Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- Modular Symbols »
The ModularSymbol class represents a single modular symbol 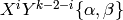 .
.
AUTHOR:
TESTS:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11).2.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
{-1/9, 0}
sage: loads(dumps(s)) == s
True
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
The modular symbol 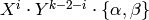 .
.
For a symbol of the form 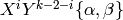 , return
, return 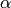 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11,4).1.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^2*{-1/6, 0}
sage: s.alpha()
-1/6
sage: type(s.alpha())
<class 'sage.modular.cusps.Cusp'>
Act on this symbol by the element 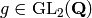 .
.
INPUT:
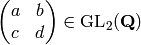 .
.OUTPUT:
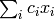 , where
, where 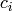 are
scalars and
are
scalars and 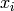 are ModularSymbol objects, such that the sum
are ModularSymbol objects, such that the sum
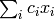 is the image of this symbol under the action of g.
No reduction is performed modulo the relations that hold in
self.space().
is the image of this symbol under the action of g.
No reduction is performed modulo the relations that hold in
self.space().The action of 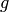 on symbols is by
on symbols is by
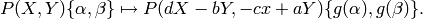
Note that for us we have 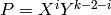 , which simplifies computation
of the polynomial part slightly.
, which simplifies computation
of the polynomial part slightly.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11,2).1.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
{-1/8, 0}
sage: a=1;b=2;c=3;d=4; s.apply([a,b,c,d])
{15/29, 1/2}
sage: x = -1/8; (a*x+b)/(c*x+d)
15/29
sage: x = 0; (a*x+b)/(c*x+d)
1/2
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11,4).1.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^2*{-1/6, 0}
sage: s.apply([a,b,c,d])
16*X^2*{11/21, 1/2} - 16*X*Y*{11/21, 1/2} + 4*Y^2*{11/21, 1/2}
sage: P = s.polynomial_part()
sage: X,Y = P.parent().gens()
sage: P(d*X-b*Y, -c*X+a*Y)
16*X^2 - 16*X*Y + 4*Y^2
sage: x=-1/6; (a*x+b)/(c*x+d)
11/21
sage: x=0; (a*x+b)/(c*x+d)
1/2
sage: type(s.apply([a,b,c,d]))
<class 'sage.structure.formal_sum.FormalSum'>
For a symbol of the form 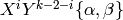 , return
, return 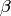 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11,4).1.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^2*{-1/6, 0}
sage: s.beta()
0
sage: type(s.beta())
<class 'sage.modular.cusps.Cusp'>
For a symbol of the form 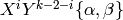 , return
, return 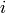 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11).2.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]
sage: s.i()
0
sage: s = ModularSymbols(1,28).0.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^22*Y^4*{0, Infinity}
sage: s.i()
22
Returns a representation of self as a formal sum of Manin symbols. (The result is not cached.)
EXAMPLES:
sage: M = ModularSymbols(11,4)
sage: s = M.1.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^2*{-1/6, 0}
sage: s.manin_symbol_rep()
-[Y^2,(1,1)] - 2*[X*Y,(-1,0)] - [X^2,(-6,1)] - [X^2,(-1,0)]
sage: M(s.manin_symbol_rep()) == M([2,-1/6,0])
True
Return the polynomial part of this symbol, i.e. for a symbol of the
form 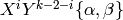 , return
, return 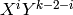 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11).2.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]
sage: s.polynomial_part()
1
sage: s = ModularSymbols(1,28).0.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]; s
X^22*Y^4*{0, Infinity}
sage: s.polynomial_part()
X^22*Y^4
The list of Manin symbols to which this symbol belongs.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(11).2.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]
sage: s.space()
Manin Symbol List of weight 2 for Gamma0(11)
Return the weight of the modular symbols space to which this symbol
belongs; i.e. for a symbol of the form 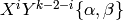 , return
, return 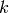 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: s = ModularSymbols(1,28).0.modular_symbol_rep()[0][1]
sage: s.weight()
28