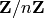 for
for  small.¶
small.¶AUTHORS:
This is a compiled implementation of dense matrices over
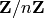 for
for  small.
small.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = matrix(Integers(37),3,range(9),sparse=False); a
[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]
sage: a.rank()
2
sage: type(a)
<type 'sage.matrix.matrix_modn_dense.Matrix_modn_dense'>
sage: a[0,0] = 5
sage: a.rank()
3
sage: parent(a)
Full MatrixSpace of 3 by 3 dense matrices over Ring of integers modulo 37
sage: a^2
[ 3 23 31]
[20 17 29]
[25 16 0]
sage: a+a
[10 2 4]
[ 6 8 10]
[12 14 16]
sage: b = a.new_matrix(2,3,range(6)); b
[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
sage: a*b
...
TypeError: unsupported operand parent(s) for '*': 'Full MatrixSpace of 3 by 3 dense matrices over Ring of integers modulo 37' and 'Full MatrixSpace of 2 by 3 dense matrices over Ring of integers modulo 37'
sage: b*a
[15 18 21]
[20 17 29]
sage: TestSuite(a).run()
sage: TestSuite(b).run()
sage: a.echelonize(); a
[1 0 0]
[0 1 0]
[0 0 1]
sage: b.echelonize(); b
[ 1 0 36]
[ 0 1 2]
We create a matrix group and coerce it to GAP:
sage: M = MatrixSpace(GF(3),3,3)
sage: G = MatrixGroup([M([[0,1,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]]), M([[0,1,0],[1,0,0],[0,0,1]])])
sage: G
Matrix group over Finite Field of size 3 with 2 generators:
[[[0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0]], [[0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1]]]
sage: gap(G)
Group(
[ [ [ 0*Z(3), Z(3)^0, 0*Z(3) ], [ 0*Z(3), 0*Z(3), Z(3)^0 ], [ Z(3)^0, 0*Z(3),
0*Z(3) ] ],
[ [ 0*Z(3), Z(3)^0, 0*Z(3) ], [ Z(3)^0, 0*Z(3), 0*Z(3) ],
[ 0*Z(3), 0*Z(3), Z(3)^0 ] ] ])
TESTS:
sage: M = MatrixSpace(GF(5),2,2)
sage: A = M([1,0,0,1])
sage: A - int(-1)
[2 0]
[0 2]
sage: B = M([4,0,0,1])
sage: B - int(-1)
[0 0]
[0 2]
sage: Matrix(GF(5),0,0, sparse=False).inverse()
[]
Bases: sage.matrix.matrix_dense.Matrix_dense
Returns the characteristic polynomial of self.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = Mat(GF(7),3,3)(range(3)*3)
sage: A.charpoly()
x^3 + 4*x^2
sage: A = Mat(Integers(6),3,3)(range(9))
sage: A.charpoly()
x^3
ALGORITHM: Uses LinBox if self.base_ring() is a field, otherwise use Hessenberg form algorithm.
Return the determinant of this matrix.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = matrix(GF(101),5,range(25))
sage: m.det()
0
sage: m = matrix(Integers(4), 2, [2,2,2,2])
sage: m.det()
0
TESTS:
sage: m = random_matrix(GF(3), 3, 4)
sage: m.determinant()
...
ValueError: self must be a square matrix
Puts self in row echelon form.
INPUT:
 Gauss elimination implemented in Sage.
Gauss elimination implemented in Sage.OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = matrix(GF(97),3,4,range(12))
sage: a.echelonize(); a
[ 1 0 96 95]
[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 0 0 0 0]
sage: a.pivots()
[0, 1]
Return the lift of this matrix to the integers.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = matrix(GF(7),2,3,[1..6])
sage: a.lift()
[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
sage: a.lift().parent()
Full MatrixSpace of 2 by 3 dense matrices over Integer Ring
Subdivisions are preserved when lifting:
sage: a.subdivide([], [1,1]); a
[1||2 3]
[4||5 6]
sage: a.lift()
[1||2 3]
[4||5 6]
Return the requested matrix window.
EXAMPLES:
sage: a = matrix(GF(7),3,range(9)); a
[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 0 1]
sage: type(a)
<type 'sage.matrix.matrix_modn_dense.Matrix_modn_dense'>
We test the optional check flag.
sage: matrix(GF(7),[1]).matrix_window(0,1,1,1)
...
IndexError: matrix window index out of range
sage: matrix(GF(7),[1]).matrix_window(0,1,1,1, check=False)
Matrix window of size 1 x 1 at (0,1):
[1]
Returns the minimal polynomial of self.
INPUT:
- var - a variable name
- algorithm - ‘generic’ ‘linbox’ (default)
- proof – (default: True); whether to provably return the true minimal polynomial; if False, we only guarantee to return a divisor of the minimal polynomial. There are also certainly cases where the computed results is frequently not exactly equal to the minimal polynomial (but is instead merely a divisor of it).
WARNING: If proof=True, minpoly is insanely slow compared to proof=False.
EXAMPLES:
sage: R.<x>=GF(3)[]
sage: A = matrix(GF(3),2,[0,0,1,2])
sage: A.minpoly()
x^2 + x
Minpoly with proof=False is dramatically (“millions” of times!) faster than minpoly with proof=True. This matters since proof=True is the default, unless you first type ‘’proof.linear_algebra(False)’‘.
sage: A.minpoly(proof=False) in [x, x+1, x^2+x] True
Randomize density proportion of the entries of this matrix, leaving the rest unchanged.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = matrix(GF(5), 5, 5, 0)
sage: A.randomize(0.5); A
[0 0 0 2 0]
[0 3 0 0 2]
[4 0 0 0 0]
[4 0 0 0 0]
[0 1 0 0 0]
sage: A.randomize(); A
[3 3 2 1 2]
[4 3 3 2 2]
[0 3 3 3 3]
[3 3 2 2 4]
[2 2 2 1 4]
Return the rank of this matrix.
EXAMPLES:
sage: m = matrix(GF(7),5,range(25))
sage: m.rank()
2
Rank is not implemented over the integers modulo a composite yet.
sage: m = matrix(Integers(4), 2, [2,2,2,2])
sage: m.rank()
...
NotImplementedError: Echelon form not implemented over 'Ring of integers modulo 4'.