Navigation
- index
- modules |
- next |
- previous |
- Sage Reference v4.5.1 »
- 2D Graphics »
Bases: sage.plot.primitive.GraphicPrimitive
Primitive class that initializes the (line) arrow graphics type
EXAMPLES:
We create an arrow graphics object, then take the 0th entry in it to get the actual Arrow graphics primitive:
sage: P = arrow((0,1), (2,3))[0]
sage: type(P)
<class 'sage.plot.arrow.Arrow'>
sage: P
Arrow from (0.0,1.0) to (2.0,3.0)
Returns a bounding box for this arrow.
EXAMPLES:
sage: d = arrow((1,1), (5,5)).get_minmax_data()
sage: d['xmin']
1.0
sage: d['xmax']
5.0
Takes 2D plot and places it in 3D.
EXAMPLES:
sage: A = arrow((0,0),(1,1))[0].plot3d()
sage: A.jmol_repr(A.testing_render_params())[0]
'draw line_1 diameter 2 arrow {0.0 0.0 0.0} {1.0 1.0 0.0} '
Note that we had to index the arrow to get the Arrow graphics primitive. We can also change the height via the plot3d method of Graphics, but only as a whole:
sage: A = arrow((0,0),(1,1)).plot3d(3)
sage: A.jmol_repr(A.testing_render_params())[0][0]
'draw line_1 diameter 2 arrow {0.0 0.0 3.0} {1.0 1.0 3.0} '
Optional arguments place both the head and tail outside the
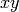 -plane, but at different heights. This must be done on
the graphics primitive obtained by indexing:
-plane, but at different heights. This must be done on
the graphics primitive obtained by indexing:
sage: A=arrow((0,0),(1,1))[0].plot3d(3,4)
sage: A.jmol_repr(A.testing_render_params())[0]
'draw line_1 diameter 2 arrow {0.0 0.0 3.0} {1.0 1.0 4.0} '
Bases: sage.plot.primitive.GraphicPrimitive
Returns a dictionary with the bounding box data.
EXAMPLES:
sage: from sage.plot.arrow import CurveArrow
sage: b = CurveArrow(path=[[(0,0),(.5,.5),(1,0)],[(.5,1),(0,0)]],options={})
sage: d = b.get_minmax_data()
sage: d['xmin']
0.0
sage: d['xmax']
1.0
If tailpoint and headpoint are provided, returns an arrow from (xmin, ymin) to (xmax, ymax). If tailpoint or headpoint is None and path is not None, returns an arrow along the path. (See further info on paths in bezier_path).
INPUT:
EXAMPLES:
A straight, blue arrow:
sage: arrow((1, 1), (3, 3))
Make a red arrow:
sage: arrow((-1, -1), (2, 3), color=(1,0,0))
sage: arrow((-1, -1), (2, 3), color='red')
You can change the width of an arrow:
sage: arrow((1, 1), (3, 3), width=5, arrowsize=15)
A pretty circle of arrows:
sage: sum([arrow((0,0), (cos(x),sin(x)), hue=x/(2*pi)) for x in [0..2*pi,step=0.1]]).show(aspect_ratio=1)
If we want to draw the arrow between objects, for example, the boundaries of two lines, we can use the arrowshorten option to make the arrow shorter by a certain number of points:
sage: line([(0,0),(1,0)],thickness=10)+line([(0,1),(1,1)], thickness=10)+arrow((0.5,0),(0.5,1), arrowshorten=10,rgbcolor=(1,0,0))
Extra options will get passed on to show(), as long as they are valid:
sage: arrow((-2, 2), (7,1), frame=True)
sage: arrow((-2, 2), (7,1)).show(frame=True)