Bases: sage.combinat.sf.multiplicative.SymmetricFunctionAlgebra_multiplicative
Bases: sage.combinat.sf.classical.SymmetricFunctionAlgebra_classical.Element
Expands the symmetric function as a symmetric polynomial in n variables.
EXAMPLES:
sage: p = SFAPower(QQ)
sage: a = p([2])
sage: a.expand(2)
x0^2 + x1^2
sage: a.expand(3, alphabet=['a','b','c'])
a^2 + b^2 + c^2
sage: p([2,1,1]).expand(2)
x0^4 + 2*x0^3*x1 + 2*x0^2*x1^2 + 2*x0*x1^3 + x1^4
sage: p([7]).expand(4)
x0^7 + x1^7 + x2^7 + x3^7
sage: p([7]).expand(4,alphabet='t')
t0^7 + t1^7 + t2^7 + t3^7
sage: p([7]).expand(4,alphabet='x,y,z,t')
x^7 + y^7 + z^7 + t^7
Returns the image of self under the Frobenius / omega automorphism.
EXAMPLES:
sage: p = SFAPower(QQ)
sage: a = p([2,1]); a
p[2, 1]
sage: a.omega()
-p[2, 1]
Returns the standard scalar product of self and x.
Note that the power-sum symmetric functions are orthogonal under
this scalar product. The value of 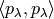 is given by the size of the centralizer in
is given by the size of the centralizer in 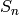 of a
permutation of cycle type
of a
permutation of cycle type 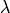 .
.
EXAMPLES:
sage: p = SFAPower(QQ)
sage: p4 = Partitions(4)
sage: matrix([ [p(a).scalar(p(b)) for a in p4] for b in p4])
[ 4 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 3 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 8 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 4 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 24]