This is the Sage interface to John Cremona’s eclib C++ library for arithmetic on elliptic curves. The classes defined in this module give Sage interpreter-level access to some of the functionality of eclib. For most purposes, it is not necessary to directly use these classes. Instead, one can create an EllipticCurve and call methods that are implemented using this module.
Note
This interface is a direct library-level interface to eclib, including the 2-descent program mwrank.
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
The mwrank_EllipticCurve class represents an elliptic curve using the Curvedata class from eclib, called here an ‘mwrank elliptic curve’.
Create the mwrank elliptic curve with invariants
ainvs, which is a list of 5 or less integers 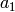 ,
,
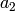 ,
, 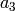 ,
, 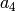 , and
, and 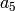 .
.
If strictly less than 5 invariants are given, then the first
ones are set to 0, so, e.g., [3,4] means 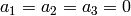 and
and
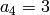 ,
, 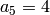 .
.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
We create the elliptic curve 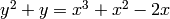 :
:
sage: e = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 1, 1, -2, 0])
sage: e.ainvs()
[0, 1, 1, -2, 0]
This example illustrates that omitted  -invariants default to
-invariants default to  :
:
sage: e = mwrank_EllipticCurve([3, -4])
sage: e
y^2 = x^3 + 3*x - 4
sage: e.ainvs()
[0, 0, 0, 3, -4]
The entries of the input list are coerced to int. If this is impossible, then an error is raised:
sage: e = mwrank_EllipticCurve([3, -4.8]); e
...
TypeError: ainvs must be a list or tuple of integers.
When you enter a singular model you get an exception:
sage: e = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0])
...
ArithmeticError: Invariants (= [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) do not describe an elliptic curve.
Return the Cremona-Prickett-Siksek height bound. This is a
floating point number  such that if
such that if  is a point on the
curve, then the naive logarithmic height
is a point on the
curve, then the naive logarithmic height 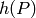 is less than
is less than
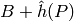 , where
, where 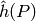 is the canonical height of
is the canonical height of
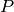 .
.
Warning
We assume the model is minimal!
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 0, -1002231243161, 0])
sage: E.CPS_height_bound()
14.163198527061496
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: E.CPS_height_bound()
0.0
Returns the  -invariants of this mwrank elliptic curve.
-invariants of this mwrank elliptic curve.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-1,0])
sage: E.ainvs()
[0, 0, 1, -1, 0]
Returns True if the last two_descent() call provably correctly computed the rank. If two_descent() hasn’t been called, then it is first called by certain() using the default parameters.
The result is True if and only if the results of the methods rank() and rank_bound() are equal.
EXAMPLES:
A 2-descent does not determine 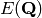 with certainty
for the curve
with certainty
for the curve 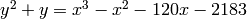 :
:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 1, -120, -2183])
sage: E.two_descent(False)
...
sage: E.certain()
False
sage: E.rank()
0
The previous value is only a lower bound; the upper bound is greater:
sage: E.rank_bound()
2
In fact the rank of 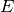 is actually 0 (as one could see by
computing the
is actually 0 (as one could see by
computing the 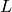 -function), but Sha has order 4 and the
2-torsion is trivial, so mwrank cannot conclusively
determine the rank in this case.
-function), but Sha has order 4 and the
2-torsion is trivial, so mwrank cannot conclusively
determine the rank in this case.
Return the conductor of this curve, computed using Cremona’s implementation of Tate’s algorithm.
Note
This is independent of PARI’s.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([1, 1, 0, -6958, -224588])
sage: E.conductor()
2310
Return a list of the generators for the Mordell-Weil group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0])
sage: E.gens()
[[0, -1, 1]]
Returns the isogeny class of this mwrank elliptic curve.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,-1,1,0,0])
sage: E.isogeny_class()
([[0, -1, 1, 0, 0], [0, -1, 1, -10, -20], [0, -1, 1, -7820, -263580]], [[0, 5, 0], [5, 0, 5], [0, 5, 0]])
Returns the rank of this curve, computed using two_descent().
In general this may only be a lower bound for the rank; an upper bound may be obtained using the function rank_bound(). To test whether the value has been proved to be correct, use the method certain().
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -900, -10098])
sage: E.rank()
0
sage: E.certain()
True
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 1, -929, -10595])
sage: E.rank()
0
sage: E.certain()
False
Returns an upper bound for the rank of this curve, computed using two_descent().
If the curve has no 2-torsion, this is equal to the 2-Selmer rank. If the curve has 2-torsion, the upper bound may be smaller than the bound obtained from the 2-Selmer rank minus the 2-rank of the torsion, since more information is gained from the 2-isogenous curve or curves.
EXAMPLES:
The following is the curve 960D1, which has rank 0, but Sha of order 4:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -900, -10098])
sage: E.rank_bound()
0
sage: E.rank()
0
In this case the rank was computed using a second descent, which is able to determine (by considering a 2-isogenous curve) that Sha is nontrivial. If we deliberately stop the second descent, the rank bound is larger:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -900, -10098])
sage: E.two_descent(second_descent = False, verbose=False)
sage: E.rank_bound()
2
In contrast, for the curve 571A, also with rank 0 and Sha of order 4, we only obtain an upper bound of 2:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 1, -929, -10595])
sage: E.rank_bound()
2
In this case the value returned by rank() is only a lower bound in general (though this is correct):
sage: E.rank()
0
sage: E.certain()
False
Return the regulator of the saturated Mordell-Weil group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0])
sage: E.regulator()
0.05111140823996884
Compute the saturation of the Mordell-Weil group at all primes up to bound.
INPUT:
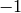 (the default) to
saturate at all primes,
(the default) to
saturate at all primes, 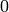 for no saturation, or
for no saturation, or  (a
positive integer) to saturate at all primes up to
(a
positive integer) to saturate at all primes up to  .
.EXAMPLES:
Since the 2-descent automatically saturates at primes up to 20, it is not easy to come up with an example where saturation has any effect:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 0, -1002231243161, 0])
sage: E.gens()
[[-1001107, -4004428, 1]]
sage: E.saturate()
sage: E.gens()
[[-1001107, -4004428, 1]]
Returns the rank of the 2-Selmer group of the curve.
EXAMPLES:
The following is the curve 960D1, which has rank 0, but Sha of order 4. The 2-torsion has rank 2, and the Selmer rank is 3:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -900, -10098])
sage: E.selmer_rank()
3
Nevertheless, we can obtain a tight upper bound on the rank since a second descent is performed which establishes the 2-rank of Sha:
sage: E.rank_bound()
0
To show that this was resolved using a second descent, we do the computation again but turn off second_descent:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -900, -10098])
sage: E.two_descent(second_descent = False, verbose=False)
sage: E.rank_bound()
2
For the curve 571A, also with rank 0 and Sha of order 4, but with no 2-torsion, the Selmer rank is strictly greater than the rank:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 1, -929, -10595])
sage: E.selmer_rank()
2
sage: E.rank_bound()
2
In cases like this with no 2-torsion, the rank upper bound is always equal to the 2-Selmer rank. If we ask for the rank, all we get is a lower bound:
sage: E.rank()
0
sage: E.certain()
False
Set the verbosity of printing of output by the two_descent() and other functions.
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0])
sage: E.saturate() # no output
sage: E.gens()
[[0, -1, 1]]
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 1, -1, 0])
sage: E.set_verbose(1)
sage: E.saturate() # produces the following output
Basic pair: I=48, J=-432
disc=255744
2-adic index bound = 2
By Lemma 5.1(a), 2-adic index = 1
2-adic index = 1
One (I,J) pair
Looking for quartics with I = 48, J = -432
Looking for Type 2 quartics:
Trying positive a from 1 up to 1 (square a first...)
(1,0,-6,4,1) --trivial
Trying positive a from 1 up to 1 (...then non-square a)
Finished looking for Type 2 quartics.
Looking for Type 1 quartics:
Trying positive a from 1 up to 2 (square a first...)
(1,0,0,4,4) --nontrivial...(x:y:z) = (1 : 1 : 0)
Point = [0:0:1]
height = 0.051111408239968840235886099756942021609538202280854
Rank of B=im(eps) increases to 1 (The previous point is on the egg)
Exiting search for Type 1 quartics after finding one which is globally soluble.
Mordell rank contribution from B=im(eps) = 1
Selmer rank contribution from B=im(eps) = 1
Sha rank contribution from B=im(eps) = 0
Mordell rank contribution from A=ker(eps) = 0
Selmer rank contribution from A=ker(eps) = 0
Sha rank contribution from A=ker(eps) = 0
Searching for points (bound = 8)...done:
found points of rank 1
and regulator 0.051111408239968840235886099756942021609538202280854
Processing points found during 2-descent...done:
now regulator = 0.051111408239968840235886099756942021609538202280854
Saturating (bound = -1)...done:
points were already saturated.
Return the Silverman height bound. This is a floating point
number 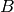 such that if
such that if 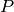 is a point on the curve, then the
naive logarithmic height
is a point on the curve, then the
naive logarithmic height 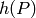 is less than
is less than 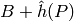 ,
where
,
where 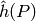 is the canonical height of
is the canonical height of 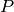 .
.
Warning
We assume the model is minimal!
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, 0, 0, -1002231243161, 0])
sage: E.silverman_bound()
18.295452104682472
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: E.silverman_bound()
6.2848333699724028
Compute 2-descent data for this curve.
INPUT:
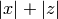 in
quartic point search.
in
quartic point search.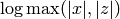 , i.e. logarithmic.
, i.e. logarithmic.OUTPUT:
Nothing – nothing is returned.
TESTS (see #7992):
sage: EllipticCurve([0, prod(prime_range(10))]).mwrank_curve().two_descent()
sage: EllipticCurve([0, prod(prime_range(100))]).mwrank_curve().two_descent()
...
...
RuntimeError
Bases: sage.structure.sage_object.SageObject
The mwrank_MordellWeil class represents a subgroup of a Mordell-Weil group. Use this class to saturate a specified list of points on an mwrank_EllipticCurve, or to search for points up to some bound.
INPUT:
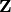 -basis for the subgroup generated by the points found
so far is stored; if zero, no processing is done and all
points found are stored).
-basis for the subgroup generated by the points found
so far is stored; if zero, no processing is done and all
points found are stored).EXAMPLE:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([1,0,1,4,-6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: []
sage: EQ.search(2) # output below
The previous command produces the following output:
P1 = [0:1:0] is torsion point, order 1
P1 = [1:-1:1] is torsion point, order 2
P1 = [2:2:1] is torsion point, order 3
P1 = [9:23:1] is torsion point, order 6
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.search(2)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
Example to illustrate the verbose parameter:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E, verbose=False)
sage: EQ.search(1) # no output
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E, verbose=True)
sage: EQ.search(1) # output below
The previous command produces the following output:
P1 = [0:1:0] is torsion point, order 1
P1 = [-3:0:1] is generator number 1
saturating up to 20...Checking 2-saturation
Points have successfully been 2-saturated (max q used = 7)
Checking 3-saturation
Points have successfully been 3-saturated (max q used = 7)
Checking 5-saturation
Points have successfully been 5-saturated (max q used = 23)
Checking 7-saturation
Points have successfully been 7-saturated (max q used = 41)
Checking 11-saturation
Points have successfully been 11-saturated (max q used = 17)
Checking 13-saturation
Points have successfully been 13-saturated (max q used = 43)
Checking 17-saturation
Points have successfully been 17-saturated (max q used = 31)
Checking 19-saturation
Points have successfully been 19-saturated (max q used = 37)
done
P2 = [-2:3:1] is generator number 2
saturating up to 20...Checking 2-saturation
possible kernel vector = [1,1]
This point may be in 2E(Q): [14:-52:1]
...and it is!
Replacing old generator #1 with new generator [1:-1:1]
Points have successfully been 2-saturated (max q used = 7)
Index gain = 2^1
Checking 3-saturation
Points have successfully been 3-saturated (max q used = 13)
Checking 5-saturation
Points have successfully been 5-saturated (max q used = 67)
Checking 7-saturation
Points have successfully been 7-saturated (max q used = 53)
Checking 11-saturation
Points have successfully been 11-saturated (max q used = 73)
Checking 13-saturation
Points have successfully been 13-saturated (max q used = 103)
Checking 17-saturation
Points have successfully been 17-saturated (max q used = 113)
Checking 19-saturation
Points have successfully been 19-saturated (max q used = 47)
done (index = 2).
Gained index 2, new generators = [ [1:-1:1] [-2:3:1] ]
P3 = [-14:25:8] is generator number 3
saturating up to 20...Checking 2-saturation
Points have successfully been 2-saturated (max q used = 11)
Checking 3-saturation
Points have successfully been 3-saturated (max q used = 13)
Checking 5-saturation
Points have successfully been 5-saturated (max q used = 71)
Checking 7-saturation
Points have successfully been 7-saturated (max q used = 101)
Checking 11-saturation
Points have successfully been 11-saturated (max q used = 127)
Checking 13-saturation
Points have successfully been 13-saturated (max q used = 151)
Checking 17-saturation
Points have successfully been 17-saturated (max q used = 139)
Checking 19-saturation
Points have successfully been 19-saturated (max q used = 179)
done (index = 1).
P4 = [-1:3:1] = -1*P1 + -1*P2 + -1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [0:2:1] = 2*P1 + 0*P2 + 1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [2:13:8] = -3*P1 + 1*P2 + -1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [1:0:1] = -1*P1 + 0*P2 + 0*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [2:0:1] = -1*P1 + 1*P2 + 0*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [18:7:8] = -2*P1 + -1*P2 + -1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [3:3:1] = 1*P1 + 0*P2 + 1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [4:6:1] = 0*P1 + -1*P2 + -1*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [36:69:64] = 1*P1 + -2*P2 + 0*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [68:-25:64] = -2*P1 + -1*P2 + -2*P3 (mod torsion)
P4 = [12:35:27] = 1*P1 + -1*P2 + -1*P3 (mod torsion)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
Example to illustrate the process points (pp) parameter:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E, verbose=False, pp=1)
sage: EQ.search(1); EQ # generators only
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E, verbose=False, pp=0)
sage: EQ.search(1); EQ # all points found
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[-3:0:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8], [-1:3:1], [0:2:1], [2:13:8], [1:0:1], [2:0:1], [18:7:8], [3:3:1], [4:6:1], [36:69:64], [68:-25:64], [12:35:27]]
Return a list of the generating points in this Mordell-Weil group.
OUTPUT:
(list) A list of lists of length 3, each holding the
primitive integer coordinates ![[x,y,z]](../../../_images/math/7fb8275e9558bb632b9a648d4f52db70997a4b81.png) of a generating
point.
of a generating
point.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.search(1)
sage: EQ.points()
[[1, -1, 1], [-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8]]
This function allows one to add points to a mwrank_MordellWeil object.
Process points in the list v, with saturation at primes up to sat. If sat is zero (the default), do no saturation.
INPUT:
OUTPUT:
None. But note that if the verbose flag is set, then there will be some output as a side-effect.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: E.gens()
[[1, -1, 1], [-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8]]
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.process([[1, -1, 1], [-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8]])
Output of previous command:
P1 = [1:-1:1] is generator number 1
P2 = [-2:3:1] is generator number 2
P3 = [-14:25:8] is generator number 3
sage: EQ.points()
[[1, -1, 1], [-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8]]
Example to illustrate the saturation parameter sat:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.process([[1547, -2967, 343], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]], sat=20)
sage: EQ.points()
[[-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8], [1, -1, 1]]
Here the processing was followed by saturation at primes up to 20. Now we prevent this initial saturation:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.process([[1547, -2967, 343], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]], sat=0)
sage: EQ.points()
[[1547, -2967, 343], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
375.42919921875
sage: EQ.saturate(2) # points were not 2-saturated
(False, '2', '[ ]')
sage: EQ.points()
[[-2, 3, 1], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
93.8572998046875
sage: EQ.saturate(3) # points were not 3-saturated
(False, '3', '[ ]')
sage: EQ.points()
[[-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
10.4285888671875
sage: EQ.saturate(5) # points were not 5-saturated
(False, '5', '[ ]')
sage: EQ.points()
[[-2, 3, 1], [-14, 25, 8], [1, -1, 1]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
0.4171435534954071
sage: EQ.saturate() # points are now saturated
(True, '1', '[ ]')
Return the rank of this subgroup of the Mordell-Weil group.
OUTPUT:
(int) The rank of this subgroup of the Mordell-Weil group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,-1,1,0,0])
sage: E.rank()
0
A rank 3 example:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.rank()
0
sage: EQ.regulator()
1.0
The preceding output is correct, since we have not yet tried to find any points on the curve either by searching or 2-descent:
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: []
Now we do a very small search:
sage: EQ.search(1)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
sage: EQ.rank()
3
sage: EQ.regulator()
0.4171435534954071
We do in fact now have a full Mordell-Weil basis.
Return the regulator of the points in this subgroup of the Mordell-Weil group.
Note
eclib can compute the regulator to arbitrary precision, but the interface currently returns the output as a float.
OUTPUT:
(float) The regulator of the points in this subgroup.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,-1,1,0,0])
sage: E.regulator()
1.0
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: E.regulator()
0.41714355875838399
Saturate this subgroup of the Mordell-Weil group.
INPUT:
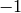 (the default), an
upper bound is computed for the primes at which the subgroup
may not be saturated, and this is used; however, if the
computed bound is greater than a value set by the eclib
library (currently 97) then no saturation will be attempted
at primes above this.
(the default), an
upper bound is computed for the primes at which the subgroup
may not be saturated, and this is used; however, if the
computed bound is greater than a value set by the eclib
library (currently 97) then no saturation will be attempted
at primes above this.OUTPUT:
(3-tuple) (ok, index, unsatlist) where:
 but cannot be divided by
but cannot be divided by  . (Note that eclib
uses floating point methods based on elliptic logarithms to
divide points.)
. (Note that eclib
uses floating point methods based on elliptic logarithms to
divide points.)Note
We emphasize that if this function returns True as the first return argument (ok), and if the default was used for the parameter max_prime, then the points in the basis after calling this function are saturated at all primes, i.e., saturating at the primes up to max_prime are sufficient to saturate at all primes. Note that the function might not have needed to saturate at all primes up to max_prime. It has worked out what prime you need to saturate up to, and that prime might be smaller than max_prime.
Note
Currently (May 2010), this does not remember the result of calling search(). So calling search() up to height 20 then calling saturate() results in another search up to height 18.
EXAMPLES:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
We initialise with three points which happen to be 2, 3 and 5 times the generators of this rank 3 curve. To prevent automatic saturation at this stage we set the parameter sat to 0 (which is in fact the default):
sage: EQ.process([[1547, -2967, 343], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]], sat=0)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1547:-2967:343], [2707496766203306:864581029138191:2969715140223272], [-13422227300:-49322830557:12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
375.42919921875
Now we saturate at 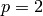 , and gain index 2:
, and gain index 2:
sage: EQ.saturate(2) # points were not 2-saturated
(False, '2', '[ ]')
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[-2:3:1], [2707496766203306:864581029138191:2969715140223272], [-13422227300:-49322830557:12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
93.8572998046875
Now we saturate at 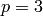 , and gain index 3:
, and gain index 3:
sage: EQ.saturate(3) # points were not 3-saturated
(False, '3', '[ ]')
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[-2:3:1], [-14:25:8], [-13422227300:-49322830557:12167000000]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
10.4285888671875
Now we saturate at 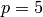 , and gain index 5:
, and gain index 5:
sage: EQ.saturate(5) # points were not 5-saturated
(False, '5', '[ ]')
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[-2:3:1], [-14:25:8], [1:-1:1]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
0.4171435534954071
Finally we finish the saturation. The output here shows that the points are now provably saturated at all primes:
sage: EQ.saturate() # points are now saturated
(True, '1', '[ ]')
Of course, the process() function would have done all this automatically for us:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.process([[1547, -2967, 343], [2707496766203306, 864581029138191, 2969715140223272], [-13422227300, -49322830557, 12167000000]], sat=5)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[-2:3:1], [-14:25:8], [1:-1:1]]
sage: EQ.regulator()
0.4171435534954071
But we would still need to use the saturate() function to verify that full saturation has been done:
sage: EQ.saturate()
(True, '1', '[ ]')
The preceding command produces the following output as a side-effect. It proves that the index of the points in their saturation is at most 3, then proves saturation at 2 and at 3, by reducing the points modulo all primes of good reduction up to 11, respectively 13:
saturating basis...Saturation index bound = 3
Checking saturation at [ 2 3 ]
Checking 2-saturation
Points were proved 2-saturated (max q used = 11)
Checking 3-saturation
Points were proved 3-saturated (max q used = 13)
done
Search for new points, and add them to this subgroup of the Mordell-Weil group.
INPUT:
Note
On 32-bit machines, this must be < 21.48 else
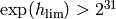 and overflows. On 64-bit machines, it
must be at most 43.668. However, this bound is a logarithmic
bound and increasing it by just 1 increases the running time
by (roughly)
and overflows. On 64-bit machines, it
must be at most 43.668. However, this bound is a logarithmic
bound and increasing it by just 1 increases the running time
by (roughly) 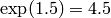 , so searching up to even 20
takes a very long time.
, so searching up to even 20
takes a very long time.
Note
The search is carried out with a quadratic sieve, using code adapted from a version of Michael Stoll’s ratpoints program. It would be preferable to use a newer version of ratpoints.
EXAMPLES:
A rank 3 example, where a very small search is sufficient to find a Mordell-Weil basis:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0,0,1,-7,6])
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.search(1)
sage: EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[1:-1:1], [-2:3:1], [-14:25:8]]
In the next example, a search bound of 12 is needed to find a non-torsion point:
sage: E = mwrank_EllipticCurve([0, -1, 0, -18392, -1186248]) #1056g4
sage: EQ = mwrank_MordellWeil(E)
sage: EQ.search(11); EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: []
sage: EQ.search(12); EQ
Subgroup of Mordell-Weil group: [[4413270:10381877:27000]]
Set the global NTL real number precision. This has a massive effect on the speed of mwrank calculations. The default (used if this function is not called) is n=15, but it might have to be increased if a computation fails. In this case, one must recreate the mwrank curve from scratch after resetting this precision.
INPUT:
Warning
This change is global and affects all of Sage.
EXAMPLES:
sage: mwrank_set_precision(20)