EXAMPLES: We create 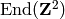 and compute a
basis.
and compute a
basis.
sage: M = FreeModule(IntegerRing(),2)
sage: E = End(M)
sage: B = E.basis()
sage: len(B)
4
sage: B[0]
Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[1 0]
[0 0]
Domain: Ambient free module of rank 2 over the principal ideal domain ...
Codomain: Ambient free module of rank 2 over the principal ideal domain ...
We create 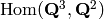 and
compute a basis.
and
compute a basis.
sage: V3 = VectorSpace(RationalField(),3)
sage: V2 = VectorSpace(RationalField(),2)
sage: H = Hom(V3,V2)
sage: H
Set of Morphisms from Vector space of dimension 3 over Rational Field
to Vector space of dimension 2 over Rational Field in Category of
vector spaces over Rational Field
sage: B = H.basis()
sage: len(B)
6
sage: B[0]
Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[1 0]
[0 0]
[0 0]...
TESTS:
sage: H = Hom(QQ^2, QQ^1)
sage: loads(dumps(H)) == H
True
See trac 5886:
sage: V = (QQ^2).span_of_basis([[1,2],[3,4]])
sage: V.hom([V.0, V.1])
Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[1 0]
[0 1]...
Bases: sage.categories.homset.HomsetWithBase
Return a basis for this space of free module homomorphisms.
EXAMPLES:
sage: H = Hom(QQ^2, QQ^1)
sage: H.basis()
(Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[1]
[0]
Domain: Vector space of dimension 2 over Rational Field
Codomain: Vector space of dimension 1 over Rational Field,
Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[0]
[1]
Domain: Vector space of dimension 2 over Rational Field
Codomain: Vector space of dimension 1 over Rational Field)
Return identity morphism in an endomorphism ring.
EXAMPLE:
sage: V=VectorSpace(QQ,5)
sage: H=V.Hom(V)
sage: H.identity()
Free module morphism defined by the matrix
[1 0 0 0 0]
[0 1 0 0 0]
[0 0 1 0 0]
[0 0 0 1 0]
[0 0 0 0 1]
Domain: Vector space of dimension 5 over Rational Field
Codomain: Vector space of dimension 5 over Rational Field
Return True if x is a Free module homspace.
EXAMPLES:
sage: H = Hom(QQ^3, QQ^2)
sage: sage.modules.free_module_homspace.is_FreeModuleHomspace(H)
True
sage: sage.modules.free_module_homspace.is_FreeModuleHomspace(2)
False