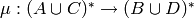 corresponds to
corresponds to 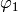 extended by
extended by 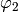 if
if
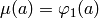 if
if 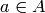 and
and 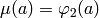 otherwise.
otherwise.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
WordMorphism
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba')
sage: n = WordMorphism({0:1,1:0,'a':5})
sage: print m.extend_by(n)
WordMorphism: 0->1, 1->0, a->ab, b->ba
sage: print n.extend_by(m)
WordMorphism: 0->1, 1->0, a->5, b->ba
sage: print m.extend_by(m)
WordMorphism: a->ab, b->ba
TESTS:
sage: m.extend_by(WordMorphism({})) == m
True
sage: m.extend_by(WordMorphism('')) == m
True
sage: m.extend_by(4)
...
TypeError: other (=4) is not a WordMorphism
Returns the fixed point of self beginning by the given letter.
A fixed point of morphism 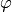 is a word
is a word 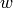 such that
such that
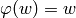 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES:
Infinite fixed point:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba').fixed_point(letter='a')
word: abbabaabbaababbabaababbaabbabaabbaababba...
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').fixed_point(letter='a')
word: abaababaabaababaababaabaababaabaababaaba...
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->b,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='a')
word: abbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb...
Infinite fixed point of an erasing morphism:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='a')
word: ab
Finite fixed point:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->b,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='b')
word: b
Finite fixed point of an erasing morphism:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abc,b->,c->')
sage: fp = m.fixed_point('a'); fp
word: abc
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->ba,b->')
sage: m('ba')
word: ba
sage: m.fixed_point('a') #todo: not implemented
word: ba
Fixed point of a power of a morphism:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->ba,b->ab')
sage: (m^2).fixed_point(letter='a')
word: abbabaabbaababbabaababbaabbabaabbaababba...
TESTS:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='b')
...
TypeError: self must be prolongable on b
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='c')
...
TypeError: self must be prolongable on c
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->,c->ba').fixed_point(letter='d')
...
TypeError: letter (=d) is not in the domain alphabet (=Ordered Alphabet ['a', 'b', 'c'])
sage: WordMorphism('a->aa,b->aac').fixed_point(letter='a')
...
TypeError: self (=WordMorphism: a->aa, b->aac) is not a endomorphism
Returns True if self has a conjugate in class 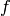 -
-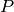 .
.
DEFINITION : Let 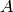 be an alphabet. We say that a
primitive substitution
be an alphabet. We say that a
primitive substitution 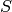 is in the class P if there
exists a palindrome
is in the class P if there
exists a palindrome  and for each
and for each 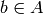 a
palindrome
a
palindrome 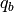 such that
such that 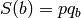 for all
for all
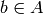 . [1]
. [1]
Let 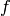 be an involution on
be an involution on 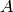 . We say that a morphism
. We say that a morphism
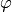 is in class
is in class 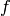 -
-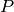 if there exists an
if there exists an
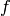 -palindrome
-palindrome  and for each
and for each 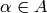 there exists an
there exists an 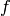 -palindrome
-palindrome 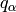 such
that
such
that 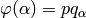 . [2]
. [2]
INPUT:
REFERENCES:
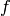 -palindromes, Memoire de maitrise en Mathematiques,
Montreal, UQAM, 2008, 109 pages.
-palindromes, Memoire de maitrise en Mathematiques,
Montreal, UQAM, 2008, 109 pages.EXAMPLES:
sage: fibo = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a')
sage: fibo.has_conjugate_in_classP()
True
sage: (fibo^2).is_in_classP()
False
sage: (fibo^2).has_conjugate_in_classP()
True
Returns True if all the non empty images of self begins with the same letter.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abcde,b->xyz')
sage: m.has_left_conjugate()
False
sage: WordMorphism('b->xyz').has_left_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('').has_left_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->,b->xyz').has_left_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->abbab,b->abb').has_left_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->abbab,b->abb,c->').has_left_conjugate()
True
Returns True if all the non empty images of self ends with the same letter.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abcde,b->xyz')
sage: m.has_right_conjugate()
False
sage: WordMorphism('b->xyz').has_right_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('').has_right_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->,b->xyz').has_right_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->abbab,b->abb').has_right_conjugate()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->abbab,b->abb,c->').has_right_conjugate()
True
Return the image of a letter
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
word
..NOTE:
The letter is assumed to be in the domain alphabet
(no check done). Hence, this method is faster
than the ``__call__`` method suitable for words input.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ac,c->a')
sage: m.image('b')
word: ac
sage: s = WordMorphism({('a', 1):[('a', 1), ('a', 2)], ('a', 2):[('a', 1)]})
sage: s.image(('a',1))
word: ('a', 1),('a', 2)
sage: s = WordMorphism({0:[1,2], 'a':(2,3,4), ():[9,8,7]})
sage: s.image(0)
word: 12
sage: s.image('a')
word: 234
sage: s.image(())
word: 987
Returns the list of all the images of the letters of the alphabet under self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').images()
[word: ab, word: a]
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').images()
[word: 5, word: asd, word: ab]
Returns the incidence matrix of the morphism. The order of the rows and column are given by the order defined on the alphabet of the domain and the codomain.
The matrix returned is over the integers. If a different ring is desired, use either the change_ring function or the matrix function.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abc,b->a,c->c')
sage: m.incidence_matrix()
[1 1 0]
[1 0 0]
[1 0 1]
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abc,b->a,c->c,d->abbccccabca,e->abc')
sage: m.incidence_matrix()
[1 1 0 3 1]
[1 0 0 3 1]
[1 0 1 5 1]
Returns True if the cardinality of the domain is zero and False otherwise.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('').is_empty()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->a').is_empty()
False
Returns True if the codomain is a subset of the domain.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').is_endomorphism()
True
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').is_endomorphism()
False
sage: WordMorphism('a->a,b->aa,c->aaa').is_endomorphism()
True
sage: Wabc = Words('abc')
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->a,b->aa,c->aaa',codomain = Wabc)
sage: m.is_endomorphism()
True
Returns True if self is an erasing morphism, i.e. the image of a letter is the empty word.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').is_erasing()
False
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').is_erasing()
False
sage: WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd,7->').is_erasing()
True
sage: WordMorphism('').is_erasing()
False
Returns True if self is the identity morphism.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->a,b->b,c->c,d->e')
sage: m.is_identity()
False
sage: WordMorphism('a->a,b->b,c->c').is_identity()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->a,b->b,c->cb').is_identity()
False
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->b,b->c,c->a')
sage: (m^2).is_identity()
False
sage: (m^3).is_identity()
True
sage: (m^4).is_identity()
False
sage: WordMorphism('').is_identity()
True
sage: WordMorphism({0:[0],1:[1]}).is_identity()
True
We check that #8618 is fixed:
sage: t = WordMorphism({'a1':['a2'], 'a2':['a1']})
sage: (t*t).is_identity()
True
Returns True if self is in class 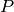 (or
(or 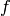 -
-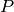 ).
).
DEFINITION : Let 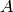 be an alphabet. We say that a
primitive substitution
be an alphabet. We say that a
primitive substitution 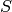 is in the class P if there
exists a palindrome
is in the class P if there
exists a palindrome  and for each
and for each 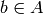 a
palindrome
a
palindrome 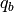 such that
such that 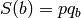 for all
for all
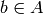 . [1]
. [1]
Let 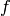 be an involution on
be an involution on 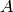 . “We say that a morphism
. “We say that a morphism
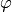 is in class
is in class 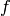 -
-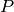 if there exists an
if there exists an
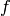 -palindrome
-palindrome  and for each
and for each 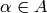 there exists an
there exists an 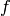 -palindrome
-palindrome 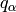 such
that
such
that 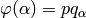 . [2]
. [2]
INPUT:
REFERENCES:
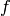 -palindromes, Memoire de maitrise en Mathematiques,
Montreal, UQAM, 2008, 109 pages.
-palindromes, Memoire de maitrise en Mathematiques,
Montreal, UQAM, 2008, 109 pages.EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->bbaba,b->bba').is_in_classP()
True
sage: tm = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba')
sage: tm.is_in_classP()
False
sage: f = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a')
sage: tm.is_in_classP(f=f)
True
sage: (tm^2).is_in_classP()
True
sage: (tm^2).is_in_classP(f=f)
False
sage: fibo = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a')
sage: fibo.is_in_classP()
True
sage: fibo.is_in_classP(f=f)
False
sage: (fibo^2).is_in_classP()
False
sage: f = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a,c->c')
sage: WordMorphism('a->acbcc,b->acbab,c->acbba').is_in_classP(f)
True
Returns True if self is an involution, i.e. its square is the identity.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->b,b->a').is_involution()
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->b,b->bb').is_involution()
False
sage: WordMorphism({0:[1],1:[0]}).is_involution()
True
TESTS:
sage: WordMorphism('').is_involution()
True
sage: WordMorphism({0:1,1:0,2:3}).is_involution()
...
TypeError: self (=WordMorphism: 0->1, 1->0, 2->3) is not a endomorphism
Returns True if self is primitive.
A morphism 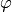 is primitive if there exists
an positive integer
is primitive if there exists
an positive integer 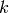 such that for all
such that for all 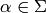 ,
,
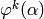 contains all the letters of
contains all the letters of 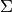 .
.
INPUT:
ALGORITHM:
Exercices 8.7.8, p.281 in [1] : (c) Letbe the least integer
such that
has all positive entries. Prove that, for all primitive matrices
, we have
. (d) Prove that the bound
is best possible.
EXAMPLES:
sage: tm = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba')
sage: tm.is_primitive()
True
sage: fibo = WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a');
sage: fibo.is_primitive()
True
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->bb,b->aa')
sage: m.is_primitive()
False
sage: f = WordMorphism({0:[1],1:[0]})
sage: f.is_primitive()
False
sage: s = WordMorphism('a->b,b->c,c->ab')
sage: s.is_primitive()
True
sage: s = WordMorphism('a->b,b->c,c->d,d->e,e->f,f->g,g->h,h->ab')
sage: s.is_primitive()
True
TESTS:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->bb,b->aac')
sage: m.is_primitive()
...
TypeError: self (=WordMorphism: a->bb, b->aac) is not a endomorphism
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->,b->',codomain=Words('ab'))
sage: m.is_primitive()
False
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->,b->')
sage: m.is_primitive()
False
REFERENCES:
Returns True if self is prolongable on letter.
A morphism 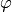 is prolongable on a letter
is prolongable on a letter  if
if  is a prefix of
is a prefix of 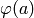 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
Boolean
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').is_prolongable(letter='a')
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').is_prolongable(letter='b')
False
sage: WordMorphism('a->ba,b->ab').is_prolongable(letter='b')
False
sage: (WordMorphism('a->ba,b->ab')^2).is_prolongable(letter='b')
True
sage: WordMorphism('a->ba,b->').is_prolongable(letter='b')
False
sage: WordMorphism('a->bb,b->aac').is_prolongable(letter='a')
False
We check that #8595 is fixed:
sage: s = WordMorphism({('a', 1) : [('a', 1), ('a', 2)], ('a', 2) : [('a', 1)]})
sage: s.is_prolongable(('a',1))
True
TESTS:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->b,c->ba').is_prolongable(letter='d')
...
TypeError: letter (=d) is not in the domain alphabet (=Ordered Alphabet ['a', 'b', 'c'])
sage: n0, n1 = matrix(2,[1,1,1,0]), matrix(2,[2,1,1,0])
sage: n = {'a':n0, 'b':n1}
sage: WordMorphism(n).is_prolongable(letter='a') #todo: not implemented
...
TypeError: codomain of self must be an instance of Words
Returns an iterator of the letters of the fixed point of self starting with letter.
If w is the iterated word, then this iterator: outputs the elements of morphism[ w[i] ], appends morphism[ w[i+1] ] to w, increments i.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abc,b->,c->')
sage: list(m._fixed_point_iterator('a'))
['a', 'b', 'c']
The morphism must be prolongable on the letter:
sage: list(m._fixed_point_iterator('b'))
...
IndexError: pop from empty list
The morphism must be an endomorphism:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->ac,b->aac')
sage: list(m._fixed_point_iterator('a'))
...
KeyError: 'c'
We check that #8595 is fixed:
sage: s = WordMorphism({('a', 1):[('a', 1), ('a', 2)], ('a', 2):[('a', 1)]})
sage: it = s._fixed_point_iterator(('a',1))
sage: it.next()
('a', 1)
Returns the list of all fixed points of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: WordMorphism('a->ab,b->ba').list_fixed_points() #not implemented
[Fixed point beginning with 'a' of the morphism WordMorphism: a->ab, b->ba,
Fixed point beginning with 'b' of the morphism WordMorphism: a->ab, b->ba]
Returns the list of all the conjugate morphisms of self.
DEFINITION:
Recall from Lothaire [1] (Section 2.3.4)
that 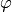 is right conjugate of
is right conjugate of 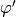 ,
noted
,
noted 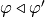 , if there exists
, if there exists
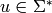 such that
such that
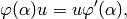
for all 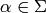 , or equivalently that
, or equivalently that
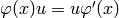 , for all words
, for all words 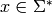 .
Clearly, this relation is not
symmetric so that we say that two morphisms
.
Clearly, this relation is not
symmetric so that we say that two morphisms 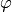 and
and
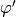 are conjugate, noted
are conjugate, noted
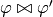 , if
, if
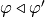 or
or
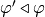 . It is easy to see that
conjugacy of morphisms is an equivalence relation.
. It is easy to see that
conjugacy of morphisms is an equivalence relation.
REFERENCES:
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abbab,b->abb')
sage: map(str, m.list_of_conjugates())
['WordMorphism: a->babba, b->bab',
'WordMorphism: a->abbab, b->abb',
'WordMorphism: a->bbaba, b->bba',
'WordMorphism: a->babab, b->bab',
'WordMorphism: a->ababb, b->abb',
'WordMorphism: a->babba, b->bba',
'WordMorphism: a->abbab, b->bab']
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->aaa,b->aa')
sage: map(str, m.list_of_conjugates())
['WordMorphism: a->aaa, b->aa']
sage: WordMorphism('').list_of_conjugates()
[Morphism from Words over Ordered Alphabet [] to Words over Ordered Alphabet []]
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->aba,b->aba')
sage: map(str, m.list_of_conjugates())
['WordMorphism: a->baa, b->baa',
'WordMorphism: a->aab, b->aab',
'WordMorphism: a->aba, b->aba']
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->abb,b->abbab,c->')
sage: map(str, m.list_of_conjugates())
['WordMorphism: a->bab, b->babba, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->abb, b->abbab, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->bba, b->bbaba, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->bab, b->babab, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->abb, b->ababb, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->bba, b->babba, c->',
'WordMorphism: a->bab, b->abbab, c->']
Returns a partition of the domain alphabet.
Let 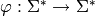 be an involution. There
exists a triple of sets
be an involution. There
exists a triple of sets 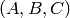 such that
such that
;
,
and
are mutually disjoint and
,
,
.
These sets are not unique.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
A tuple of three sets
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a')
sage: m.partition_of_domain_alphabet() #random ordering
({'a'}, {'b'}, {})
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a,c->c')
sage: m.partition_of_domain_alphabet() #random ordering
({'a'}, {'b'}, {'c'})
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->a,b->b,c->c')
sage: m.partition_of_domain_alphabet() #random ordering
({}, {}, {'a', 'c', 'b'})
sage: m = WordMorphism('A->T,T->A,C->G,G->C')
sage: m.partition_of_domain_alphabet() #random ordering
({'A', 'C'}, {'T', 'G'}, {})
sage: I = WordMorphism({0:oo,oo:0,1:-1,-1:1,2:-2,-2:2,3:-3,-3:3})
sage: I.partition_of_domain_alphabet() #random ordering
({0, -1, -3, -2}, {1, 2, 3, +Infinity}, {})
TESTS:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a,c->a')
sage: m.partition_of_domain_alphabet()
...
TypeError: self is not an involution
Returns a restriction of self to the given alphabet.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
WordMorphism
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = WordMorphism('a->b,b->a')
sage: print m.restrict_domain('a')
WordMorphism: a->b
sage: print m.restrict_domain('')
WordMorphism:
sage: print m.restrict_domain('A')
WordMorphism:
sage: print m.restrict_domain('Aa')
WordMorphism: a->b
The input alphabet must be iterable:
sage: print m.restrict_domain(66)
...
TypeError: 'sage.rings.integer.Integer' object is not iterable
Returns the reversal of self.
EXAMPLES:
sage: print WordMorphism('6->ab,y->5,0->asd').reversal()
WordMorphism: 0->dsa, 6->ba, y->5
sage: print WordMorphism('a->ab,b->a').reversal()
WordMorphism: a->ba, b->a