Return the logarithm of x to the given base.
Calls the log method of the object x when computing the logarithm, thus allowing use of logarithm on any object containing a log method. In other words, log works on more than just real numbers.
EXAMPLES:
sage: log(e^2)
2
sage: log(1024, 2); RDF(log(1024, 2))
10
10.0
sage: log(10, 4); RDF(log(10, 4))
log(10)/log(4)
1.66096404744
sage: log(10, 2)
log(10)/log(2)
sage: n(log(10, 2))
3.32192809488736
sage: log(10, e)
log(10)
sage: n(log(10, e))
2.30258509299405
The log function works for negative numbers, complex
numbers, and symbolic numbers too, picking the branch
with angle between 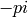 and
and 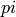 :
:
sage: log(-1+0*I)
I*pi
sage: log(CC(-1))
3.14159265358979*I
sage: log(-1.0)
3.14159265358979*I
For input zero, the following behavior occurs:
sage: log(0)
-Infinity
sage: log(CC(0))
-infinity
sage: log(0.0)
-infinity
The log function also works in finite fields as long as the base is generator of the multiplicative group:
sage: F = GF(13); g = F.multiplicative_generator(); g
2
sage: a = F(8)
sage: log(a,g); g^log(a,g)
3
8
sage: log(a,3)
...
ValueError: base (=3) for discrete log must generate multiplicative group
The log function also works for p-adics (see documentation for p-adics for more information):
sage: R = Zp(5); R
5-adic Ring with capped relative precision 20
sage: a = R(16); a
1 + 3*5 + O(5^20)
sage: log(a)
3*5 + 3*5^2 + 3*5^4 + 3*5^5 + 3*5^6 + 4*5^7 + 2*5^8 + 5^9 + 5^11 + 2*5^12 + 5^13 + 3*5^15 + 2*5^16 + 4*5^17 + 3*5^18 + 3*5^19 + O(5^20)