In Sage a “Hecke algebra” always refers to an algebra of endomorphisms of some explicit module, rather than the abstract Hecke algebra of double cosets attached to a subgroup of the modular group.
We distinguish between “anemic Hecke algebras”, which are algebras of Hecke operators whose indices do not divide some integer N (the level), and “full Hecke algebras”, which include Hecke operators coprime to the level. Morphisms in the category of Hecke modules are not required to commute with the action of the full Hecke algebra, only with the anemic algebra.
Return the anemic Hecke algebra associated to the Hecke module M. This checks whether or not the object already exists in memory, and if so, returns the existing object rather than a new one.
EXAMPLES:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra() # indirect doctest
Anemic Hecke algebra acting on Cuspidal subspace of dimension 1 of Modular Forms space of dimension 2 for Modular Group SL(2,Z) of weight 12 over Rational Field
We test uniqueness:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra() is CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra()
True
We can’t ensure uniqueness when loading and saving objects from files, but we can ensure equality:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra() is loads(dumps(CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra()))
False
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra() == loads(dumps(CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra()))
True
Return the full Hecke algebra associated to the Hecke module M. This checks whether or not the object already exists in memory, and if so, returns the existing object rather than a new one.
EXAMPLES:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra() # indirect doctest
Full Hecke algebra acting on Cuspidal subspace of dimension 1 of Modular Forms space of dimension 2 for Modular Group SL(2,Z) of weight 12 over Rational Field
We test uniqueness:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra() is CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra()
True
We can’t ensure uniqueness when loading and saving objects from files, but we can ensure equality:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra() is loads(dumps(CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra()))
False
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra() == loads(dumps(CuspForms(1, 12).hecke_algebra()))
True
Bases: sage.modular.hecke.algebra.HeckeAlgebra_base
An anemic Hecke algebra, generated by Hecke operators with index coprime to the level.
Return a generator over all Hecke operator 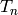 for
for
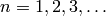 , with
, with  coprime to the
level. This is an infinite sequence.
coprime to the
level. This is an infinite sequence.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(12,2).anemic_hecke_algebra()
sage: g = T.gens()
sage: g.next()
Hecke operator T_1 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 5 for Gamma_0(12) of weight 2 with sign 0 over Rational Field
sage: g.next()
Hecke operator T_5 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 5 for Gamma_0(12) of weight 2 with sign 0 over Rational Field
Return the  -th Hecke operator, for
-th Hecke operator, for  any
positive integer coprime to the level.
any
positive integer coprime to the level.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(Gamma1(5),3).anemic_hecke_algebra()
sage: T.hecke_operator(2)
Hecke operator T_2 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 4 for Gamma_1(5) of weight 3 with sign 0 and over Rational Field
sage: T.hecke_operator(5)
...
IndexError: Hecke operator T_5 not defined in the anemic Hecke algebra
Return True, since this the anemic Hecke algebra.
EXAMPLES:
sage: H = CuspForms(3, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra()
sage: H.is_anemic()
True
Bases: sage.rings.ring.CommutativeAlgebra
Base class for algebras of Hecke operators on a fixed Hecke module.
Return a basis for this Hecke algebra as a free module over its base ring.
EXAMPLE:
sage: ModularSymbols(Gamma1(3), 3).hecke_algebra().basis()
[Hecke operator on Modular Symbols space of dimension 2 for Gamma_1(3) of weight 3 with sign 0 and over Rational Field defined by:
[1 0]
[0 1],
Hecke operator on Modular Symbols space of dimension 2 for Gamma_1(3) of weight 3 with sign 0 and over Rational Field defined by:
[0 0]
[0 2]]
Return the discriminant of this Hecke algebra, i.e. the
determinant of the matrix 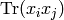 where
where 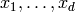 is a basis for self, and
is a basis for self, and 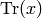 signifies
the trace (in the sense of linear algebra) of left
multiplication by
signifies
the trace (in the sense of linear algebra) of left
multiplication by 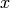 on the algebra (not the trace of the
operator
on the algebra (not the trace of the
operator 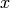 acting on the underlying Hecke module!). For
further discussion and conjectures see Calegari + Stein,
Conjectures about discriminants of Hecke algebras of prime
level, Springer LNCS 3076.
acting on the underlying Hecke module!). For
further discussion and conjectures see Calegari + Stein,
Conjectures about discriminants of Hecke algebras of prime
level, Springer LNCS 3076.
EXAMPLE:
sage: BrandtModule(3, 4).hecke_algebra().discriminant()
1
sage: ModularSymbols(65, sign=1).cuspidal_submodule().hecke_algebra().discriminant()
6144
sage: ModularSymbols(1,4,sign=1).cuspidal_submodule().hecke_algebra().discriminant()
1
Return the  -th Hecke operator.
-th Hecke operator.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(11).hecke_algebra()
sage: T.gen(2)
Hecke operator T_2 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 3 for Gamma_0(11) of weight 2 with sign 0 over Rational Field
Return a generator over all Hecke operator 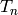 for
for
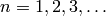 . This is infinite.
. This is infinite.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(1,12).hecke_algebra()
sage: g = T.gens()
sage: g.next()
Hecke operator T_1 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 3 for Gamma_0(1) of weight 12 with sign 0 over Rational Field
sage: g.next()
Hecke operator T_2 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 3 for Gamma_0(1) of weight 12 with sign 0 over Rational Field
Return the matrix of the n-th Hecke operator 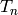 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(1,12).hecke_algebra()
sage: T.hecke_matrix(2)
[ -24 0 0]
[ 0 -24 0]
[4860 0 2049]
Return the  -th Hecke operator
-th Hecke operator 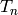 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(1,12).hecke_algebra()
sage: T.hecke_operator(2)
Hecke operator T_2 on Modular Symbols space of dimension 3 for Gamma_0(1) of weight 12 with sign 0 over Rational Field
Return True if this Hecke algebra is Noetherian as a ring. This is true if and only if the base ring is Noetherian.
EXAMPLES:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra().is_noetherian()
True
Return the level of this Hecke algebra, which is (by definition) the level of the Hecke module on which it acts.
EXAMPLE:
sage: ModularSymbols(37).hecke_algebra().level()
37
Return the underlying matrix space of this module.
EXAMPLES:
sage: CuspForms(3, 24, base_ring=Qp(5)).anemic_hecke_algebra().matrix_space()
Full MatrixSpace of 7 by 7 dense matrices over 5-adic Field with capped relative precision 20
The Hecke module on which this algebra is acting.
EXAMPLES:
sage: T = ModularSymbols(1,12).hecke_algebra()
sage: T.module()
Modular Symbols space of dimension 3 for Gamma_0(1) of weight 12 with sign 0 over Rational Field
The size of the set of generators returned by gens(), which is clearly infinity. (This is not necessarily a minimal set of generators.)
EXAMPLES:
sage: CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra().ngens()
+Infinity
The rank of this Hecke algebra as a module over its base ring. Not implemented at present.
EXAMPLE:
sage: ModularSymbols(Gamma1(3), 3).hecke_algebra().rank()
...
NotImplementedError
Bases: sage.modular.hecke.algebra.HeckeAlgebra_base
A full Hecke algebra (including the operators 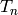 where
where  is not
assumed to be coprime to the level).
is not
assumed to be coprime to the level).
The subalgebra of self generated by the Hecke operators of index coprime to the level.
EXAMPLE:
sage: H = CuspForms(3, 12).hecke_algebra()
sage: H.anemic_subalgebra()
Anemic Hecke algebra acting on Cuspidal subspace of dimension 3 of Modular Forms space of dimension 5 for Congruence Subgroup Gamma0(3) of weight 12 over Rational Field
Return False, since this the full Hecke algebra.
EXAMPLES:
sage: H = CuspForms(3, 12).hecke_algebra()
sage: H.is_anemic()
False
Return True if x is of type HeckeAlgebra.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.modular.hecke.algebra import is_HeckeAlgebra
sage: is_HeckeAlgebra(CuspForms(1, 12).anemic_hecke_algebra())
True
sage: is_HeckeAlgebra(ZZ)
False