AUTHORS:
TODO:
The basic idea is very simple. Let G be an abelian group and
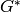 its dual (i.e., the group of homomorphisms from G to
its dual (i.e., the group of homomorphisms from G to
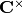 ). Let
). Let 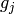 ,
,
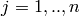 , denote generators of
, denote generators of 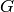 - say
- say
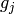 is of order
is of order 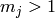 . There are generators
. There are generators
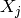 ,
, 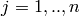 , of
, of 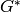 for which
for which
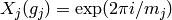 and
and 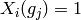 if
if 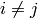 . These are used to construct
. These are used to construct 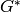 in
the DualAbelianGroup class below.
in
the DualAbelianGroup class below.
Sage supports multiplicative abelian groups on any prescribed
finite number 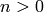 of generators. Use the
AbelianGroup function to create an abelian group,
the DualAbelianGroup function to create its dual,
and then the gen and gens functions
to obtain the corresponding generators. You can print the
generators as arbitrary strings using the optional
names argument to the
DualAbelianGroup function.
of generators. Use the
AbelianGroup function to create an abelian group,
the DualAbelianGroup function to create its dual,
and then the gen and gens functions
to obtain the corresponding generators. You can print the
generators as arbitrary strings using the optional
names argument to the
DualAbelianGroup function.
Create the dual group of the multiplicative abelian group
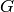 .
.
INPUT:
OUTPUT: The dual group of G.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F = AbelianGroup(5, [2,5,7,8,9], names='abcde')
sage: (a, b, c, d, e) = F.gens()
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F,names='ABCDE')
sage: A,B,C,D,E = Fd.gens()
sage: A(a) ## random
-1.0000000000000000 + 0.00000000000000013834419720915037*I
sage: A(b); A(c); A(d); A(e)
1.00000000000000
1.00000000000000
1.00000000000000
1.00000000000000
Bases: sage.groups.group.AbelianGroup
Dual of abelian group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F = AbelianGroup(5,[3,5,7,8,9],names = list("abcde"))
sage: DualAbelianGroup(F)
Dual of Abelian Group isomorphic to Z/3Z x Z/5Z x Z/7Z x Z/8Z x Z/9Z over Complex Field with 53 bits of precision
sage: F = AbelianGroup(4,[15,7,8,9],names = list("abcd"))
sage: DualAbelianGroup(F)
Dual of Abelian Group isomorphic to Z/15Z x Z/7Z x Z/8Z x Z/9Z over Complex Field with 53 bits of precision
The 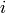 -th generator of the abelian group.
-th generator of the abelian group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F = AbelianGroup(3,[1,2,3],names='a')
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F, names="A")
sage: Fd.0
A0
sage: Fd.1
A1
sage: Fd.invariants()
[2, 3]
The invariants of the dual group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F = AbelianGroup(1000)
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F)
sage: invs = Fd.invariants(); len(invs)
1000
This can be slow for 10000 or more generators.
Return True since this group is commutative.
EXAMPLES:
sage: G = AbelianGroup([2,3,9])
sage: Gd = DualAbelianGroup(G)
sage: Gd.is_commutative()
True
sage: Gd.is_abelian()
True
Return list of all elements of this group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: G = AbelianGroup([2,3], names = "ab")
sage: Gd = DualAbelianGroup(G, names = "AB")
sage: Gd.list()
[1, B, B^2, A, A*B, A*B^2]
The number of generators of the dual group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: F = AbelianGroup(1000)
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F)
sage: Fd.ngens()
1000
This can be slow for 10000 or more generators.
Return the order of this group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: G = AbelianGroup([2,3,9])
sage: Gd = DualAbelianGroup(G)
sage: Gd.order()
54
Return a random element of this dual group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: G = AbelianGroup([2,3,9])
sage: Gd = DualAbelianGroup(G)
sage: Gd.random_element()
X0*X1^2*X2
sage: N = 43^2-1
sage: G = AbelianGroup([N],names="a")
sage: Gd = DualAbelianGroup(G,names="A")
sage: a, = G.gens()
sage: A, = Gd.gens()
sage: x = a^(N/4); y = a^(N/3); z = a^(N/14)
sage: X = Gd.random_element(); X
A^615
sage: len([a for a in [x,y,z] if abs(X(a)-1)>10^(-8)])
2
Return True if 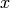 is the dual group of an abelian group.
is the dual group of an abelian group.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.groups.abelian_gps.dual_abelian_group import is_DualAbelianGroup
sage: F = AbelianGroup(5,[3,5,7,8,9],names = list("abcde"))
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F)
sage: is_DualAbelianGroup(Fd)
True
sage: F = AbelianGroup(3,[1,2,3],names='a')
sage: Fd = DualAbelianGroup(F)
sage: Fd.gens()
(X0, X1)
sage: F.gens()
(a0, a1)